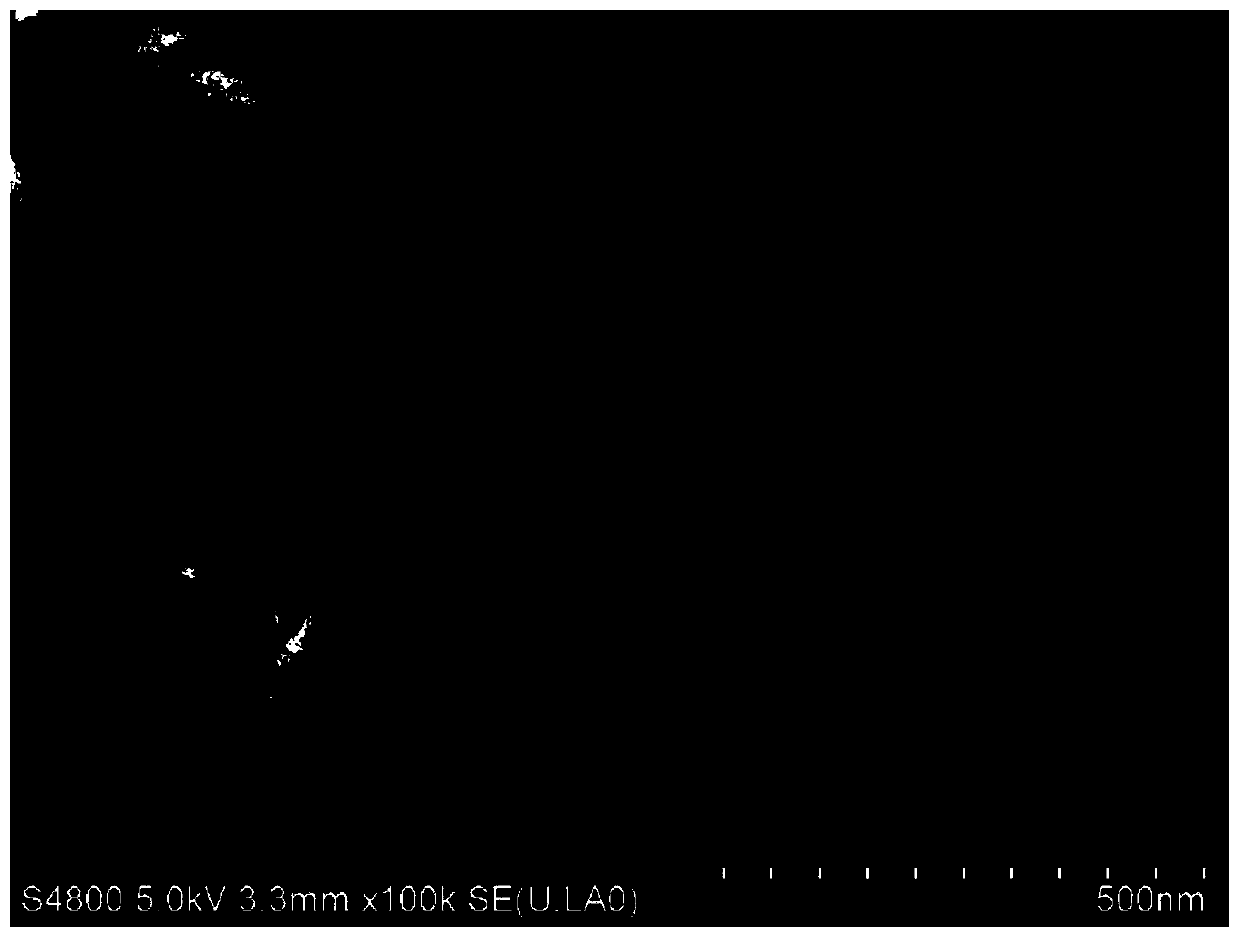
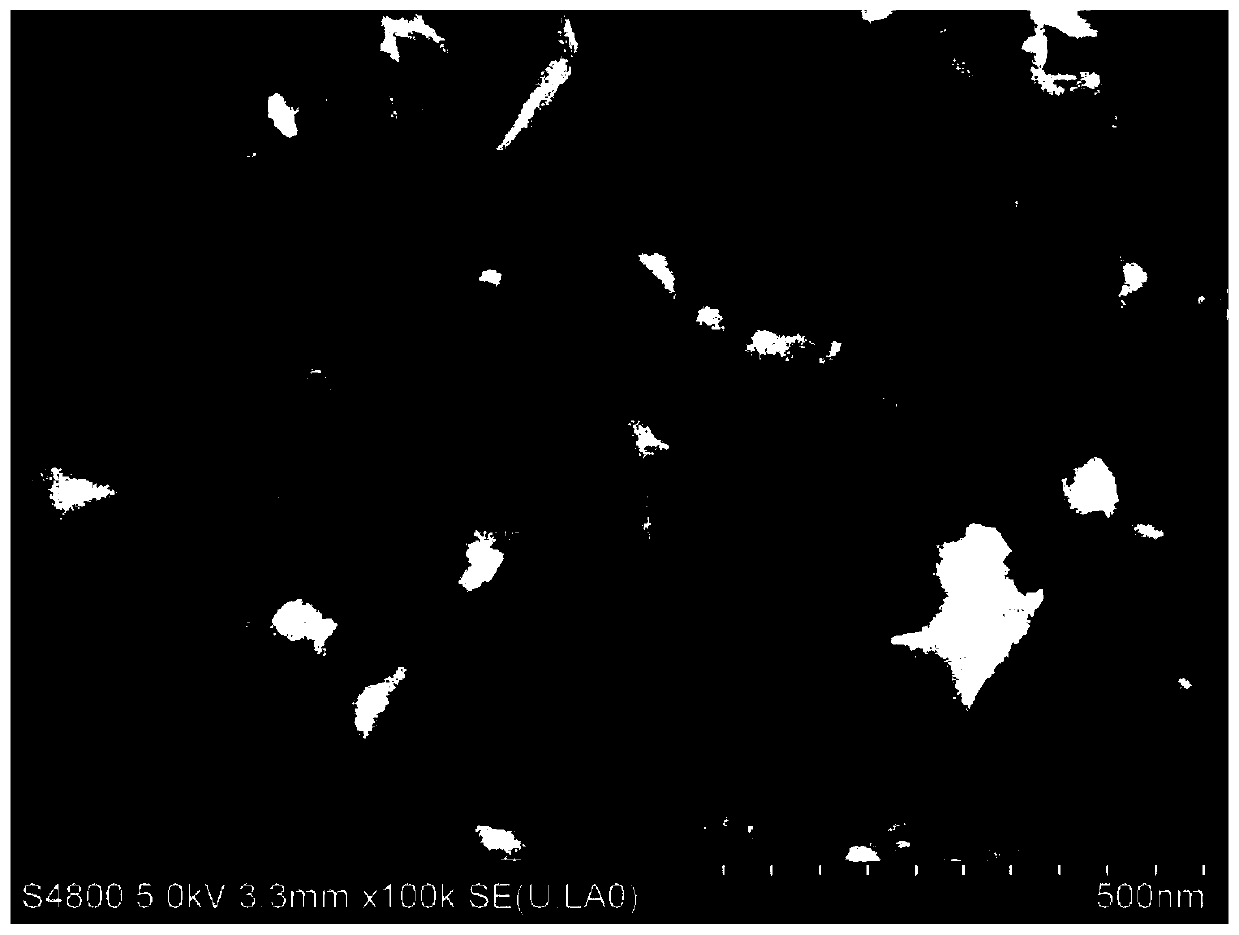
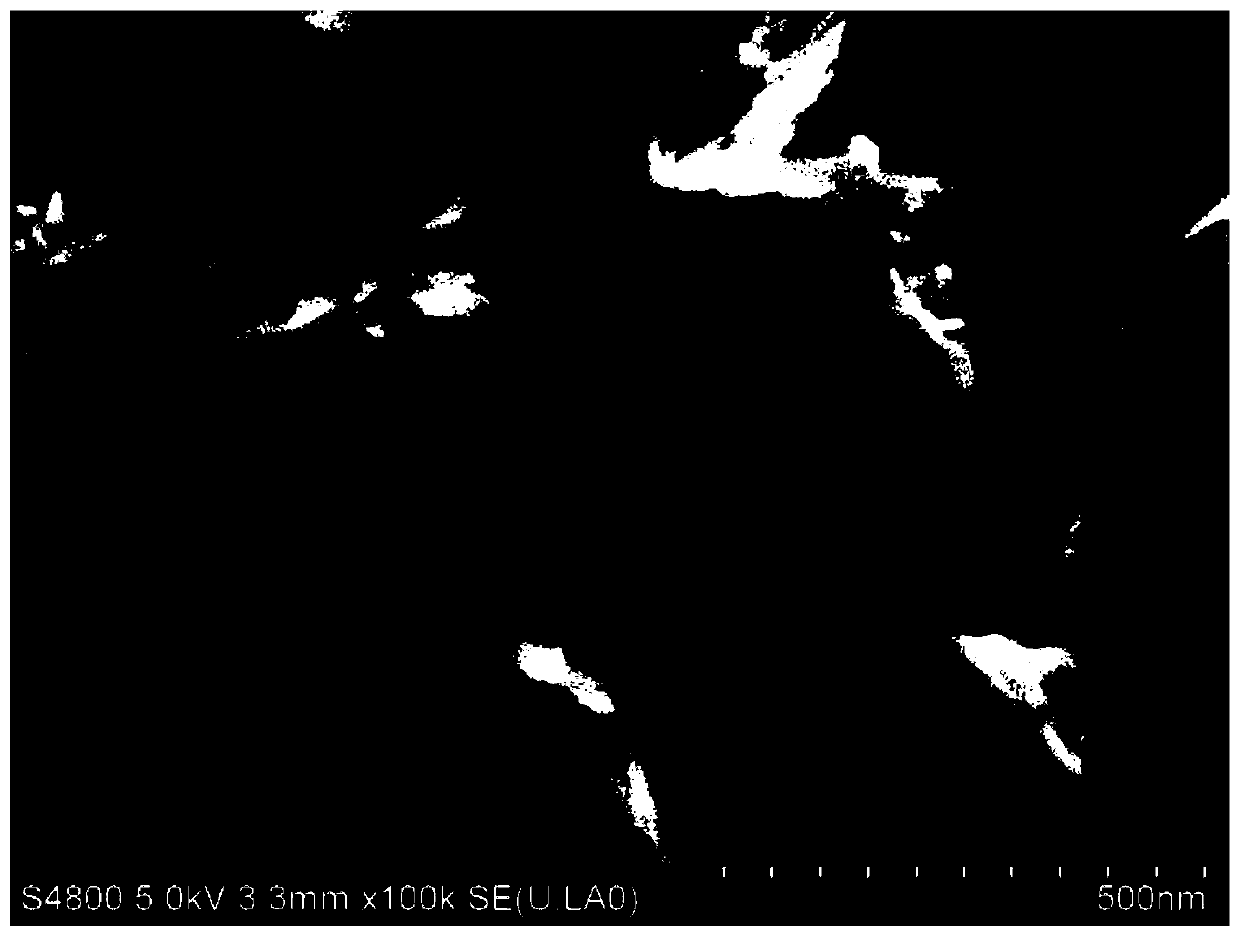
Preparation of nanoparticles with controllable morphology based on the sandwich interface method and its preparation method
A nanoparticle and sandwich technology, which is applied in nanotechnology, chemical instruments and methods, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problem that the shape and size of nano-β-calcium silicate hollow spheres are difficult to control, and the diffusion of nanoparticles cannot be precisely controlled. It is not easy to solve the problems of industrialized production and achieve the effect of low equipment requirements, short production cycle and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] (1) Preparation of calcium nitrate upper layer inverse microemulsion
[0055] First, add 3mL of emulsifier TX-100 and 1.5mL of n-pentanol into 30mL of cyclohexane to obtain an upper layer mixed solution, and then weigh 0.1181g of calcium nitrate, the raw material used to prepare the upper layer of inverse microemulsion, and dissolve it into 1mL of an aqueous solution , and then use a micro-injector to add the aqueous solution dropwise to the upper mixed solution, and use a multi-head magnetic heating stirrer to fully disperse it at room temperature until a clear and transparent calcium nitrate upper layer inverse microemulsion phase is obtained;
