Artemisia apiacea bZIP-type transcription factor encoding sequence, cloning method and application
A coding sequence and transcription factor technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as complex synthetic pathways and difficult single gene modification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1, the cloning of embodiment 1 Artemisia annua AabZIP6 gene
[0047] 1. Artemisia annua was cultivated in an artificial climate chamber under the photoperiod of 18h / 6h (light / dark), 25°C;
[0048] 2. Extraction of total RNA from leaves of Artemisia annua. Take about 100 mg of tender young Artemisia annua leaf tissue material, put it in liquid nitrogen and grind it into powder, and extract the total RNA of the leaf according to the method of the plant total RNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical, Beijing). 3 μL of the obtained plant total RNA was subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis to identify the quality of the total RNA, and then the concentration of the total RNA was measured on a NanoDrop (Thermo Fisher, USA) spectrophotometer.
[0049] 3. Gene cloning. Using the extracted total RNA as a template (500ng), according to the reverse transcription kit PrimeScript1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (TaKaRa, Dalian) instructions, reverse transcription to pro...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2, the construction of the plant expression vector comprising AabZIP6 gene
[0057] 1. Construction of the intermediate vector pENTR-TOPO-AabZIP6.
[0058] Design and amplify the AabZIP6 gene open reading frame sequence according to the sequence information of SEQ ID NO.1, and the amplification primers are as follows:
[0059] Forward primer P3: 5'-CACCATGTCGAGGCCACCTCGACTTCC-3'
[0060] Reverse primer P4: 5'-GTTAATATGAAGCTTGCCCATGTC-3'
[0061] The pENTR / D-TOPO vector was purchased from Invitrogen Company, and it is the entry vector of the company's Gateway cloning technology. According to the requirements of the product specification, four bases of CACC were added before the ATG base of the forward primer. Using the pLB-AabZIP6 plasmid as a template, PCR amplification was performed with the blunt end high-fidelity enzyme KOD. After the PCR product was recovered and purified, it was connected to the pENTR-TOPO vector by the method of Gateway cloning tech...
Embodiment 3
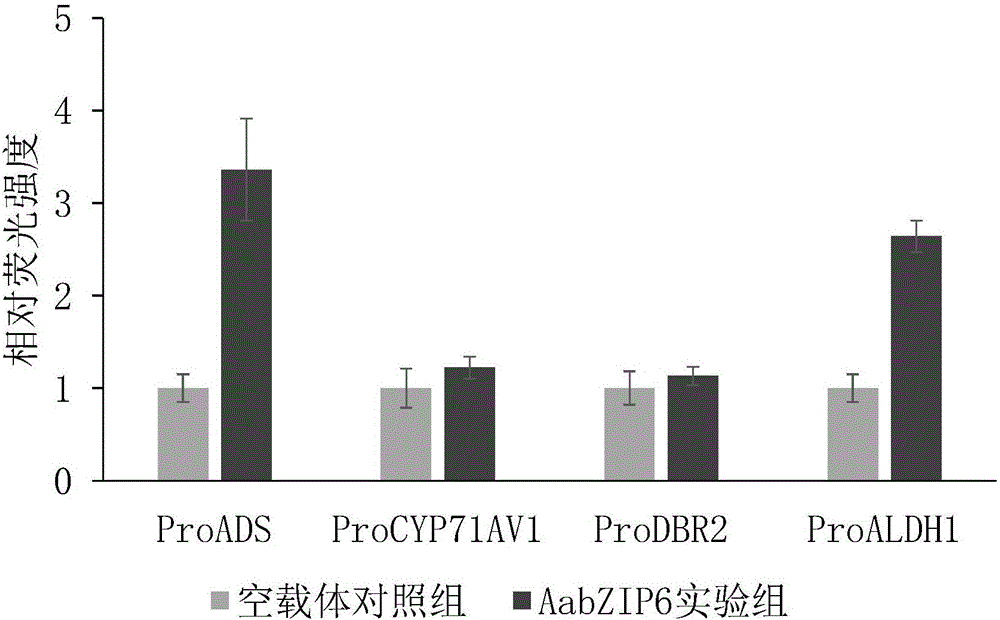
[0063] Example 3. Construction of dual fluorescein reporter vectors for artemisinin synthesis pathway-specific gene promoters
[0064] 1. PCR amplification of the promoter of the specific gene of the artemisinin synthesis pathway. According to the sequence information of the ADS gene promoter (GenBank: DQ448297.1) in the NCBI database, design the ADS gene promoter amplification specific primers, the forward and reverse specific primers contain Kpn I and Pst I restriction sites respectively, and the primer sequences are as follows :
[0065] ProADS F 5'-ggtaccACCGGGGACCTCTAGAGATC-3',
[0066] ProADS R 5'-ctgcagGATTTTACAAACTTTGAA-3'.
[0067] Similarly, according to the sequence information of the CYP71AV1 gene promoter (GenBank: FJ870128.1) in the NCBI database, CYP71AV1 promoter-specific primers containing Kpn I and Pst I restriction sites were designed, and the primer sequences were as follows:
[0068] ProCYP F 5'-ggtaccATGGGTCAATTTCGGGTTG-3',
[0069] ProCYP R 5'-ctgc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com