Method for separating and recycling selenium and tellurium from copper anode mud
A copper anode slime, separation and recovery technology, applied in metallurgy and chemical industry, can solve the problems of high reagent consumption, low tellurium recovery rate, less than 50%, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
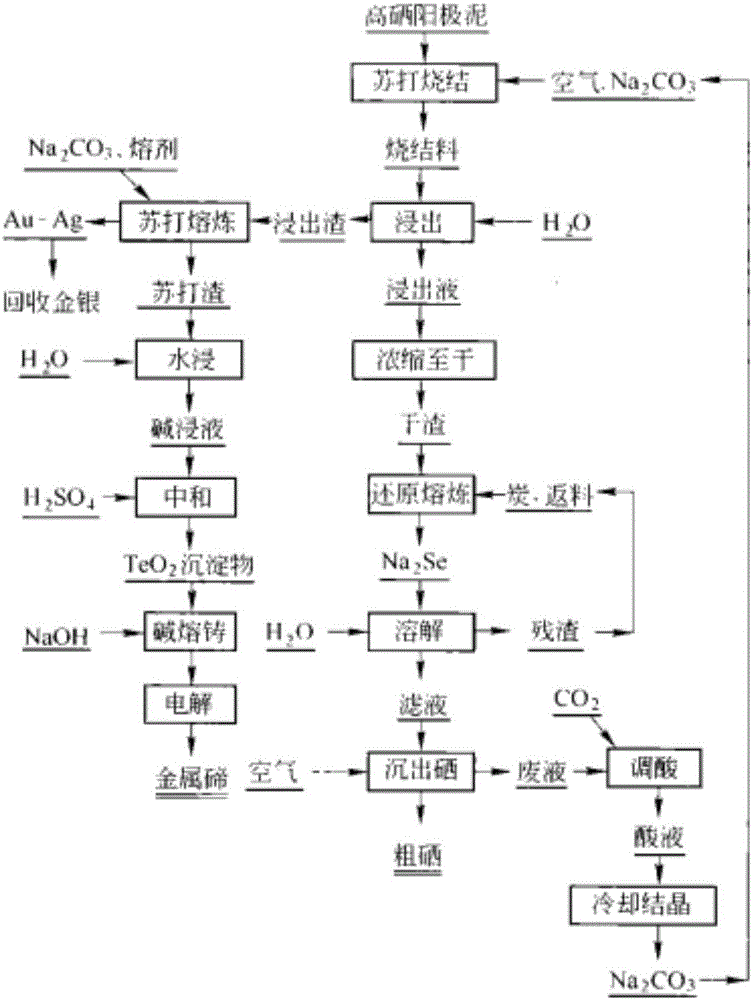
[0049] Take 100g of copper anode slime, add 35g of anhydrous sodium carbonate, grind and mix well, and then sinter in a muffle furnace at 600°C for 3.5h. After the sintered slag is finely ground, add water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3g / ml, stir and leaching at 95°C for 1.5 h, filtered to obtain leaching solution and leaching residue. The leaching solution was acidified with sulfuric acid to pH 5.1, and the precipitated TeO was separated by filtration. 2 After that, continue to add sulfuric acid to acidify to H + The concentration is 1mol / L, slowly add sodium sulfite to reduce the Se in it according to twice the theoretical amount, stir at 85°C for 2.5h to precipitate the selenium in it, and filter to obtain coarse selenium powder and selenium-precipitated liquid; the coarse selenium powder contains Se up to 98.7 %, the selenium-precipitated solution contains Se of 0.02g / L. Add 100g / L H 2 SO 4 solution, stirred and leached at 95°C for 1.5h, filtered to obtain acid leac...
