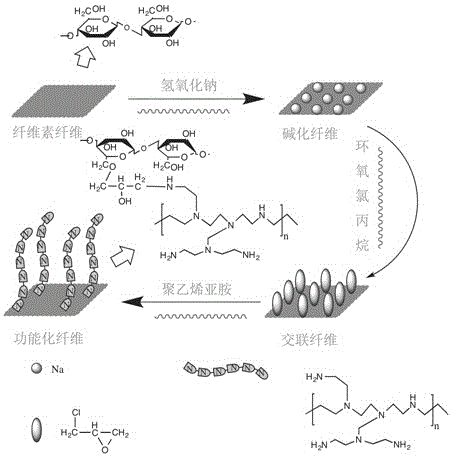
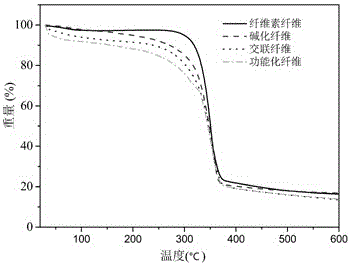
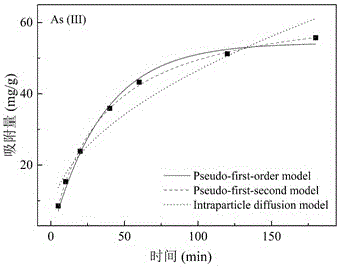
Method for rapidly modifying cellulose fiber by microwave and application thereof
A cellulose fiber and fast technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of large flow resistance, difficulty in application, lack of emergency treatment technology, and low adsorption capacity of disposal materials, so as to solve the problems of improving disposal efficiency and response speed, shortening preparation time, The effect of saving reaction raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] In this embodiment, modified cellulose fiber is used as the raw material for adsorption, and As(III) ions are selected as the target pollutant. The specific technical scheme is as follows:
[0037] 1. Activation of fibrils
[0038] Weigh 1 g of cellulose fiber, add 100 mL of 10% NaOH aqueous solution ( V:V ), mixed thoroughly and then transferred to a microwave reaction bottle, set the microwave power to 200 W, the heating temperature to 2 min×5 groups, a total of 10 min, with an interval of 30 s between the two groups to prevent the explosion caused by the high temperature. boil. After the reaction is completed, the activated fibers are taken out, washed with hot water and ethanol to neutrality, and dried in a drying oven at 60° C. to constant weight.
[0039] 2. Microwave-assisted cross-linking of activated fibers
[0040] After fully mixing 1 g of activated cellulose fiber with 25 mL of epichlorohydrin, add it into a reaction flask containing 25 mL of dimethyl sul...
Embodiment 2
[0048] In this embodiment, modified cellulose fibers are used as adsorption raw materials, and As(V) ions are selected as target pollutants. The specific technical scheme is as follows:
[0049] 1. Activation of fibrils
[0050] Weigh 1 g of cellulose fiber, add 100 mL of 10% NaOH aqueous solution ( V:V ), mixed thoroughly and then transferred to a microwave reaction bottle, set the microwave power to 200 W, the heating temperature to 2 min×5 groups, a total of 10 min, with an interval of 30 s between the two groups to prevent the explosion caused by the high temperature. boil. After the reaction is completed, the activated fibers are taken out, washed with hot water and ethanol to neutrality, and dried in a drying oven at 60° C. to constant weight.
[0051] 2. Microwave-assisted cross-linking of activated fibers
[0052] After fully mixing 1 g of activated cellulose fiber with 25 mL of epichlorohydrin, add it into a reaction flask containing 25 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com