Microwave photonic zero-intermediate-frequency receiving device and method
A receiving device and microwave photon technology, applied in the field of microwave technology and optical communication, can solve the problems of few microwave photon zero-IF receiving technology, complex structure, difficult to suppress image interference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following The described embodiment:
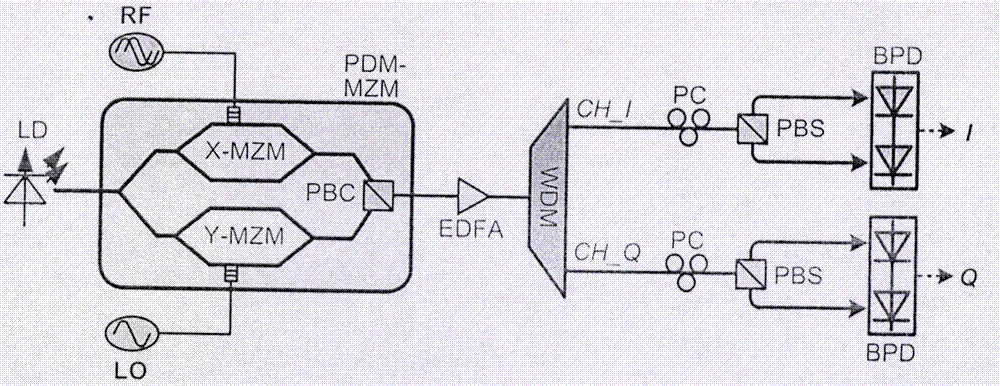
[0023] In this example, the device includes LD, two radio frequency signal sources, PDM-MZM, EDFA, WDM, PC, PBS and BPD. The output port of the LD is connected to the optical input port of the modulator, and the output ports of the two RF signal sources are respectively connected to the two RF input ports of the modulator. The modulator is connected to the EDFA, and the EDFA is connected to the WDM common port. Connect PC, PBS and BPD respectively.
[0024] In this example, the specific implementation steps of the method are:
[0025] Step 1: The LD generates a cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com