Method for producing sour tea by direct vat set bacterial fermentation
A direct-injection, bacterial agent technology, used in the food industry for tea making and food fields, to achieve the effect of fresh taste, rich sour tea aroma, and no bad smell
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: (straight-input type lactobacillus plantarum fermentation)
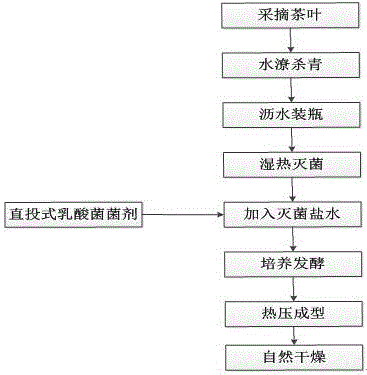
[0029] 1). Selection of tea raw materials: Fresh tea leaves with one bud and three or four leaves are used, and the tea leaves are picked in summer and autumn.
[0030] 2). Water cleaning: Blanch the picked fresh tea leaves with boiling water for 2 minutes, immediately take them out after blanching and put them in ice water for cooling, then take out the tea leaves and put them on a bamboo plaque to drain.
[0031] 3). Draining and bottling: spread the drained tea leaves thinly on the bamboo plaque, which can speed up the water loss. Then divide into 500ml glass bottles with lids, each bottle is filled with 200g tea leaves.
[0032] 4). Steam sterilization: put the tea leaves together with the glass bottle in an autoclave, and carry out steam damp heat sterilization at a temperature of about 115° C. for 40 minutes.
[0033] 5). Add sterilized saline and inoculum: cool the sterilized tea leaves ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: (direct throw type Lactobacillus brevis fermentation)
[0038] 1). Selection of tea raw materials: Fresh tea leaves with one bud and three or four leaves are used, and the tea leaves are picked in summer and autumn.
[0039] 2). Water cleaning: Blanch the picked fresh tea leaves with boiling water for 2 minutes, immediately take them out after blanching and put them in ice water for cooling, then take out the tea leaves and put them on a bamboo plaque to drain.
[0040] 3). Draining and bottling: spread the drained tea leaves thinly on the bamboo plaque, which can speed up the water loss. Then divide into 500ml glass bottles with lids, each bottle is filled with 200g tea leaves.
[0041] 4). Steam sterilization: put the tea leaves together with the glass bottle in an autoclave, and carry out steam damp heat sterilization at a temperature of about 115° C. for 40 minutes.
[0042] 5). Add sterilized saline and inoculum: cool the sterilized tea leaves to be...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Embodiment 3 control group-non-fermentation
[0047] 1). Selection of tea raw materials: Fresh tea leaves with one bud and three or four leaves are used, and the tea leaves are picked in summer and autumn.
[0048] 2). Water cleaning: Blanch the picked fresh tea leaves with boiling water for 2 minutes, immediately take them out after blanching and put them in ice water for cooling, then take out the tea leaves and put them on a bamboo plaque to drain.
[0049] 3). Draining and bottling: spread the drained tea leaves thinly on the bamboo plaque, which can speed up the water loss. Then divide into 500ml glass bottles with lids, each bottle is filled with 200g tea leaves.
[0050]4). Steam sterilization: put the tea leaves together with the glass bottle in an autoclave, and carry out steam damp heat sterilization at a temperature of about 115° C. for 40 minutes.
[0051] 5). Add sterilized saline and bacteria agent: cool the sterilized tea leaves to below 40°C, add 250ml...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com