Method for producing electrolytic zinc through high-chloride zinc ash material ammonia leaching ion exchange combined process
An ion exchange and combined process technology is applied in the field of electrolytic zinc production by ammonia leaching ion exchange combined process of high chloride zinc ash material, and achieves the effects of high resource utilization, cost reduction and water volume reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025] Example 1: The main components of a certain zinc ash 1 are as follows:
[0026] element Zinc% lead% chlorine% iron% content 56.3 1.2 17.1 1.5
[0027] Using the following treatment process:
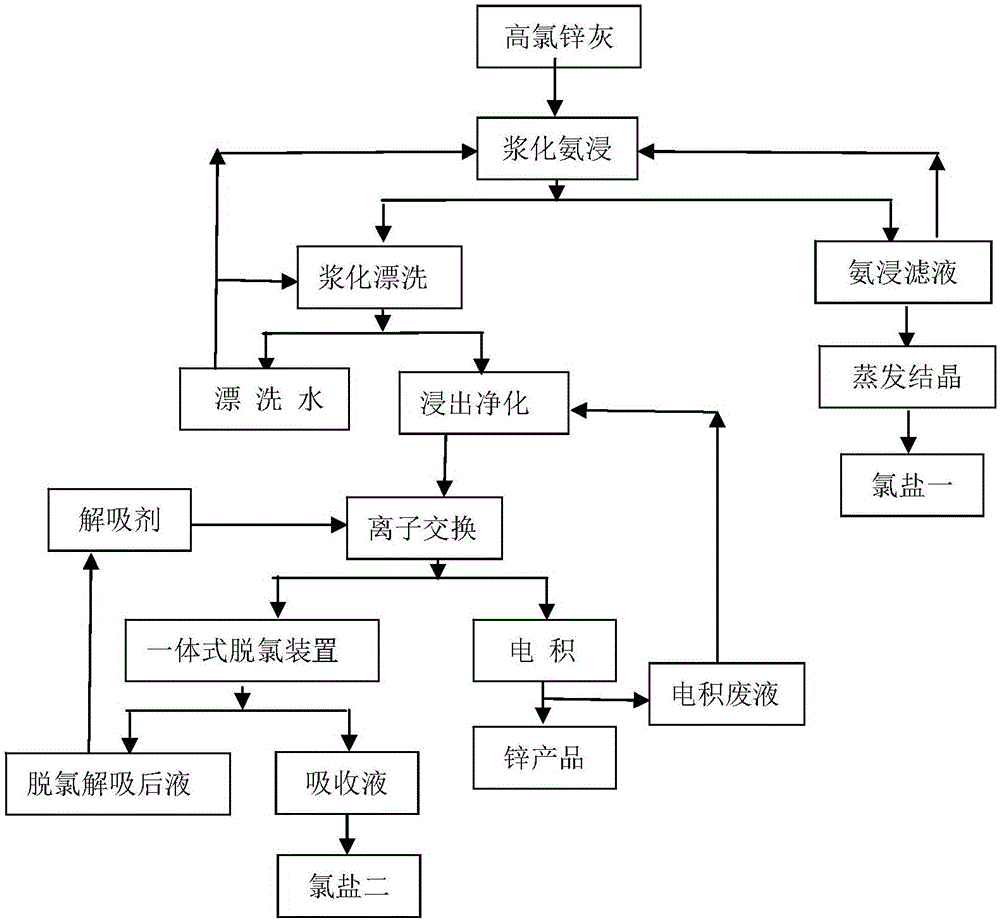
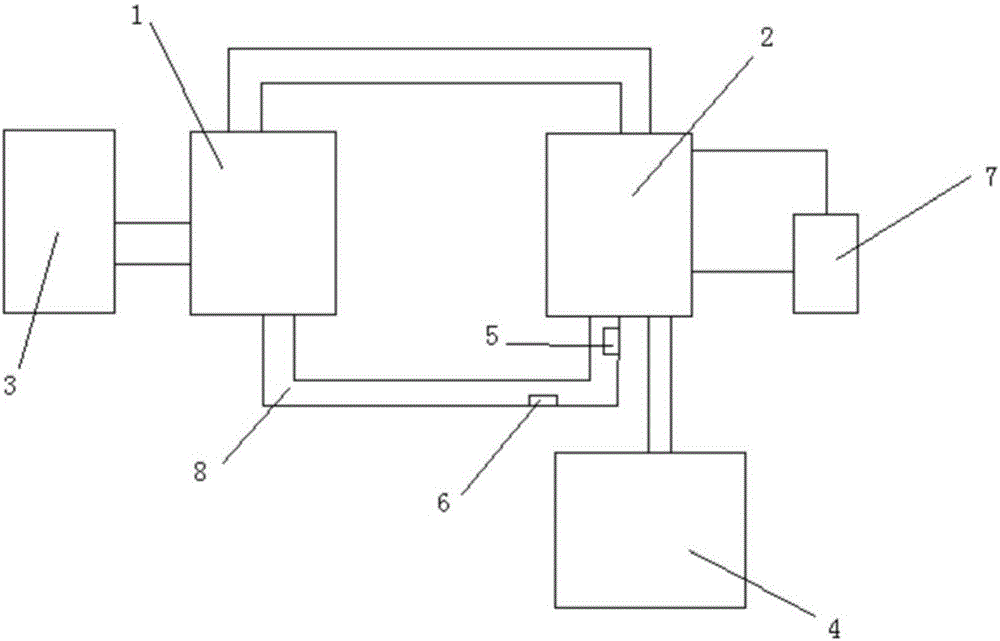
[0028] (1) Ammonia immersion in pulping: transport 6 tons of zinc ash to the pulping tank, which is a mechanical stirring tank with an effective volume of 36m 3 , use rinsing water as the pulping solution, return part of the ammonia leaching filtrate and mix it into the pulping tank to control the liquid-solid ratio to 6:1, start the agitator to stir evenly, add ammonium bicarbonate, ammonia water, etc. to carry out ammonia leaching operation, ammonia leaching process control The time is 1 h, the temperature is 40° C., and the pH at the end point is adjusted to 7. The output ammonia leaching liquid contains 82g / L of chloride ions, and the open circuit part is evaporated to recover chlorine salt 1; the output ammonia leaching residue contains 2.1% ch...
example 2
[0035] Example 2: The main components of a certain zinc ash 2 are as follows:
[0036] element Zinc% lead% chlorine% iron% content 51.2 2.2 15.9 2.5
[0037] Using the following treatment process:
[0038] (1) Ammonia immersion in pulping: transport 6 tons of zinc ash to the pulping tank, which is a mechanical stirring tank with an effective volume of 36m 3 , use rinsing water as the pulping solution, return part of the ammonia leaching filtrate and mix it into the pulping tank to control the liquid-solid ratio to 6:1, start the agitator to stir evenly, add ammonium bicarbonate, ammonia water, etc. to carry out ammonia leaching operation, ammonia leaching process control The time is 1 h, the temperature is 50° C., and the final pH is adjusted to 8. The output ammonia leaching liquid contains 86g / L of chloride ions, and the open circuit part is evaporated to recover chlorine salt one; the output ammonia leaching residue contains 1.7% chlorine.
...
example 3
[0042] Example 3: A certain zinc ash 3 main components are as follows:
[0043] element Zinc% lead% chlorine% iron% content 60.3 1.1 10.4 0.5
[0044] Using the following treatment process:
[0045] (1) Ammonia immersion in pulping: transport 6 tons of zinc ash to the pulping tank, which is a mechanical stirring tank with an effective volume of 36m 3 , use rinsing water as the pulping solution, return part of the ammonia leaching filtrate and mix it into the pulping tank to control the liquid-solid ratio to 6:1, start the agitator to stir evenly, add ammonium bicarbonate, ammonia water, etc. to carry out ammonia leaching operation, ammonia leaching process control The time is 1 h, the temperature is 30° C., and the pH at the end point is adjusted to 9. The output ammonia leaching liquid contains 84g / L of chloride ions, and the open circuit part is evaporated to recover chlorine salt 1; the output ammonia leaching residue contains 2.4% chlorine....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com