A method for detoxification and graded resource utilization of domestic waste incineration fly ash
A domestic waste incineration and recycling technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency and removing solid waste, can solve problems such as high cost, difficult recycling of useful resources, and poor harmless effect of fly ash, so as to improve efficiency, Solve the problem of seriously exceeding the standard and waste of useful resources, and the effect is remarkable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1: Preparation of permeable bricks after detoxification of fly ash
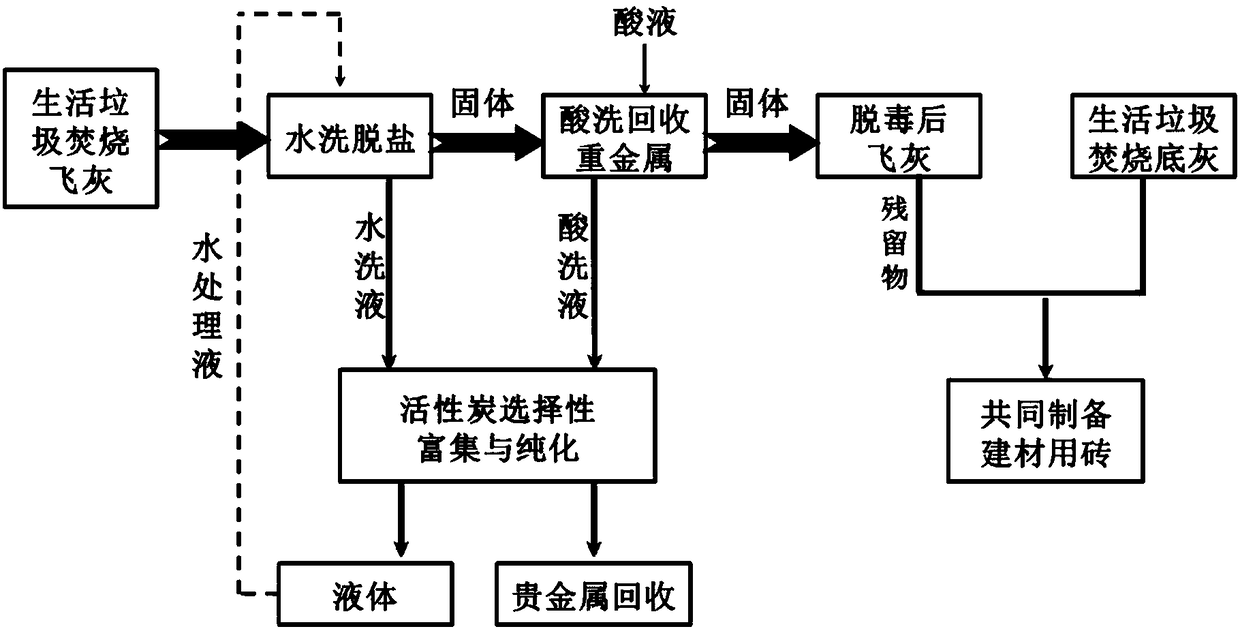
[0038] A method for detoxification and graded resource utilization of domestic waste incineration fly ash, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0039] (1) Mix domestic waste incineration fly ash and water at a mass volume ratio of 1:10g / ml, and mix with mechanical stirring for 1 hour to ensure that soluble salts and chlorine are fully dissolved to form a mortar. After washing with water, the mass of soluble salt dissolved in water accounts for about 29% of the weight of the original fly ash, and the removal rate of chlorine element in the original fly ash is as high as 87%.
