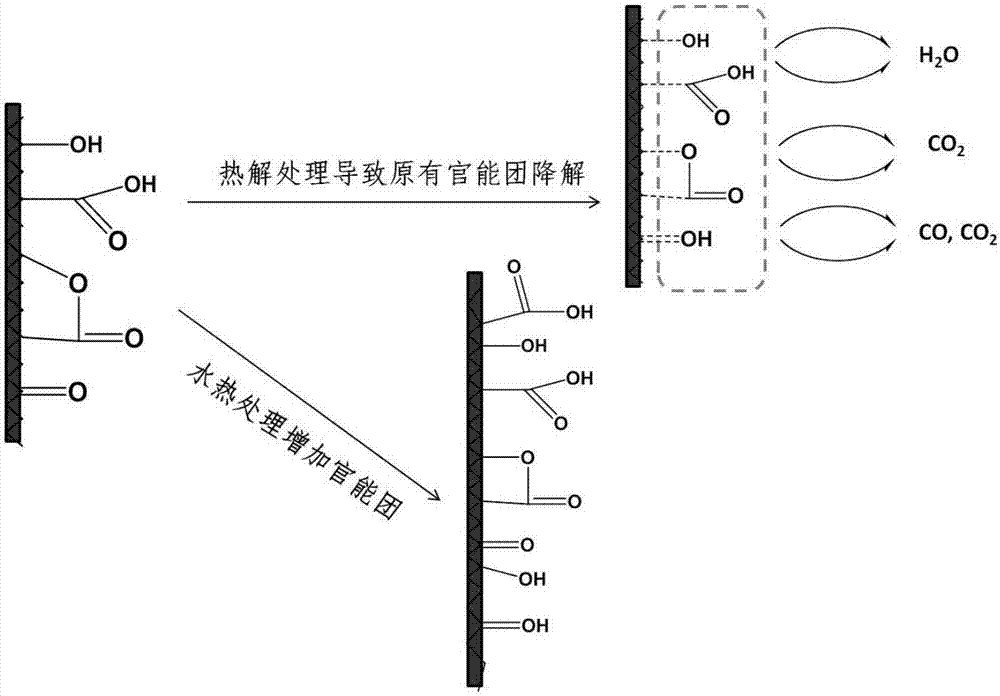
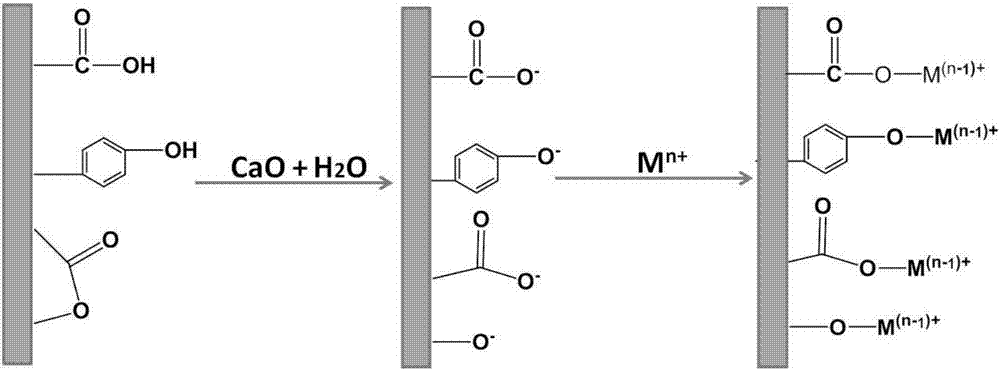
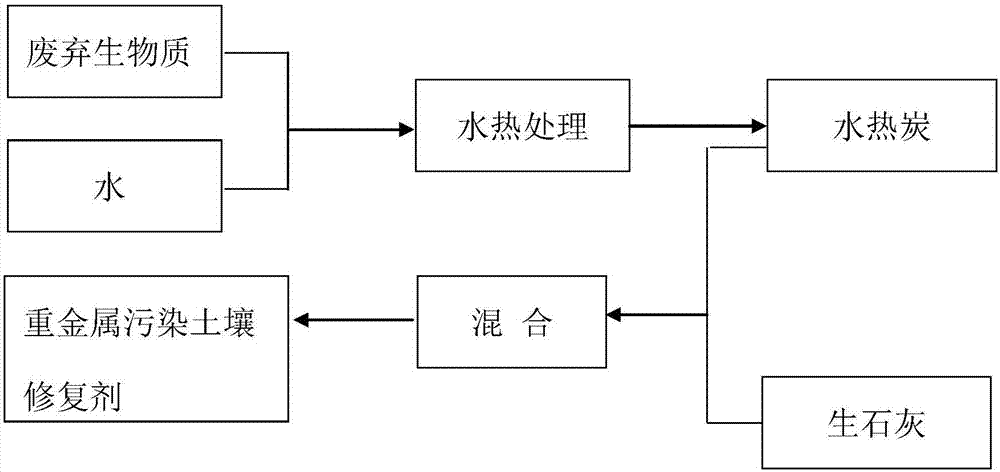
Hydrothermal carbon based heavy metal contaminated soil in-situ remediation agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of in-situ remediation agent and polluted soil, which is applied in the field of waste biomass treatment and disposal, and can solve the problems of low efficiency and long time of soil in-situ remediation agent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1. Material preparation
[0025] The pig manure was dried and crushed to less than 5mm, and set aside. Soil samples include actual polluted soil and simulated polluted soil, in which simulated polluted soil is prepared by adding target pollutants Cd and Pb to uncontaminated soil (Cd and Pb concentrations are 5mg / kg and 1000mg / kg respectively); actual polluted soil The concentrations of Cd and Pb were 7.2mg / kg and 346mg / kg respectively.
[0026] 2. Preparation of restoration agent
[0027] 1) Mix pig manure (dry basis) with water at a ratio of 1:5 and put it into a hydrothermal reactor.
[0028] 2) Heating the reactor to 200°C and maintaining it for 60 minutes; then cooling by an electric fan and internal circulating cooling water, and then performing solid-liquid separation to obtain hydrothermal charcoal;
[0029] 3) Hydrothermal charcoal and quicklime were mixed in a ratio of 4:1, and mechanically stirred for 2 hours to obtain the in-situ remediation agent for heav...
Embodiment 2
[0047] In addition to using corn stover instead of pig manure.
[0048] In the repairing agent preparation step 2), the rest is the same as that of Example 1, except for the treatment at 220° C. for 80 minutes.
[0049] Influence of remediation agent on heavy metals available to plants in soil Steps are the same as in Example 1 except that 5% remediation agent is put into the soil in 1).
[0050] The analysis results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0052] In addition to using kitchen waste instead of pig manure.
[0053] In the preparation steps of the restorative agent, 1) mix kitchen waste (dry basis) and water at a ratio of 1:5;
[0054] In the passivation of the heavy metals in the soil by the remediation agent, except that 7% of the remediation agent was added in 1), the rest was the same as in Example 1.
[0055] Influence of the remediation agent on the heavy metals available to plants in the soil Steps are the same as in Example 1 except that 1) 15% of the remediation agent is put into the soil.
[0056] The analysis results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0057] Table 1 Passivation of heavy metals in soil by remediation agents.
[0058]
[0059] Table 2 Analysis results of heavy metals in mustard roots and stems and leaves.
[0060]
[0061] It can be seen from Table 1 that the simultaneous high-efficiency passivation of two heavy metals in the polluted soil is achieved by adding 5% of the restorati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com