Specific primer set, kit and application for analyzing the diversity of Fusarium soybean root rot fungus
A technology of specificity and primer set, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problem of inability to determine whether there are pathogenic bacteria, unable to separate pathogenic Fusarium, unsuitable for Fusarium identification, etc. problems, to achieve high sensitivity, low cost, and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 specific primer
[0048] 1. Acquisition of specific primers
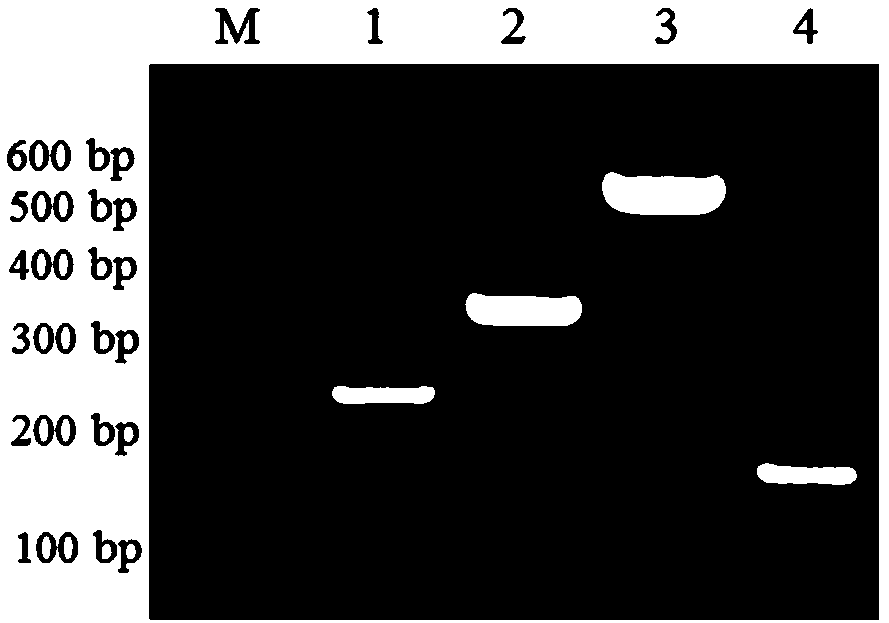
[0049] Using the universal primer EF1 / EF2 of the elongation factor EF-1α gene sequence to perform PCR amplification on different soybean root rot pathogenic Fusarium, and obtain the EF-1α gene sequence of various soybean root rot pathogenic Fusarium And submitted to GenBank, gene accession numbers are KX966232, KX966220, KX966207 and KX966200. According to the EF-1α gene sequence of Fusarium, use primer design software such as Vector NTI 11.0software (Invitrogen, USA) or NCBI online platform (https: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / Blast.cgi) to sequence Compare and find the difference sites, and design the specific primers with obvious differences in the size of the amplified fragments of the four pathogenic bacteria according to the difference sites, and obtain the specific primer sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1-4. The reverse primers are designed in the conservative segment, the common reverse primer sho...
Embodiment 2
[0068] The specific detection of embodiment 2 specific primers
[0069] 1. Acquisition and cultivation of samples to be tested
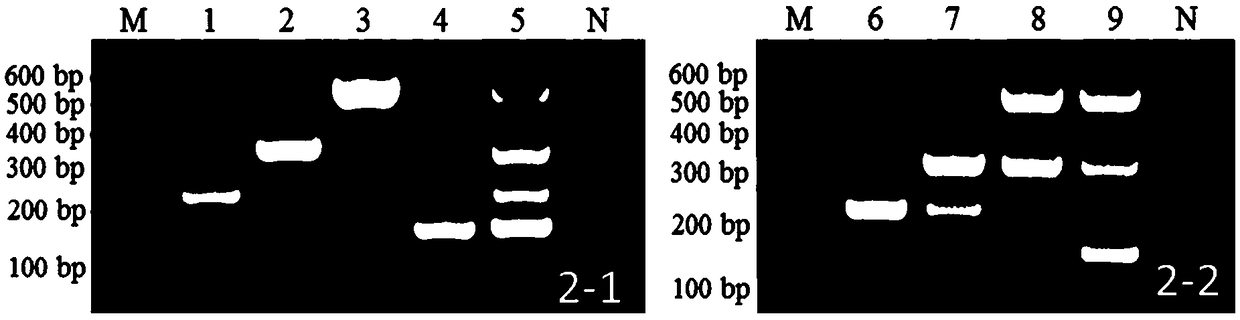
[0070] Fusarium oxysporum (F.oxysporum), Fusarium solani (F.solani) and Fusarium equiseti (F.eqμiseti) obtained from the roots of soybean root rot diseased plants were selected and identified in our laboratory. and Fusarium graminearum (F. graminearum) four purified strains of pathogenic bacteria as samples to be tested.
[0071] Inoculate the above-mentioned 4 kinds of monospore purified strains of Fusarium spp. into potato dextrose agar medium (200g potato, 10g glucose, 20g agar powder, PDA) PDA medium respectively, and place them in an incubator at 25-28°C. Cultivate for 3 to 5 days and save for later use.
[0072] 2. Extraction of DNA
[0073] Fusarium DNA was extracted by CTAB method. The specific steps are as follows: Scrape the mycelium on the PDA medium into a mortar, grind it in liquid nitrogen until it is powdery, put it into a 2mL cent...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Sensitivity detection of embodiment 3 specific primers
[0086] The DNA (100ng / μL) of a single Fusarium was detected with a Nanodrop 2000 ultra-micro spectrophotometer, and the concentration of the mixed DNA was adjusted to 100ng / μL, and then 10 gradient dilutions were made to 10 -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 、10 7 、10 -8 、10 -9 、10 -10 、10 -11 、10 -12 、10 -13 With different concentration gradients, the forward primers shown in SEQ ID NO.1-4 provided by the present invention are mixed at a volume ratio of 1:1:1:1, and the reverse primer shown in SEQ ID NO.5 is used as a common reverse primer. To the primers, and the established multiplex PCR system for amplification and electrophoresis detection, as shown in image 3 The electrophoresis results shown, according to image 3 The electropherogram shown shows that when the DNA is diluted to 10 -8 Fusarium can still be seen when folded. It can be seen that compared with the prior art, the sensitivity o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com