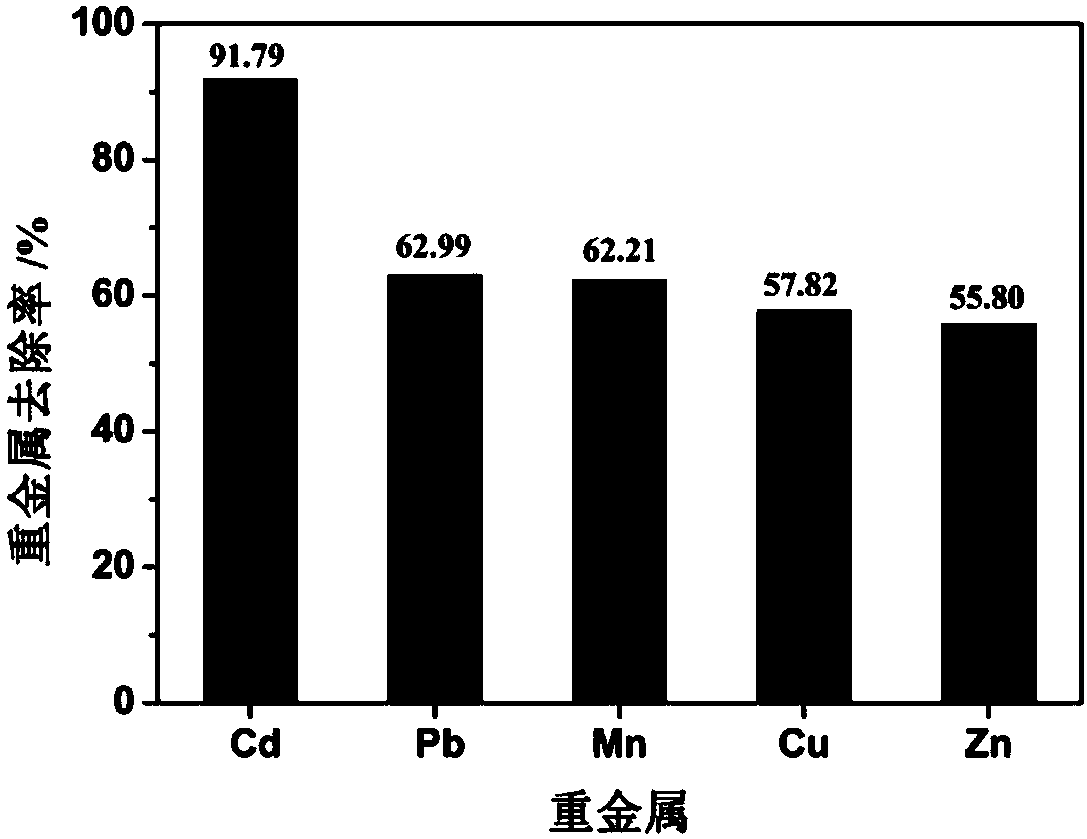
[0040] (2) The mortar obtained in the step (1) is sent into a centrifuge for dehydration, and the washing liquid and the washed fly ash are separated, wherein the washed fly ash and 1.5mol / L nitric acid preparation solution are according to the mass volume ratio of 1: Mix at a ratio of 10g / ml, pickle ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Recovery of heavy metals in fly ash
[0049] This embodiment is the recovery of heavy metals in the washing solution and pickling solution obtained in Example 1.
[0050] The washing solution from the fly ash washed with the pickling solution after the pickling of the fly ash is directly mixed, and left to settle for 1-3 hours, and the supernatant is enriched and purified with activated carbon with selective adsorption function for heavy metals (zinc, lead, copper, etc.) etc.), the activated carbon after enrichment and purification of heavy metals can be used to recover heavy metals, specifically: firstly, the heavy metals adsorbed by activated carbon are dissolved by pickling, and then separated from the solution (such as reduction precipitation method, solvent extraction method, etc.) and refining, Finally, pure heavy metal products are obtained. The recovery rate of heavy metals is as high as 80%. Activated carbon after enrichment and purification of hea...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Recovery of soluble salts in fly ash
[0053] This example is the recovery of soluble salts in the remaining liquid phase after heavy metal enrichment and purification using activated carbon with selective adsorption function in Example 1.
[0054] In this embodiment, soluble salts are precipitated through solution evaporation and concentration. The evaporation concentration temperature is 80-100° C., and the recoverable soluble salts are mainly sodium salts, magnesium salts and calcium oxides, etc., and the recovery rate of soluble salts is as high as 90%. This achieves the purpose of recovering soluble salts in water samples. After the evaporated water is condensed, it can be recycled for washing the fly ash, and a certain volume of tap water is added again according to the mixing ratio of the fly ash and water during the washing process.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com