[0056] (2) Preparation of lower layer aqueous solution liquid phase and intermediate transition layer liquid phase
[0057] Weigh 0.1140 g of the raw material trisodium phosphate used to prepare the lower aqueous solution liquid phase with a balance and dissolve it in 10 mL deionized water to obtain the lower layer aqueous sol...
Embodiment 2
[0063] (1) Preparation of calcium nitrate upper layer inverse microemulsion
[0064] First, add 3mL of emulsifier TX-100 and 1.5mL of n-pentanol to 30mL of cyclohexane to obtain an upper layer mixed solution, then weigh 0.5905g of calcium nitrate, the raw material used to prepare the upper layer of inverse microemulsion, and dissolve it into 1mL of an aqueous solution , and then use a micro-injector to add the aqueous solution dropwise to the upper mixed solution, and use a multi-head magnetic heating stirrer to fully disperse it at room temperature until a clear and transparent calcium nitrate upper layer inverse microemulsion phase is obtained;
[0065] (2) Preparation of lower aqueous solution liquid phase and intermediate transition layer
[0066] Weigh 0.5700g of the raw material trisodium phosphate used for preparing the lower aqueous solution liquid phase with a balance and dissolve it in 10mL deionized water to obtain the lower aqueous solution liquid phase; the interm...
Embodiment 3
[0072] (1) Preparation of calcium nitrate upper layer inverse microemulsion
[0073]First, add 3mL of emulsifier TX-100 and 1.5mL of n-pentanol into 30mL of cyclohexane to obtain an upper layer mixed solution, and then weigh 0.2362g of calcium nitrate, the raw material used to prepare the upper layer of inverse microemulsion, and dissolve it into 1mL of an aqueous solution , and then use a micro-injector to add the aqueous solution dropwise to the upper mixed solution, and use a multi-head magnetic heating stirrer to fully disperse it at room temperature until a clear and transparent calcium nitrate upper layer inverse microemulsion phase is obtained;
[0074] (2) Preparation of lower aqueous solution liquid phase and intermediate transition layer
[0075] The lower layer reactant trisodium phosphate used for preparing the lower layer aqueous solution liquid phase is weighed with a balance and dissolved in 10mL deionized water to obtain the lower layer aqueous solution liquid ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com