Quantitative measurement and characterization method of abrasive wear of micropowder diamond grinding wheel
A diamond grinding wheel and grinding wheel surface technology, which is applied in the field of ultra-precision machining of large-diameter optical components, can solve the problems of high cost investment, high cleanliness and vibration isolation requirements, and the inability to realize the in-situ detection of grinding wheel wear and tear, and achieve hardware cost investment The effect of reducing and avoiding measurement errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0039] The object of measurement and characterization is 1800# resin bonded diamond grinding wheel, the diameter of diamond particles is 8μm-12μm. Install the diamond grinding wheel on the spindle of the ultra-precision grinding machine, and use the grinding wheel in-situ dresser for precision modification and grinding of optical components. The quantitative measurement and characterization method of micropowder diamond grinding wheel abrasive wear in this embodiment includes the following steps:
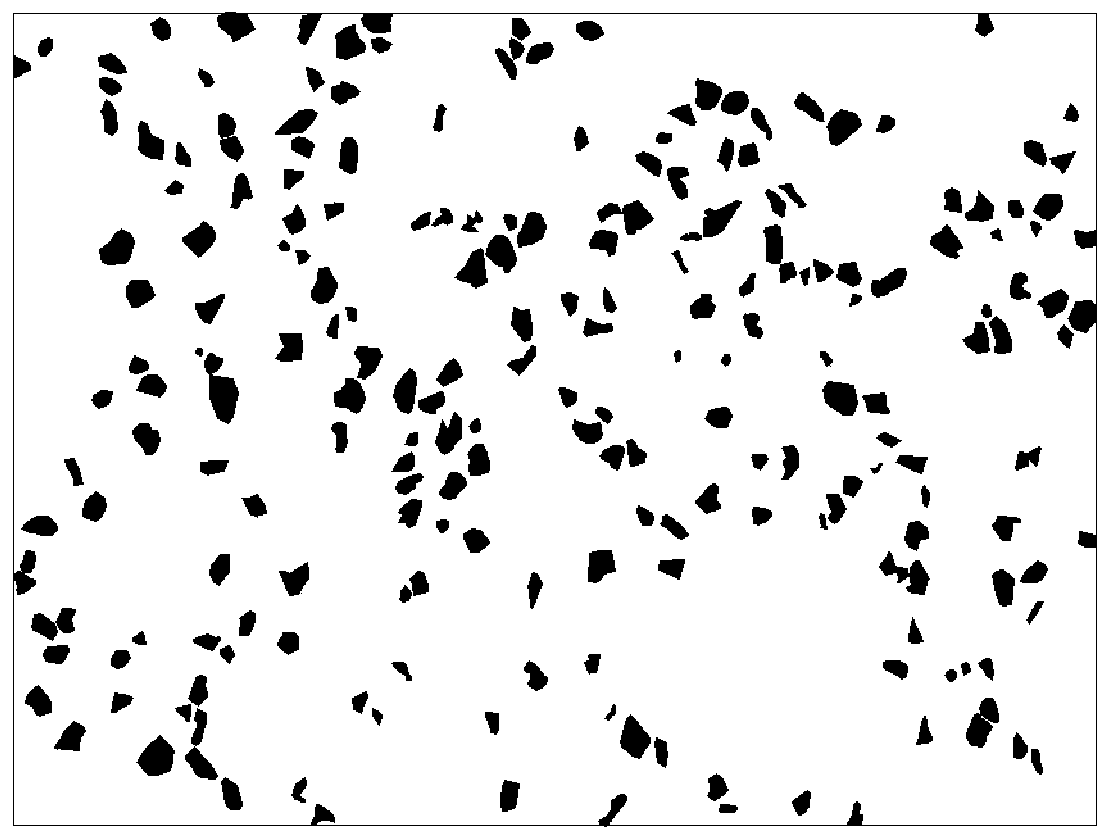
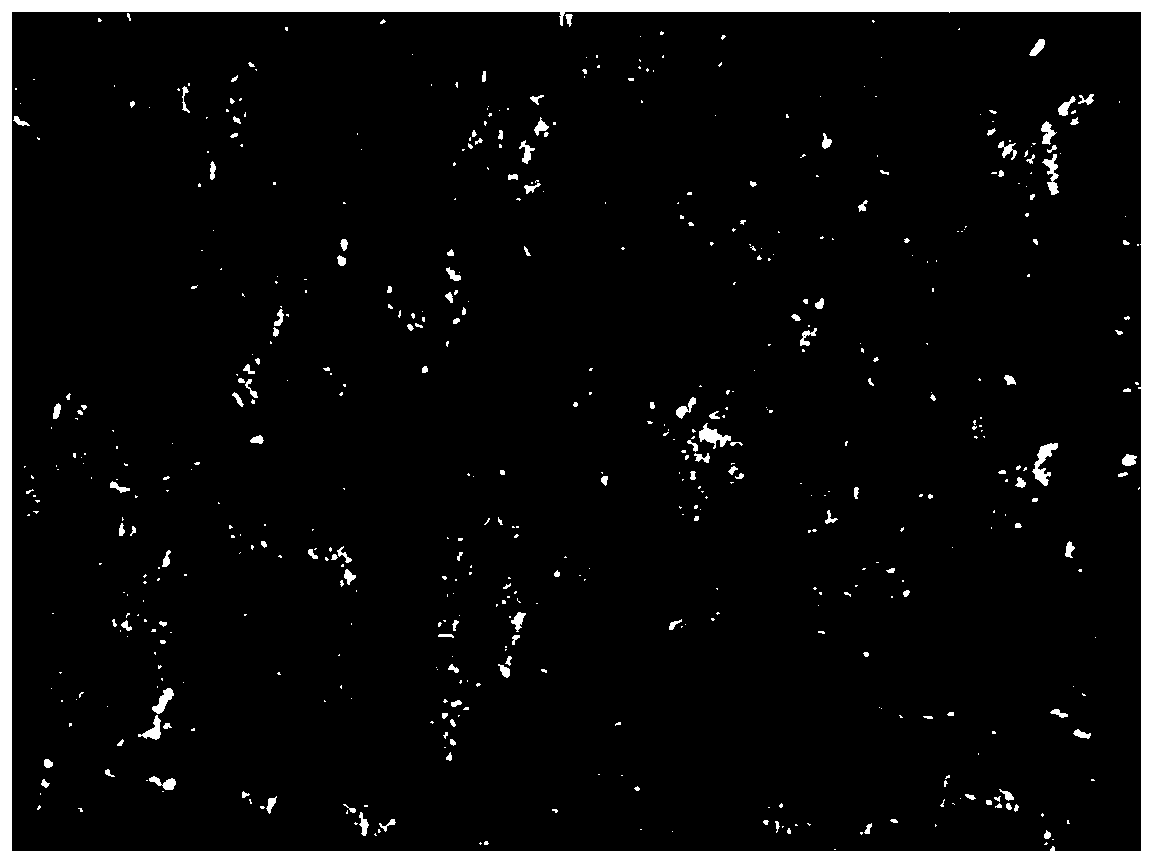
[0040] 1) Install the high-magnification microscope on the machine tool table, and observe the surface of the grinding wheel with the lens barrel vertically upward. After adjusting the focal length until the microscopic appearance of the grinding wheel is clear, take pictures to obtain the microscopic image of the worn surface of the grinding wheel, as shown in figure 1 shown;
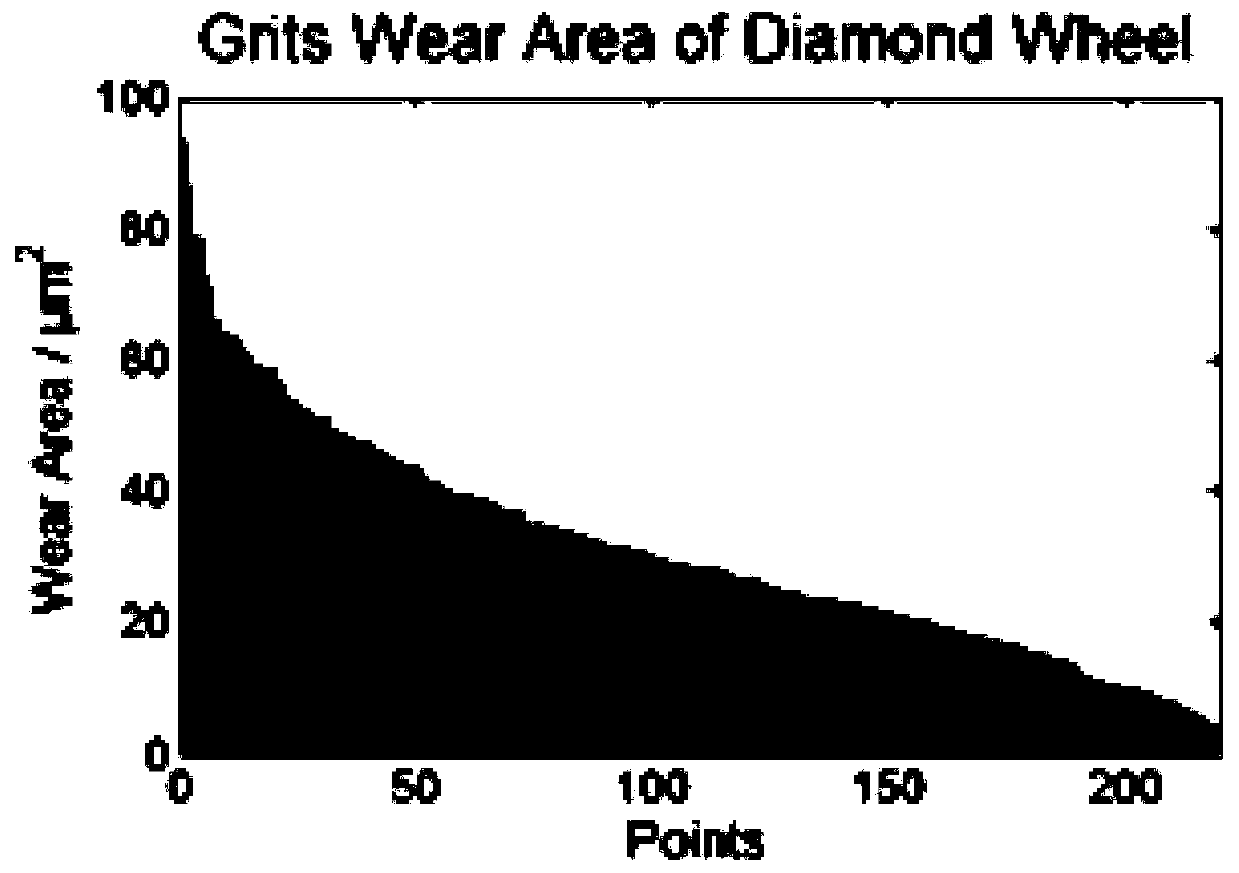
[0041] 2) The computer reads the microscopic image of the surface of the grinding wheel to obtain the im...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com