Preparation method of sponge structure iron/SiC particle-based oil-water separation enhancement layer material
An oil-water separation and structural technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of sponge structure iron/SiC particle-based oil-water separation enhancement layer materials, can solve problems such as secondary environmental pollution, and achieve strong adsorption, strong drainage, and oil-water separation efficiency. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
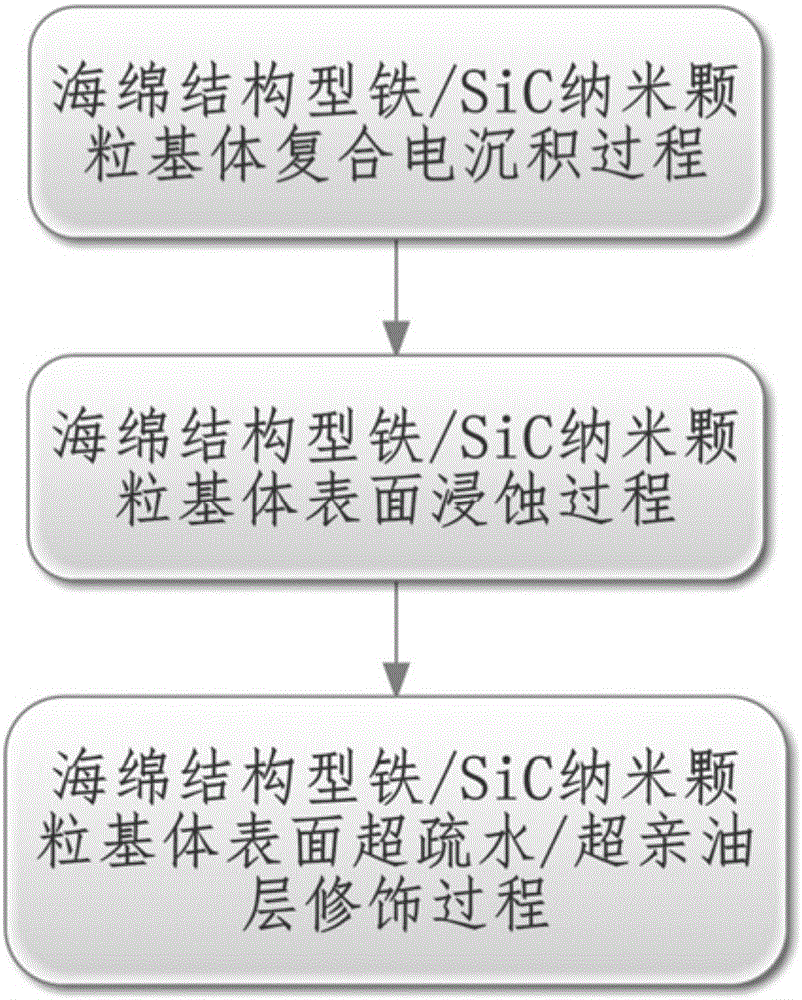
[0032] Preferred Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a method for preparing a sponge-structured iron / SiC nanoparticle composite material, comprising the following steps in order:
[0033] ① Conductive treatment of polyurethane sponge model: Mix nano-carbon powder, nano-iron powder, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose, xanthan gum, sodium silicate and deionized water to form a conductive paste. The mass percentages of each component in the above-mentioned conductive paste are respectively: nano-carbon powder 18%, nano-iron powder 20%, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose 3%, xanthan gum 5%, ammonium bicarbonate 1.5%, and the rest are Deionized water; After fully soaking the polyurethane sponge in the conductive paste, dry it in a 35°C drying oven for 4 hours to obtain a conductive polyurethane sponge model.
