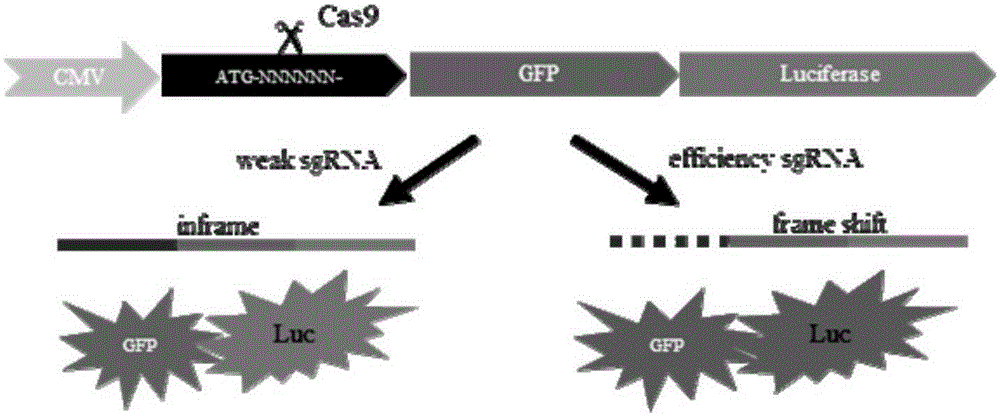
Efficient sgRNA screening system and efficient sgRNA screening method
A technology of nucleic acid constructs and reporter genes, applied in botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, viruses/bacteriophages, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and reagent consumption, inability to accurately quantify, expensive deep sequencing, etc., to achieve The effect of quick construction and easy evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] Embodiment 1, the construction of plasmid pCAG-EGFP-Luc plasmid
[0126] The pEGFP-N1 (Clontech) plasmid was linearized by Not I digestion and dephosphorylated by CIAP alkaline phosphatase; the full-length CDS of luciferase was amplified by PCR using the pGL3-Basic (Promega) plasmid as a template, and the PCR product was purified and linearized An assembly reaction (Gibson Assembly, NEB) was performed on the transformed pEGFP-N1. After heat-shock transformation of Escherichia coli, plates were spread, single clones were picked, sequenced to confirm that the sequence was completely correct, and the pCAG-EGFP-Luc plasmid was obtained, the sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
Embodiment 2
[0127] Embodiment 2, construction of pCAG-target-EGFP-Luc plasmid
[0128] 2.1. The artificially synthesized forward monomer DNA sequence is (5'-TCGAGATGN 1 N 2 N 3 ---N 60 -3'), and the reverse monomeric DNA sequence is (5'-TTCGA N' 60 ---N' 3 N' 2 N' 1 CAT-3'). Wherein, N'x is the reverse complementary sequence of Nx, N and N' represent base A, T, G or C, N 1 -N 60 Contains the sequences recognized by all sgRNAs.
[0129] 2.2. Anneal the above-synthesized two monomeric DNAs targeting the target gene to form a double-stranded DNA with cohesive ends.
[0130] 2.3. The pCAG-EGFP-Luc plasmid constructed in Example 1 was digested with Xho I and Hind III, linearized, mixed with double-stranded DNA, ligated with T4 DNA ligase, and then transformed into Escherichia coli competent DH5α. Extract the plasmid, that is, construct the pCAG-target-EGFP-Luc plasmid.
Embodiment 3
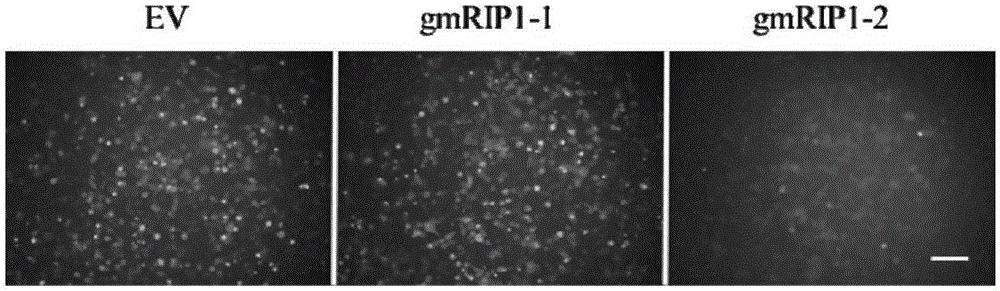
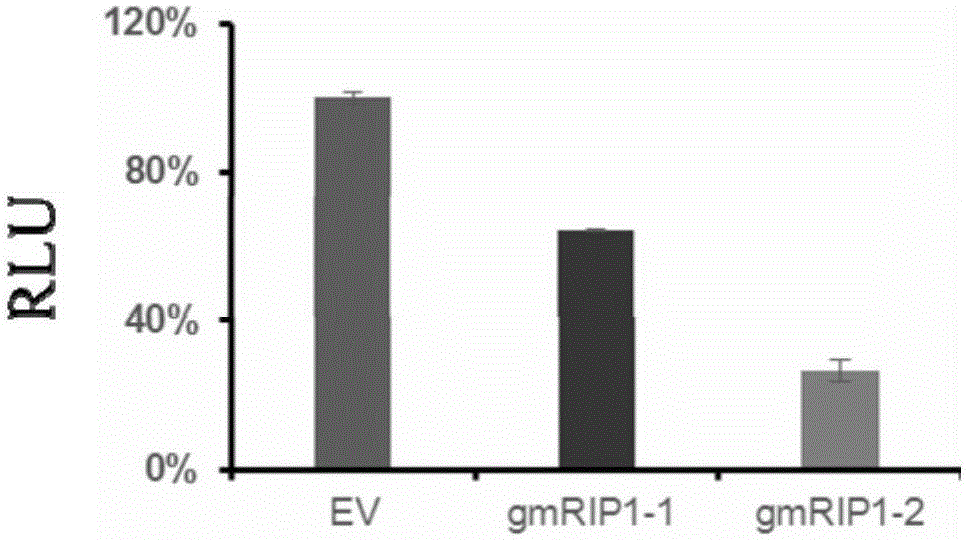
[0131] Example 3. Validation of the effectiveness of the sgRNA screening system by screening the high-efficiency sgRNA of the mouse RIP1 gene
[0132] 3.1. Construction of a fluorescent-luciferase dual reporter plasmid that mimics the mouse RIP1 genome—pCAG-mRIP1-EGFP-Luc plasmid
[0133] 3.1.1. Artificially synthesized forward monomer DNA sequence
[0134] (5'-TCGAGATGATGGCATCCAGTGACCTGCTGGAGAAGACAGACCTAGACAGCGGAGGCTTCGGGA-3', SEQ ID NO:2); and the reverse monomeric DNA sequence (5'-TTCGATCCCGAAGCCTCCGCTGTCTAGGTCTGTCTTCCAGCAGGTCACTGGATGCCATCAT-3', SEQ ID NO:3).
[0135] 3.1.2. Annealing the two monomer DNAs synthesized above for the target gene to form double-stranded DNA with cohesive ends;
[0136] 3.1.3. The pCAG-EGFP-Luc plasmid obtained in Example 1 was digested with Xho I and Hind III, linearized, mixed with double-stranded DNA, ligated with T4 DNA ligase, and transformed into Escherichia coli competent DH5α. The plasmid was extracted, that is, the pCAG-mRIP1-EGFP-Luc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com