Method for improving moisture-absorption and sweating performance of fatty polyamide fiber/polyurethane fiber fabric
A knitted fabric, moisture-absorbing and sweat-wicking technology, which is applied in the processing of textile materials, liquid/gas/steam textile material processing, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as poor wearing comfort, poor hygroscopic performance, and easy electrostatic contamination. To achieve the effect of improving the handling effect, easy to combine, and good drapability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
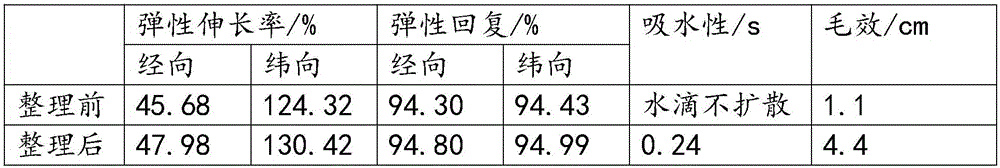
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment one, the manufacture of treatment agent 1#
[0040] Step 1, reacting 100 g of isophorone diisocyanate and 100 g of polybutyl acrylate at a temperature of 80° C. for 3 hours;
[0041] Step 2, adding 5 g of hydroquinone-bis(β-hydroxyethyl) ether, and continuing to react for 1 hour at a temperature of 80° C.;
[0042] Step 3, add 100g of succinic acid and 100g of epoxy resin, and react for 2 hours at a temperature of 150°C;
[0043] Step 4: Heat filtration, evaporate residual acid and other low-boiling point solvents under reduced pressure, filter again, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain treatment agent 1#.
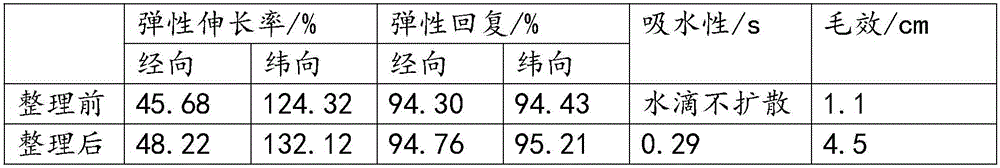
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment two, the manufacture of treatment agent 2#
[0045] Step 1, reacting 100 g of isophorone diisocyanate and 300 g of polybutyl acrylate at a temperature of 120° C. for 1 hour;
[0046] Step 2, add 15g of hydroquinone-bis(β-hydroxyethyl)ether, and continue to react for 0.5 hours at a temperature of 120°C;
[0047] Step 3, add 80g of 1,3-dihydroxymethylsuccinic acid and 150g of epoxy resin, and react at a temperature of 150°C for 5 hours;
[0048] Step 4: Heat filtration, evaporate residual acid and other low-boiling point solvents under reduced pressure, filter again, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain treatment agent 2#.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment three, the manufacture of treatment agent 3#
[0050] Step 1, reacting 100 g of isophorone diisocyanate and 500 g of polybutyl acrylate at a temperature of 100° C. for 1 hour;
[0051] Step 2, add 35g of sorbitol, and continue to react for 0.5 hours at a temperature of 120°C;
[0052] Step 3, add 100g of 1,3-dihydroxymethylsuccinic acid and 200g of epoxy resin, and react at a temperature of 110°C for 4 hours;
[0053] Step 4: Heat filtration, evaporate residual acid and other low-boiling point solvents under reduced pressure, filter again, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain treatment agent 3#.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com