Method for producing ammonium perrhenate from rhenium-enriched residues
A technology of ammonium perrhenate and rhenium-rich slag, applied in chemical instruments and methods, rhenium compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in removing impurities by alkali leaching, high production cost, and high safety requirements, and achieve equipment and raw material input. Low cost, high recovery efficiency, no environmental pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
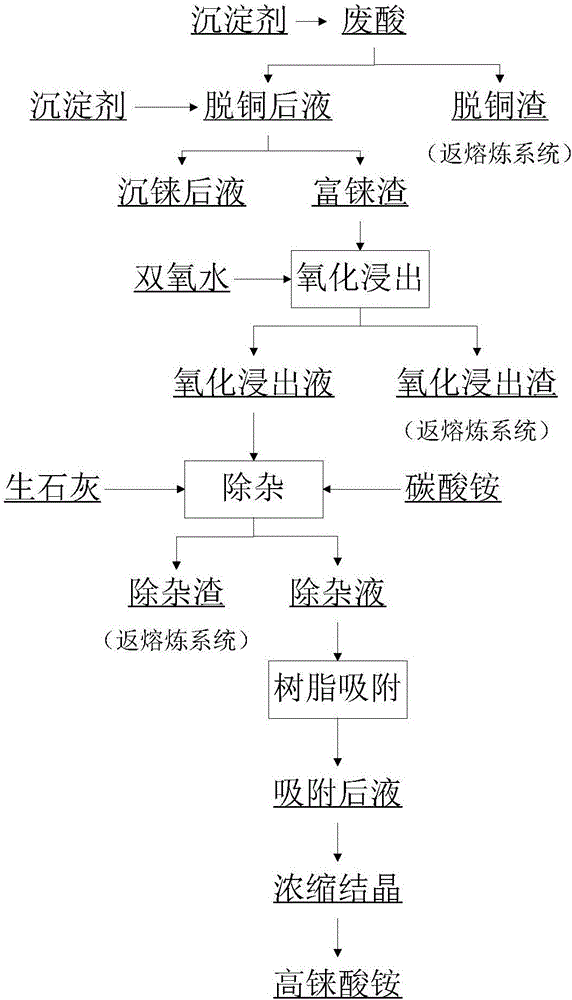
[0049] according to figure 1 The production process shown is carried out.
[0050] 1.1 Decopper operation
[0051] The composition of waste acid is shown in Table 1. Heat the spent acid to 65°C, add sodium thiosulfate according to the mass ratio of the precipitant to the copper contained in the spent acid 7.3:1, and react for 30 minutes to obtain a copper removal solution. The composition of the copper removal solution is shown in Table 2.
[0052] Table 1 waste acid composition (g / L)
[0053] Cu Fe As Re Mo Se 0.35 0.30 0.98 0.0077 0.012 0.027
[0054] Composition (g / L) of table 2 decopper solution
[0055] Cu Fe As Re Mo Se 0.0096 0.28 0.96 0.0071 0.010 0.0034
[0056] It can be seen from Table 1 and Table 2 that the copper removal rate in the copper removal solution is 97.26%, and the rhenium loss rate is 7.79%.
[0057] 1.2 Shen rhenium operation
[0058] Heat the decopper solution to 70°C, add sodium...
Embodiment 2
[0078] 2.1 Decopper operation
[0079] The composition of spent acid is shown in Table 7. Heat the spent acid to 65°C, add sodium thiosulfate according to the mass ratio of the precipitant to the copper in the spent acid 8.5:1, and react for 35 minutes to obtain a decopper solution. The composition is shown in Table 8.
[0080] Table 7 waste acid composition (g / L)
[0081] Cu Fe As Re Mo Se 0.9 0.68 1.04 0.018 0.016 0.0078
[0082] Table 8 Decopper solution composition (g / L)
[0083] Cu Fe As Re Mo Se 0.044 0.66 1.03 0.013 0.017 <0.00050
[0084] It can be seen from Table 7 and Table 8 that the copper removal rate in the liquid after decopper removal is 95.11%, and the rhenium loss rate is 27.54%.
[0085] 2.2 Shen rhenium operation
[0086] Heat the decopper solution to 72°C, add sodium thiosulfate according to the ratio of the mass (g) of the precipitating agent to the volume (L) of the waste acid (L) 3...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com