Semiconductor structure manufacturing method
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, which are applied to semiconductor devices, electric solid-state devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of easy occurrence of holes in floating gates and reduced device performance, so as to improve breakdown performance, reduce area, and improve coupling rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor structure, please refer to figure 1 , Shown as the process flow chart of the method, including the following steps:
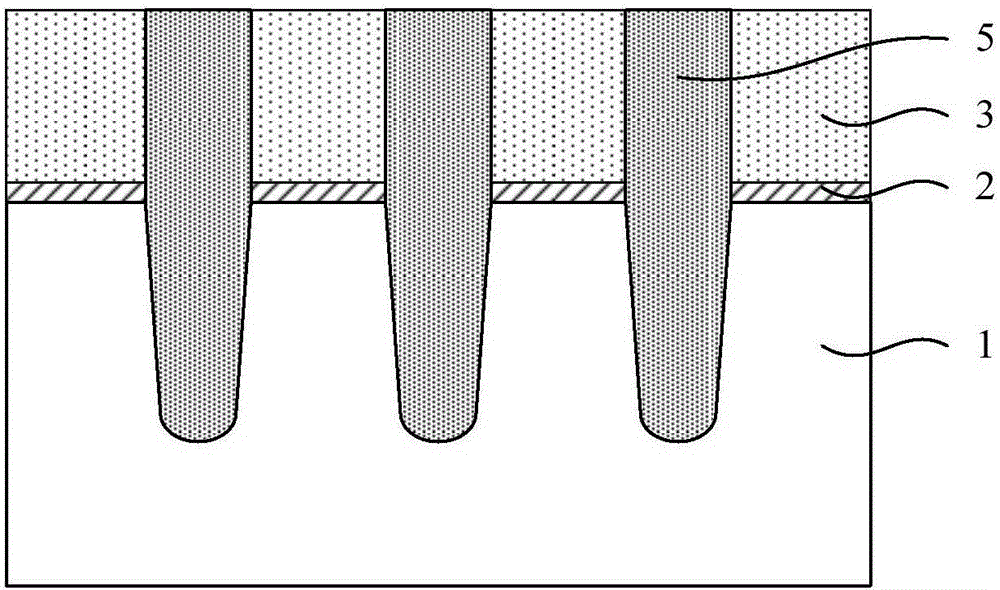
[0066] S1: Provide a substrate, sequentially form a pad oxide layer and a silicon nitride layer on the surface of the substrate, and form at least one recess that penetrates the pad oxide layer and the silicon nitride layer and penetrates into the substrate groove;
[0067] S2: Fill the groove with an insulating dielectric material to form an isolation structure, and perform planarization so that the upper surface of the isolation structure is flush with the upper surface of the silicon nitride layer;
[0068] S3: removing the silicon nitride layer of the first thickness from the top, exposing the first section of the isolation structure, and etching the isolation structure back to reduce the width of the first section of the isolation structure;
[0069] S4: further remove the second thick...
Embodiment 2
[0097] This embodiment adopts basically the same technical solution as the first embodiment, and the difference lies in the shape of the finally formed floating gate structure.
[0098] First, perform steps S1 to S4 that are basically the same as in the first embodiment to obtain Figure 7 The structure shown.
[0099] Then see Figure 15 Step S5 is performed: Step S4 is repeated several times until the silicon nitride layer 3 is etched.
[0100] Specifically, in this step, the number of repeating step S4 is 2-100 times, preferably more than 10 times. The thickness of the silicon nitride layer removed during each repetition of step S4 is the same, or all are different, or at least two different. The thickness of the silicon nitride layer removed during each repetition of step S4 ranges from 1 to 50 angstroms, preferably less than 10 angstroms.
[0101] Each time step S4 is repeated, one more small step is formed. A plurality of small steps are connected in sequence to form the incli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com