Embodiment 2
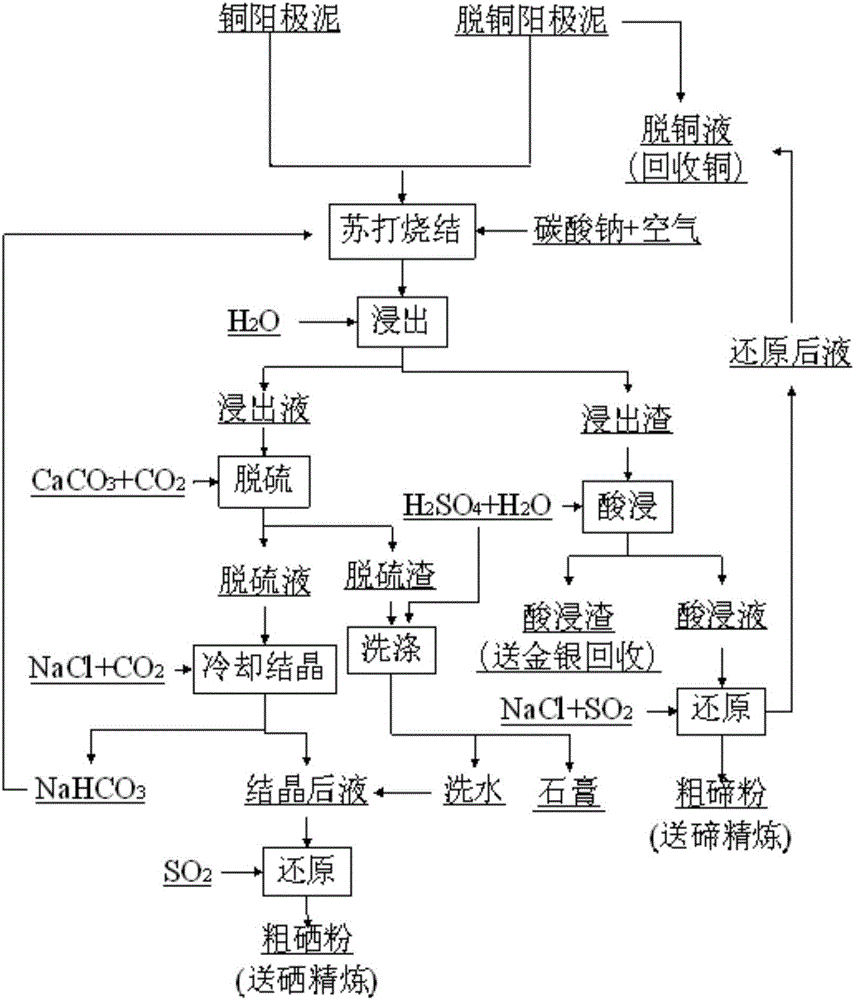
[0052] Take 10kg of decoppered anode slime, add 2kg of anhydrous sodium carbonate and 0.2kg of sodium nitrate, mix well and granulate, sinter in a multi-tang furnace at 550-630°C for 3.5h, add water to the sintered slag at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1.5g / ml , Stirring and leaching at 85°C for 2.5h, and filtering to obtain leaching solution and leaching residue. CO 2 Acidify to pH 5.5, filter and separate the TeO precipitated therein 2 Finally, according to the sulfate in the solution precipitates out in the form of gypsum twice the theoretical amount, add CaCO 3 , stirred at room temperature for 2.5 hours, filtered to obtain filtrate and filter residue; filter residue was added 1mol / L sulfuric acid solution at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:2g / ml, stirred and washed at room temperature for 1h, filtered to obtain gypsum and washing water; after adding 4kg of sodium chloride to the filtrate Repass CO 2 to 0.3MPa, cooled and crystallized at 15°C, and filtered to obtain NaHCO ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Take 100kg of decoppered anode slime, add 25kg of anhydrous sodium carbonate, grind and mix well, then sinter in a rotary kiln at 450-650°C for 2.5h, add water to the sintered slag at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:2g / ml, stir and leach at 100°C for 2h, Filter to obtain leaching solution and leaching residue. Add sodium chloride to the leaching solution to adjust the NaCl concentration to 150g / L, then cool to 0°C to crystallize, filter to obtain mixed crystals of sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate and its crystallization mother liquor; add sulfuric acid to acidify the crystallization mother liquor to pH 5.1, and filter to separate it Precipitated TeO 2 After that, add sulfuric acid to acidify to the solution acidity [H + ] is 0.1mol / L, then pass SO 2 Reduction to the Se concentration in the solution drops to 0.02g / L, and the coarse selenium powder is obtained by filtration. After the coarse selenium powder is refined by sodium sulfite dissolution-precipitation method, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com