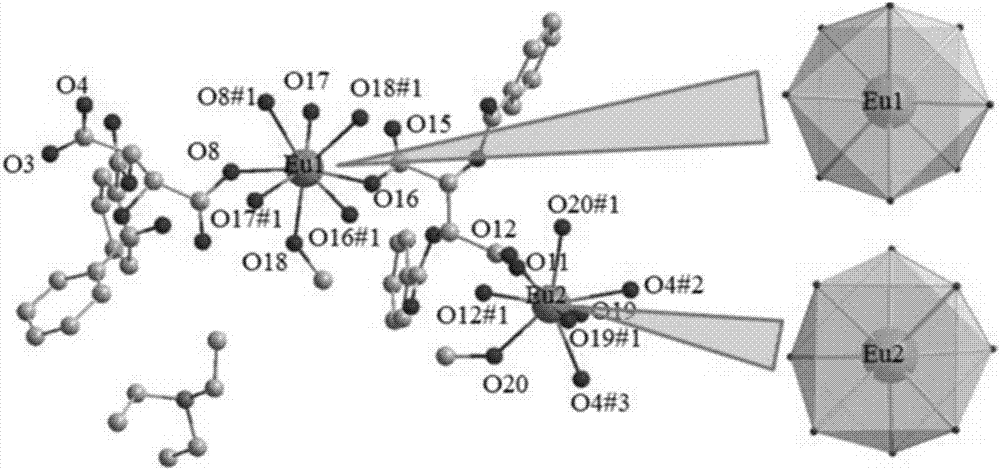
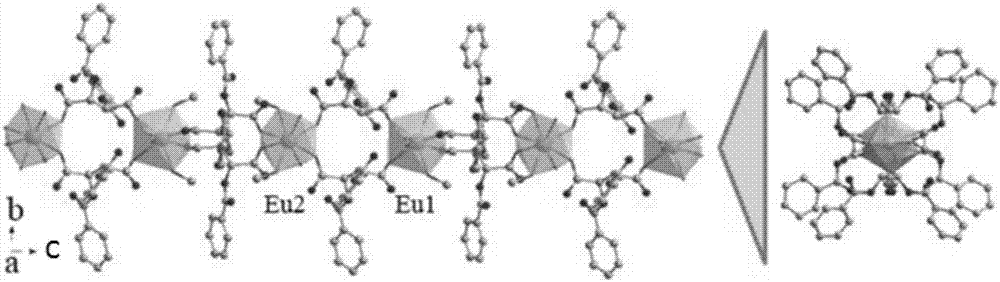
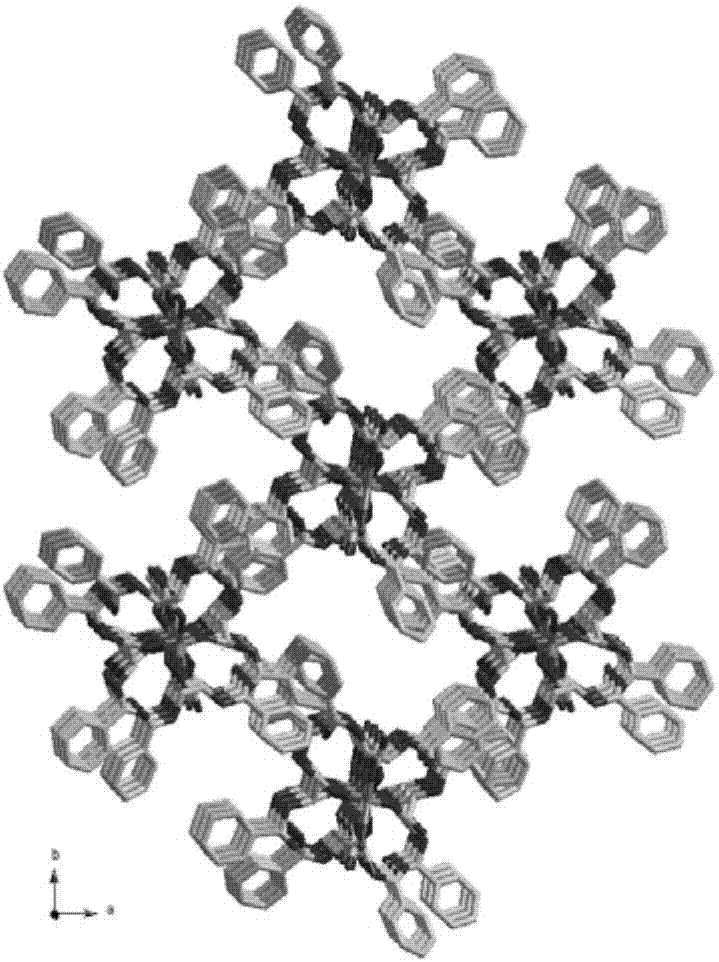
Method used for detecting manganese ions in drinking water
A technology for drinking water and manganese ions, which is applied in measurement devices, color/spectral property measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of unreported fluorescence detection of white light materials, and achieve the effect of simple preparation and low detection concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0041] Specific embodiment one: the method for detecting manganese ions in drinking water in this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0042] 1. Dissolve 0.1g~100g of dibenzoyl tartaric acid rare earth complex in 0.1mL~50mL of N,N’-dimethylformamide solvent to prepare a mixed solution;
[0043] 2. Mix the drinking water and the mixed solution at a volume ratio of 1:1, irradiate with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 320nm to 324nm, and observe the color of the solution. When the concentration of manganese ions in the drinking water is higher than 0.05ppm, the color of the solution changes from white to blue.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0044] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the rare earth complexes of dibenzoyl tartrate described in step one are samarium dibenzoyl tartrate complexes, europium dibenzoyl tartrate complexes and diphenyl The terbium formyl tartrate complex is mixed in a mass ratio of 1:1:3-6. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0045] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the preparation method of the dibenzoyl tartaric acid rare earth complex is as follows:
[0046] Add 0.1g~100g of dibenzoyl tartaric acid to 0.1mL~50mL of solvent, then add 0.1mL~2mL of deionizer until dissolved, add 0.01g~100g of rare earth chloride salt with a concentration of 0.01~1mol / L aqueous solution, stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, filtered, washed with water and methanol, and vacuum-dried at 55°C to 65°C to obtain dibenzoyl tartaric acid rare earth complexes; the rare earth chloride salts are samarium chloride, terbium or europium chloride; the solvent is methanol, water or ethanol; the deionizing agent is triethylamine, sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. Others are the same as those in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com