Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae utilizing starch and secreting antibacterial peptide
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and antimicrobial peptides, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering, fermentation engineering and evolutionary engineering, and can solve problems such as drug resistance of bacterial pathogens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
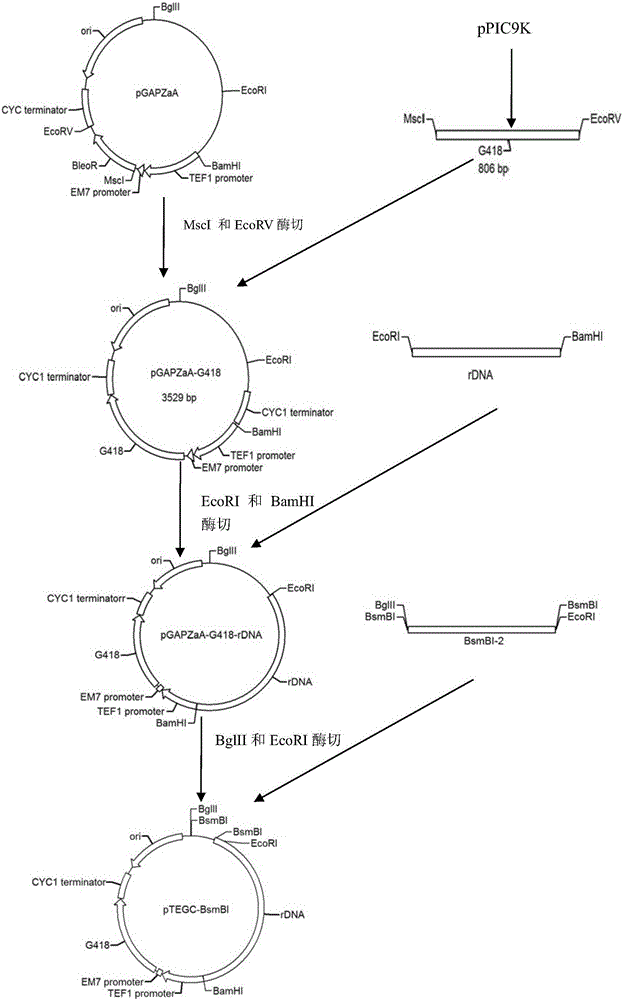
[0071] Example 1 Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae polygene co-expression vector
[0072] 1. Construction of integrated expression vector pTEGC-BsmBI
[0073] 1) Acquisition of G418 resistance gene
[0074] The target gene was amplified by PCR, and the G418 resistance gene was amplified using the G418F-MscI and G418R-EcoRV primers (Table 1) using the vector pPIC9k as a template. PCR reaction conditions: 98°C for 10s, 55°C for 15s, 72°C for 50s, 30 cycles, 72°C for 10min. It was verified by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis.
[0075] The target gene is recovered, purified, transformed into E. coli, verified, and sent for sequencing. The target fragment was recovered and purified, and stored at -20°C for future use. Connect the obtained G418 resistance gene to the T vector, transform Escherichia coli DH5α strain, culture at 37°C, extract its plasmid DNA, use G418F-MscI and G418R-EcoRV primers to screen positive strains by colony PCR, and send the positive clones to Yingw...
