Self-adaptive method for improving system stability of lcl type grid-connected inverter under weak grid conditions
A system stability and inverter technology, applied in electrical components, irreversible DC power input conversion to AC power output, circuit devices, etc., can solve the influence of grid-connected inverter stability and grid public coupling point impedance large, the power grid cannot be equivalent to an ideal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0066] The method for self-adaptively improving the stability of the LCL type grid-connected inverter system under the weak grid condition of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the embodiments and the accompanying drawings.
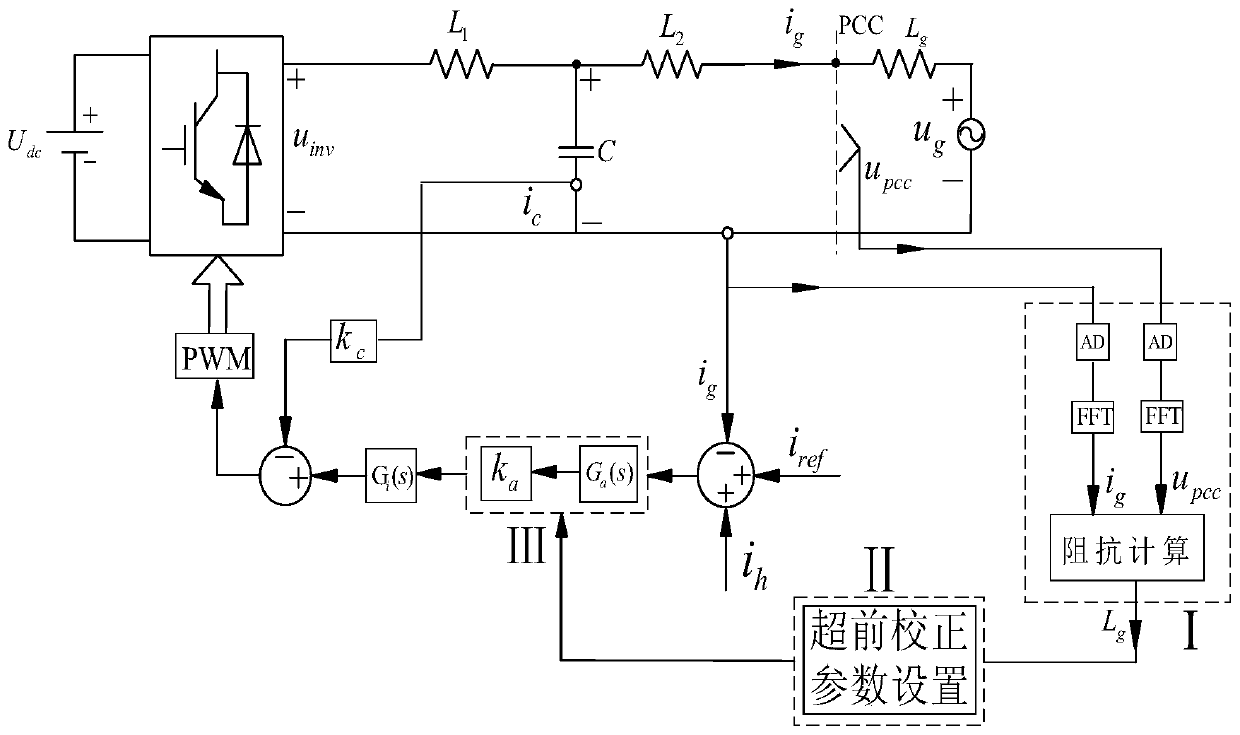
[0067] The method for self-adaptively improving the stability of the LCL type grid-connected inverter system under the weak grid condition of the present invention can add an advanced correction link in the system by measuring the grid impedance, and rely on the grid impedance to adaptively compensate the phase margin of the system, The system maintains sufficient stability margin, which ensures the safe and stable operation of the LCL type grid-connected inverter.
