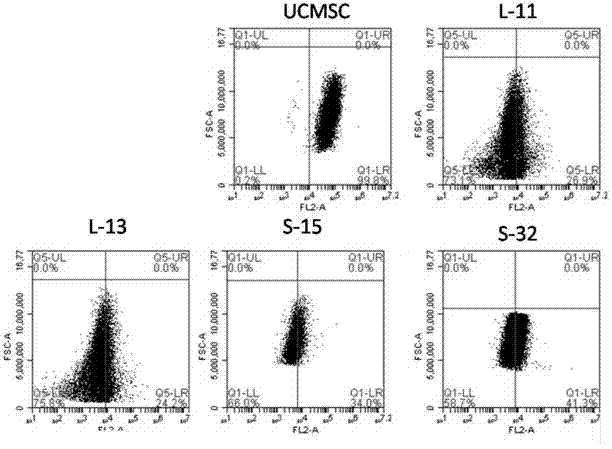
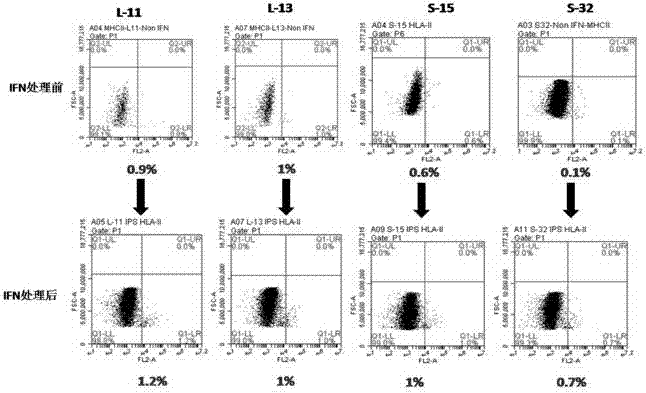
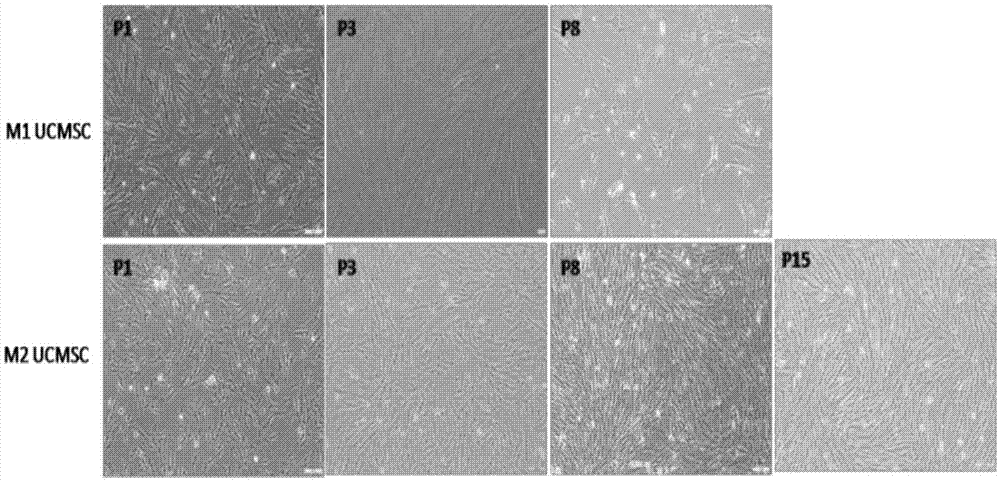
Reprogramming method for induced pluripotent stem cells
A pluripotent stem cell and reprogramming technology, applied in the field of reprogramming from adult stem cells to induced pluripotent stem cells, can solve the problems of iPSC formation, low immunogenicity, and difficulty in detecting teratomas, and achieve high reprogramming efficiency , low immunogenicity, and the effect of eliminating safety concerns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Primary isolation, cultivation and identification of UCMSC
[0045] 1. Primary isolation and culture of UCMSC
[0046] Take a fresh umbilical cord, wash it with PBS plus 100 U / mL penicillin and 100 μg / mL streptomycin to remove blood clots around the umbilical cord, and clean it up. The two ends of the umbilical cord were cut off about 1 cm and discarded, and the blood in the blood vessels was squeezed out, and washed 3 times with PBS. The tissue pieces were soaked in 75% alcohol for 1 min, and then washed 3 times with PBS. Cut the umbilical cord from the middle into a small section about 2 cm long. If there is still blood clot at this time, squeeze it out and wash it; cut it longitudinally, and bluntly separate and remove the 2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein with forceps. The umbilical cord is held in place with a pair of forceps, and Wharton's jelly is scraped away with a scalpel until only the nearly transparent amniotic membrane remains. After ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: UCMSC reprogramming induced by lentivirus
[0059] 1. Method:
[0060] 1.1 Virus packaging: co-transfect 293T cells with the target plasmids (Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc and Klf4) and Pvsvg and pCMV-dR8.91 (from Shanghai Stance Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) respectively, and package after 48 hours Viruses expressing four transcripts of Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc and Klf4 were produced, and each virus was collected for future use.
[0061] 1.2 After the UCMSCs in Example 1 are passed to the third generation, use the packaged Oct4, Sox2, c-Myc and Klf4 four transcript lentiviruses to infect 100,000 M1 or M2 at a ratio of 5 for multiplication and culture cultured UCMSCs, and inoculated on the CF-1 feeder layer;
[0062] 1.3 After 24 hours, replace the M1 or M2 proliferation medium with iPSC induction medium (containing 20% (v / v) FBS, 1% (v / v) NEAA, 1% (v / v) Glutamax-1, 100 μM β- Mercaptoethanol and 4ng / mL bFGF, 2μg / mL DOX in DMEM / F12 medium), and 50μg / mL vitamin C (Vc) and 1mM val...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Sendai virus induces UCMSC reprogramming
[0066] 1. Method:
[0067] 1.1 Resuscitate the UCMSCs in Example 1. After the cells are overgrown, the cells are seeded in 1 well of a six-well plate at a seeding density of 40,000 to 80,000 per well.
[0068] 1.2 After 48 hours, the cells were infected with KOS Sendai virus expressing Klf4, Oct4, Sox2, Sendai virus expressing c-Myc and Sendai virus expressing Klf4. The multiplicity of infection ratio of each virus was KOS:c-Myc:Klf4=5:5:3 (Wherein KOS is equal ratio tandem Klf4, Oct4 and Sox2 sequences on the same vector).
[0069] 1.3 After 24 hours, replace with fresh proliferation medium (M1 or M2), continue to culture for 6 days, and change the medium every 2 days.
[0070] 1.4 Cells were digested, inoculated in VTN-N (purchased from Lifetechnologies) coated six-well plate, and cultured with corresponding proliferation medium to make it adhere to the wall.
[0071] 1.5 After 24 hours, change to E8 medium (pur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com