Embodiment 2
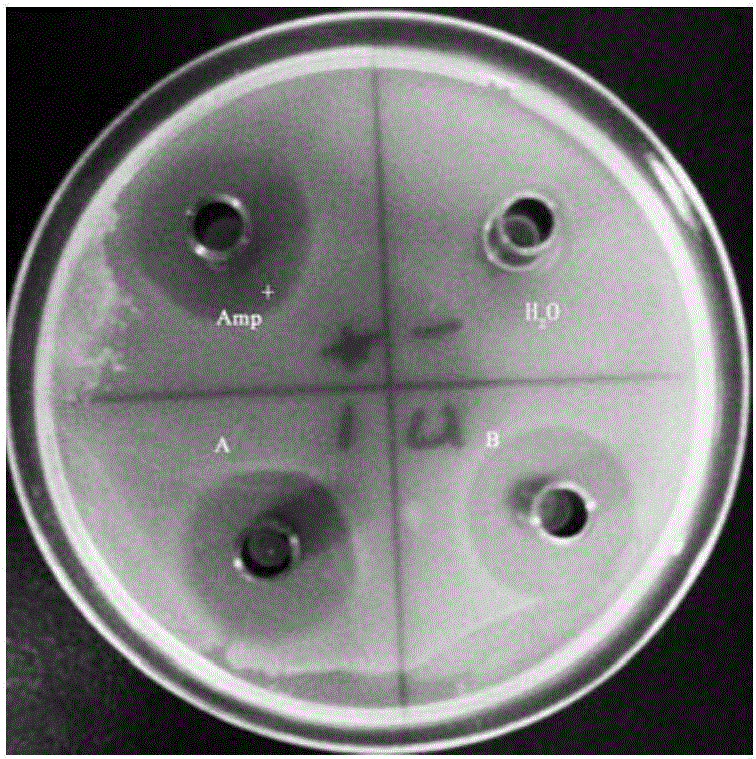
[0127] Example 2 A recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae that can efficiently utilize starch and secrete antimicrobial peptides
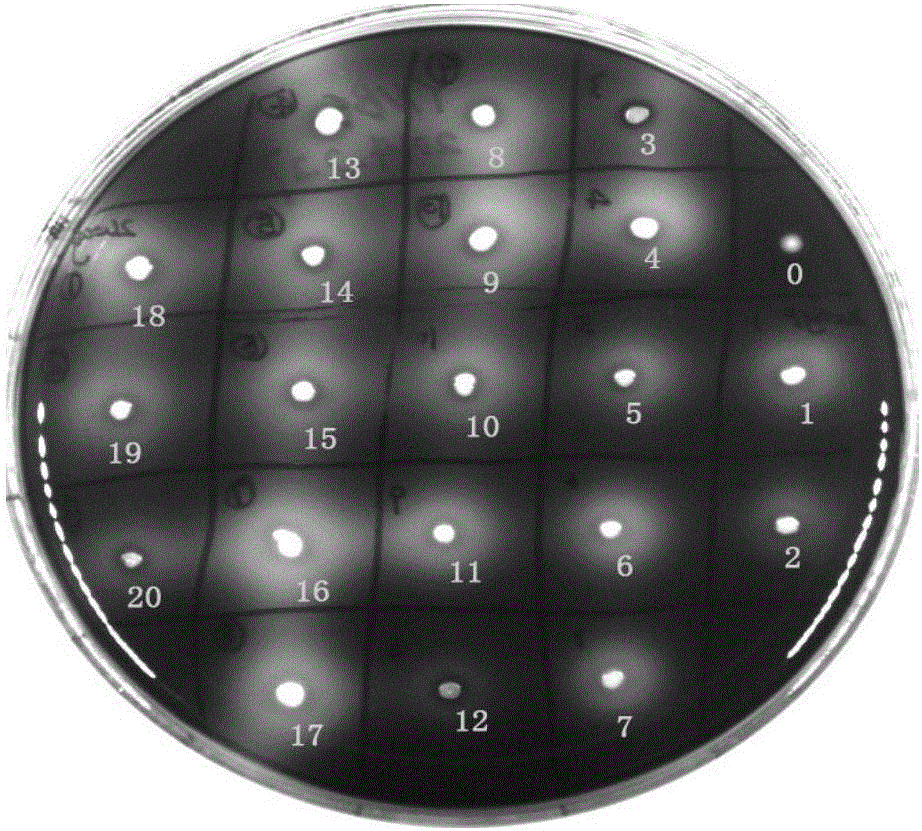
[0128] 1. Screening and verification of recombinant yeast transformants
[0129]Before the electrotransformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the sensitivity test of the resistance screening marker G418 was carried out on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It was found that the yeast was inhibited and could not grow on the YPD plate with a G418 concentration of 200 μg / ml, and the resistance concentration above 200 μg / ml was selected. Screening is performed, eg, 300 μg / ml.
[0130] The Saccharomyces cerevisiae polygene co-expression vector pTEGC-amy-ga-cath-T constructed in Example 1 was linearized with the restriction endonuclease HpaI, and transferred into Saccharomyces cerevisiae by electroporation transformation mediated by lithium acetate. The concentration was 300 μg / ml on the YPD plate and cultured for more than 48 hours, and the single colony that gre...
Embodiment 3
[0136] Example 3 Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae polygene co-expression vector
[0137] In this embodiment, the method for constructing a Saccharomyces cerevisiae multi-gene co-expression vector is the same as in Example 1, except that the antimicrobial peptide gene inserted into the carrier is an optimized gene of Plectasin (base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3), Others are the same as in Example 1, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae polygene co-expression vector constructed in this example is named pTEGC-amy-ga-plec.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com