Structured detergent particles and granular detergent compositions containing the same
A structured detergent and granular technology, applied in detergent compositions, surface active detergent compositions, organic detergent compositions, etc., can solve the problem of narrow process operation window, caking of finished products, and difficulty in preparing highly active LAS particles And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
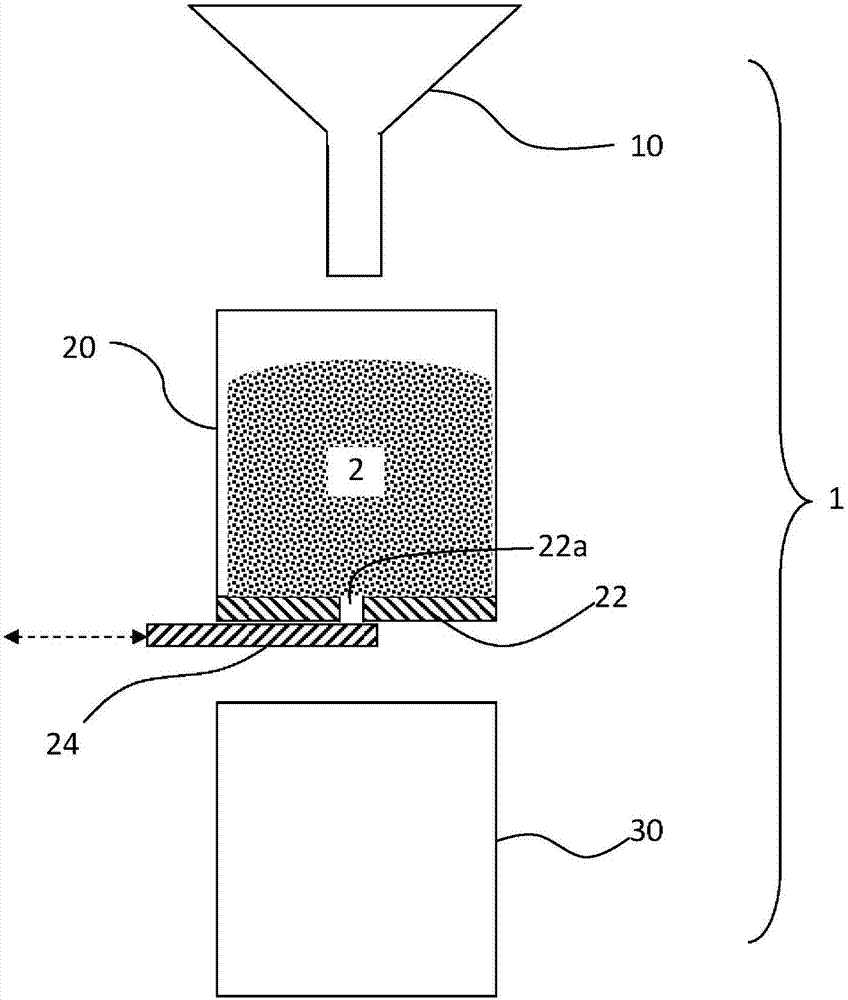
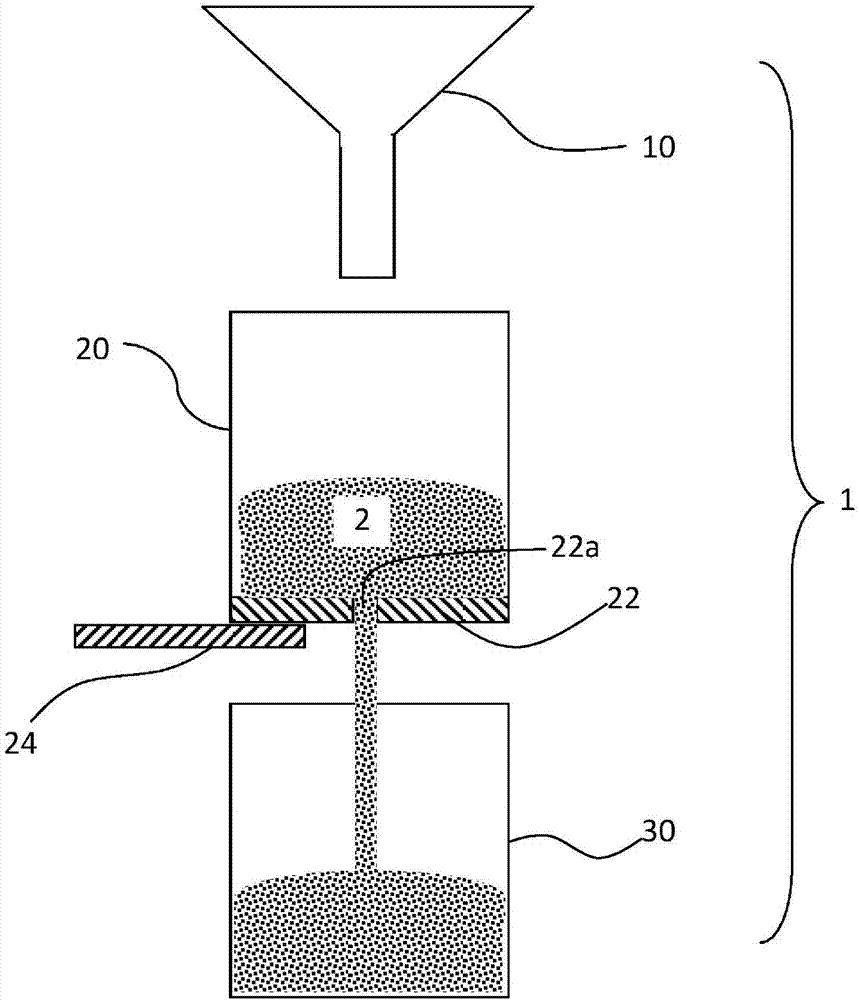
[0073] Example 1: Demonstration of inventive particles (agglomerates comprising 80% LAS and 16.8% silica) versus comparative Comparative Test of Flowability Improvement of Granules (Spray Dried Powder Containing 80% LAS and 10% Silica)
[0074] 1.1. By first according to the present invention, using a BRAUN CombiMax K600 food mixer, at a speed of level 8, 416.67 grams of LAS paste (90% active substance), 83.33 grams of precipitated hydrophilic silica powder (under the trade name SN340 Commercially available from Evonik Industries Ag) agglomerated to form 500 grams of structured particles, and then dried such structured particles to remove 31 grams of water, so as to obtain 469 grams of the final particles of the present invention, the preparation of structured particles comprising the scope of the present invention A first particle sample of the particles (hereinafter "the particles of the invention"). Such dry structured particles have a LAS active content of about 80% by...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Example 2: Comparative Tests Showing Reduced Moisture Uptake by Granules of the Invention Compared to Comparative Granules
[0096] 2.1. Repeat the steps 1.1-1.2 in Example 1 to prepare the inventive granules and comparative granules.
