Method for extracting, purifying and detecting anthriscus nemorosa volatile oil and application of method
A technology for the purification method of A. chinensis and its purification method, which is applied in the fields of anti-oxidation, discovery and identification of volatile oil components of A. spp. , There are no problems such as the volatile oil of ginseng ginseng, which achieves the effect of low water content, avoiding quality reduction, and improving extraction rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
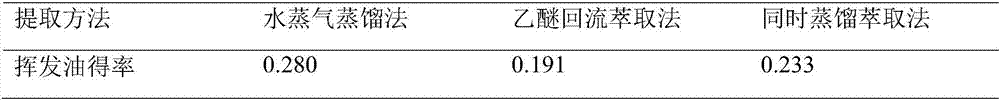
[0083] The method for extracting and purifying the volatile oil of E. japonicus of embodiment 1
[0084] (1) Take 500g of fresh ginseng, wash and dry it, and then powder it to a particle size of 60 mesh, add 1000g of distilled water, stir and carry out steam distillation, and the extraction time of distillation is 4 hours to obtain a water system containing volatile oil;
[0085] (2) Add ether to the water system containing volatile oil for extraction, discard the separated water layer, add anhydrous sodium sulfate to the ether solution containing volatile oil for dehydration, filter and recover ether to obtain dry and pure volatile oil.
Embodiment 2
[0086] The detection method of the volatile oil of embodiment 2 spinosa ginseng
[0087] Adopt GC-MS to detect the volatile oil of the spinosa ginseng that embodiment 1 obtains, concrete detection condition is as follows: HP-5MS chromatographic column (30m * 0.25mm * 0.25 μ m); Carrier gas: helium; Flow velocity: 1.2mL / min , the solvent is delayed for 4 minutes; heating program: the initial temperature is 60°C, hold for 1 minute, raise the temperature to 200°C at 15°C / min, hold for 5 minutes, then rise to 280°C at 5°C / min, and hold for 2 minutes. Ionization method: EI, 70eV; ion source temperature: 250°C; carrier gas: helium; column flow rate: 1.2mL / min. A total of 45 chemical components were detected in the volatile oil of E. japonicus. The specific chemical components and their relative contents are shown in Table 2.
[0088] Table 2 The chemical composition of the volatile oil of A. japonicus
[0089]
[0090]
Embodiment 3
[0091] Example 3 Anti-oxidation test of the volatile oil of E. japonicus
[0092] 1. Preparation of DPPH test solution Preparation of 0.08mmol / L DPPH solution: Precisely weigh 8.0mg of DPPH, dissolve it with absolute ethanol and set the volume to a 200ml brown volumetric flask to obtain a DPPH solution with a concentration of 0.004%, and store it away from light ,spare.
[0093] 2. Experimental steps: Take 1.0ml of each sample solution (0.24, 0.48, 0.72, 0.96, 1.20mg / ml) of different concentrations, put it into a 10ml centrifuge tube, add 3.0ml of DPPH solution, and react at room temperature for 30min in the dark. At the same time, absolute ethanol was used as a blank, and the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 517 nm. Calculate the DPPH free radical scavenging rate according to the following formula.
[0094] DPPH free radical scavenging rate (%)=A0-(As-Ac) / A0×100%
[0095] In the formula, A0—absorbance value of 1.0ml distilled water+3.0ml DPPH solution, As—absorba...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com