Bis-indenofluorene conjugated polymer laser gain material and preparing method and application thereof
A technology of conjugated polymers and laser gain, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low mobility and insufficient stability, and achieve low laser threshold, reversible redox characteristics, The effect of high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of compound 3
[0036]
[0037] The first step: under the protection of light and nitrogen, fluorene bisboronate (4.13g, 3.93mmol), methyl o-bromobenzoate ((3.38g, 15.72mmol), tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 (0.23g, 0.2mmol), phase transfer catalyst tetrabutylammonium bromide (566.72mg, 1.76mmol), toluene solution (20mL), 2M K 2 CO 3 The solution (10 mL) was added into a 50 mL reaction bottle, and reacted at 95° C. for 24 hours. After the reaction, extract with dichloromethane and water, collect the organic phase, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filter with suction, distill off the solvent, and the obtained solid is purified by chromatographic column to obtain compound 1 (3.65g, 87%).
[0038]Step II: Under the condition of nitrogen protection, add p-bromhexylbenzene (19.28g, 80mmol) and anhydrous tetrahydrofuran solution (50mL) into a 250mL reaction flask, cool to -78°C, and after half an hour of reaction, slow...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Compound 3 from Example 1 was used to prepare block copolymer A.
[0042]
[0043] Wherein, the synthetic route is as follows respectively:
[0044] reaction route Figure 1 :
[0045]
[0046] The synthetic steps of block copolymer A are as follows:
[0047] Under light protection and nitrogen protection, compound 3 (178mg, 0.1mmol), benzothiadiazole borate (38.9mg, 0.1mmol), tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 (11.5mg, 0.01mmol), phase transfer catalyst tetrabutylammonium bromide (25mg, 0.05mmol), toluene solution (4.5mL), 2M K 2 CO 3 The solution (1.5 mL) was added into a 15 mL reaction bottle, and reacted at 95° C. for 72 hours. After the reaction, the copolymer A was obtained through alumina column purification, methanol precipitation, and extraction after the reaction.
[0048] Copolymer A: GPC measured Mn=10554, PDI)=1.32.
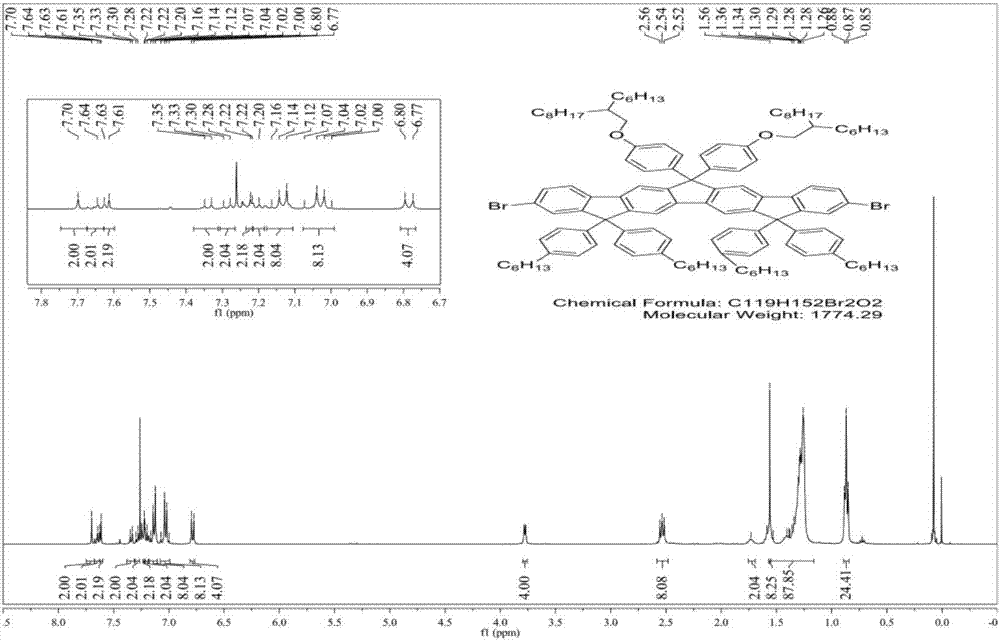
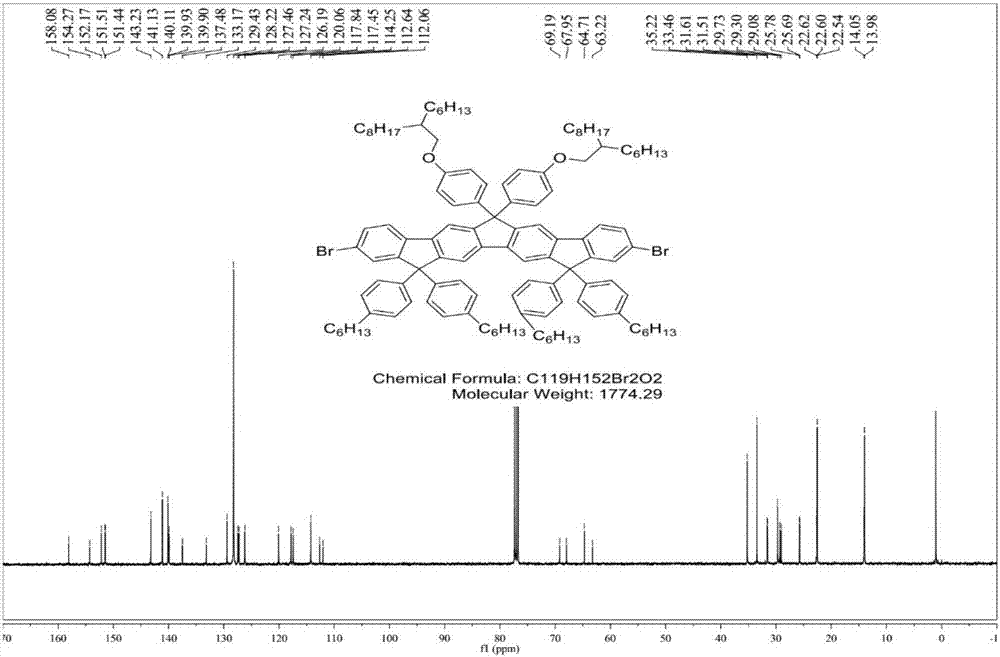
[0049] Compound 3: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ7.70(s,2H),7.64(s,2H),7.62(d,J=5.3Hz,2H),7.34(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),7....
Embodiment 3
[0051] Fabrication of Organic Electroluminescent Devices
[0052] OLEDs devices were prepared by solution method, and their device structures were: indium tin oxide (ITO) / PEDOT:PSS (30nm) / emissive layer (EML, 60nm) / 1,3,5-tris(N-phenylimidazole- 2-yl)-benzene (TPBI, 40 nm) / lithium fluoride (LiF, 1 nm) / aluminum (Al, 100 nm) (emissive layer: copolymer A). The maximum luminance of the device is 14082cd / m 2 , At the same time, a high current efficiency of 3.15cd / A was also observed, which is currently a yellow single-layer electroluminescent device with excellent performance.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum luminance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Emission peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com