[0034] ② Sponge structure type iron / SiC nanoparticle matrix composite electrodeposition treatment: the concentration is analytically pure iron oxide, hydrochloric acid with a ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Preferred embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a method for preparing a sponge-structured iron / SiC nanoparticle composite material with reduced surface energy, comprising the following steps in order:
[0039] ① Conductive treatment of polyurethane sponge model: Mix nano-carbon powder, nano-iron powder, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose, xanthan gum, sodium silicate and deionized water to form a conductive paste. The mass percentages of each component in the above-mentioned conductive paste are respectively: nano-carbon powder 18%, nano-iron powder 20%, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose 3%, xanthan gum 5%, ammonium bicarbonate 1.5%, and the rest are Deionized water; After fully soaking the polyurethane sponge in the conductive paste, dry it in a 35°C drying oven for 4 hours to obtain a conductive polyurethane sponge model.
[0040] ② Sponge structure type iron / SiC nanoparticle matrix composite electrodeposition treatment: the concentration is analytically pure iron oxid...
Embodiment 3
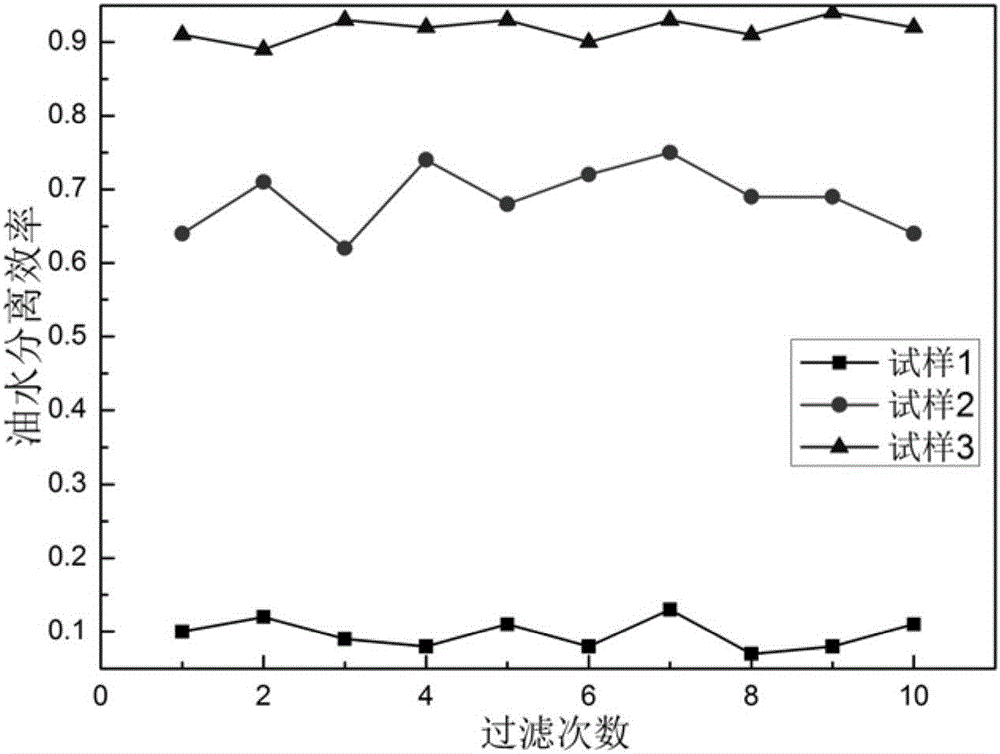
[0045] Preferred embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a preparation method of a sponge-structured iron / SiC nanoparticle-based superhydrophobic / superoleophilic reinforcement layer oil-water separation material, comprising the following steps in order:
[0046] ① Conductive treatment of polyurethane sponge model: Mix nano-carbon powder, nano-iron powder, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose, xanthan gum, sodium silicate and deionized water to form a conductive paste. The mass percentages of each component in the above-mentioned conductive paste are respectively: nano-carbon powder 18%, nano-iron powder 20%, ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose 3%, xanthan gum 5%, ammonium bicarbonate 1.5%, and the rest are Deionized water; After fully soaking the polyurethane sponge in the conductive paste, dry it in a 35°C drying oven for 4 hours to obtain a conductive polyurethane sponge model.
[0047] ② Sponge structure type iron / SiC nanoparticle matrix composite electrodeposition treatment: the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com