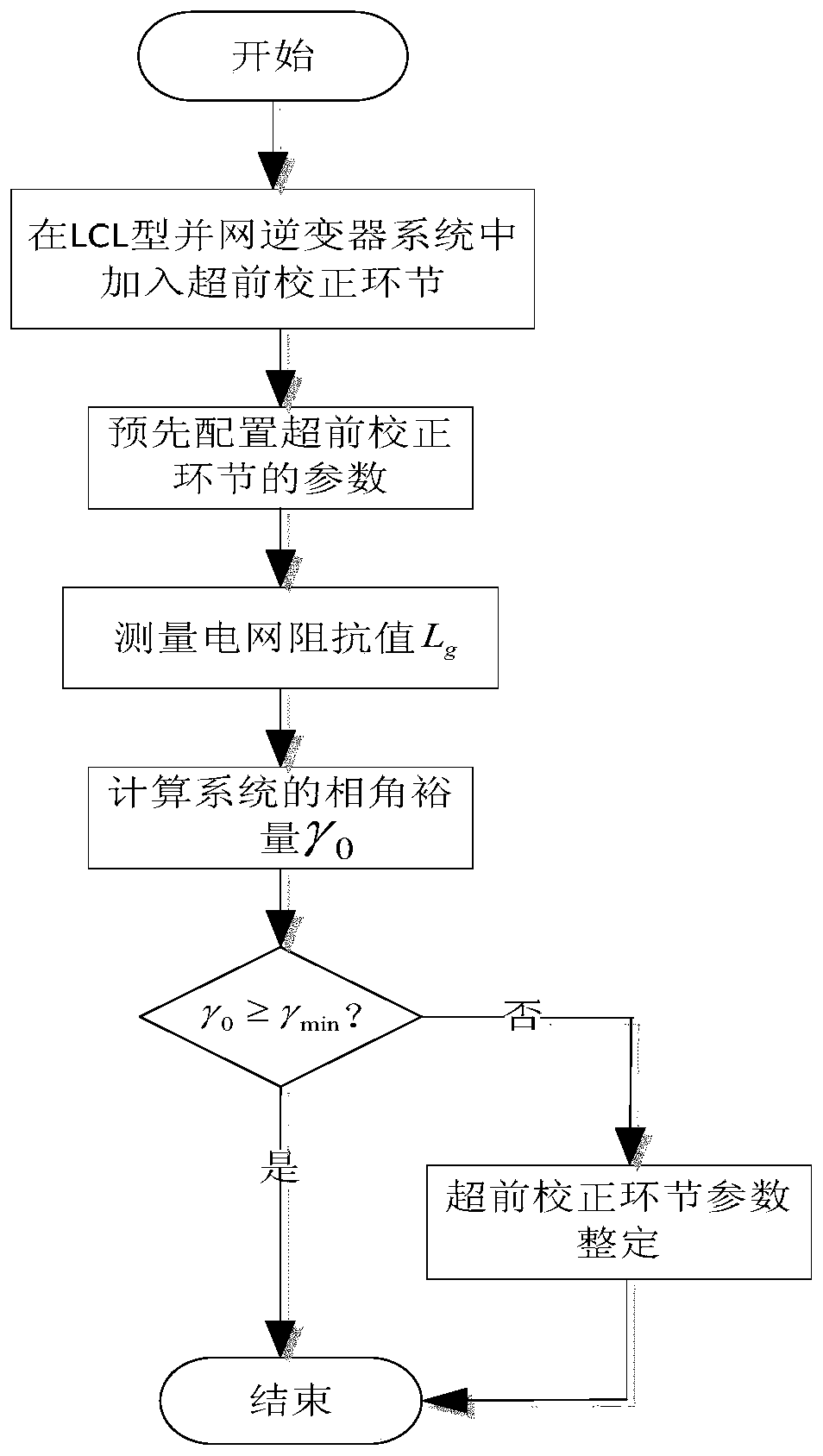
[0068] Such as figure 2 As shown, the self-adaptive method for improving the stability of the LCL type grid-connected inverter system under weak grid conditions of the present invention includes the following steps:
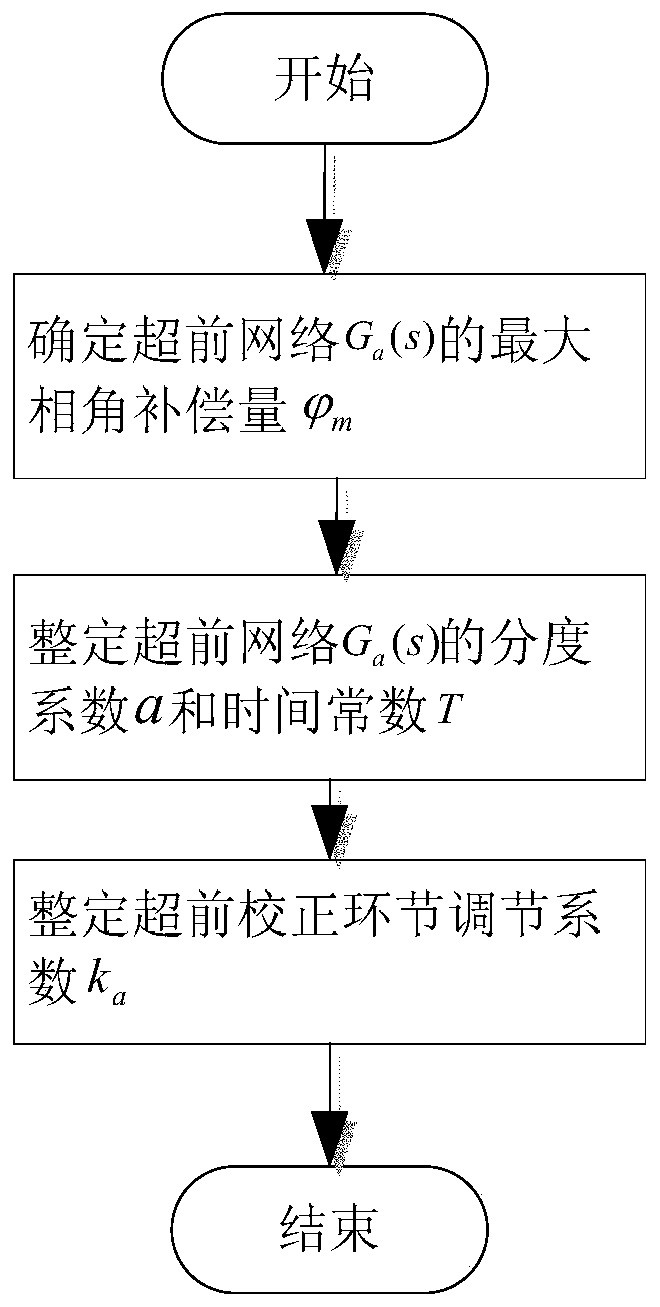
[0069] 1) Add an advanced correcti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com