[0097] 2.2. On a METTLER TOLEDO XP504 balance with a deviation of 0.1 mg, using a circular sample pan with a diameter of 9.5 cm, weigh about 10 grams of the particles of the invention.
[0098] 2.3. Close the glass cover of the balance and keep the room condition at 25°C / 50%RH.
[0099] 2.4. Record the weight at 0 minutes, 60 minutes, 90 minutes, and 120 minutes.
[0100] 2.5. For the same amount of comparative particles (about 10 grams), repeat steps 2.2-2.4.
[0101] 2.6. The moisture absorption of each particle is calculated as:
[0102] Moisture absorption % at X minutes = (weight at X minutes - weight at 0 minutes) * 100 / weight at 0 minutes
[0103] 2.7. The following are the water absorption results, as listed in Table IV:
...
Embodiment 3
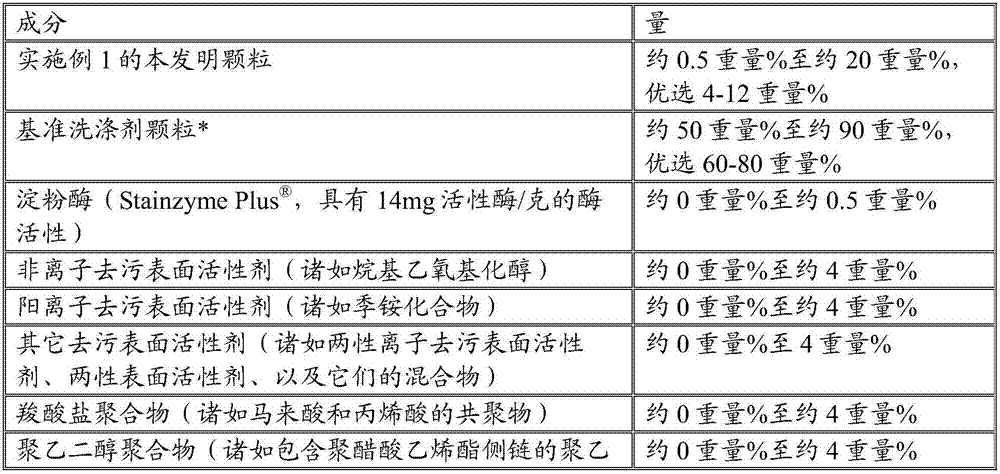
[0107] Example 3: Exemplary Formulations of Granular Laundry Detergent Compositions
[0108]
[0109]
[0110]
[0111] *The base granule is a spray dried detergent granule containing about 12-13% by weight LAS, about 70-75% by weight sodium sulfate, about 8-10% by weight silicate and less than 3% by weight moisture.
[0112] All enzyme levels are expressed as rug active enzyme protein per 100 g of detergent composition.
[0113] The surfactant component is available from BASF (Ludwigshafen, Germany) Shell Chemicals (London, UK); Stepan (Northfield, Ill., USA); Huntsman (Huntsman, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA); Clariant (Sulzbach, Germany)
[0114] Sodium tripolyphosphate is available from Rhodia (Paris, France).
[0115] Zeolites are available from Industrial Zeolite (UK) Ltd (Grays, Essex, UK).
[0116] Citric acid and sodium citrate are available from Jungbunzlauer (Basel, Switzerland).
[0117] NOBS is sodium nonanoyloxybenzenesulfonate supplied by Eastman (...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com