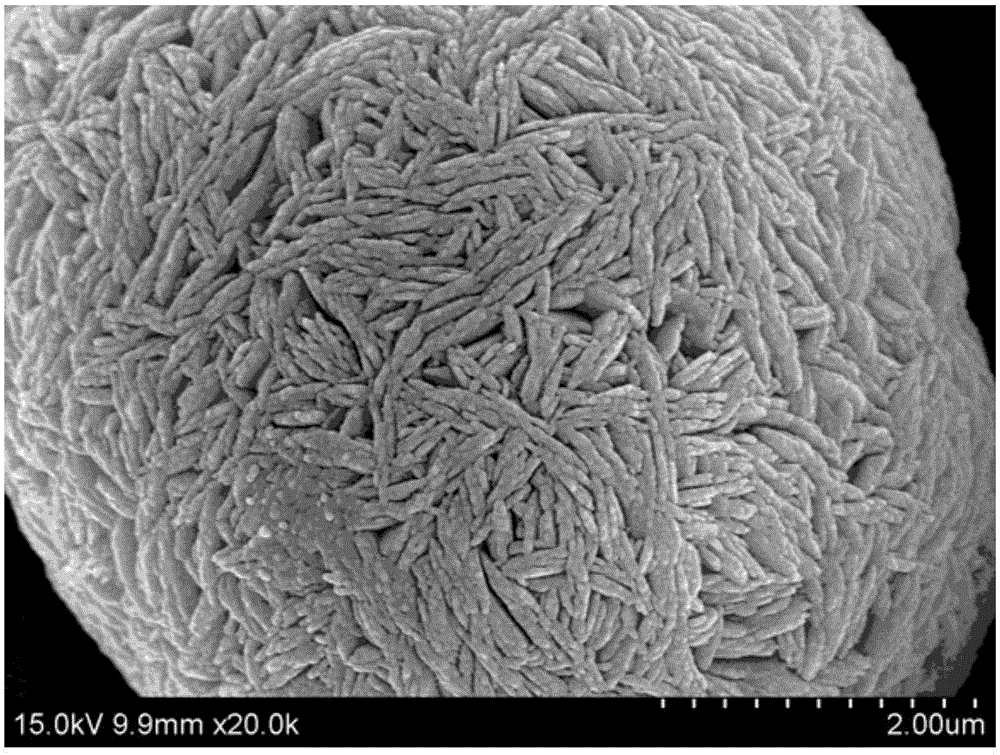
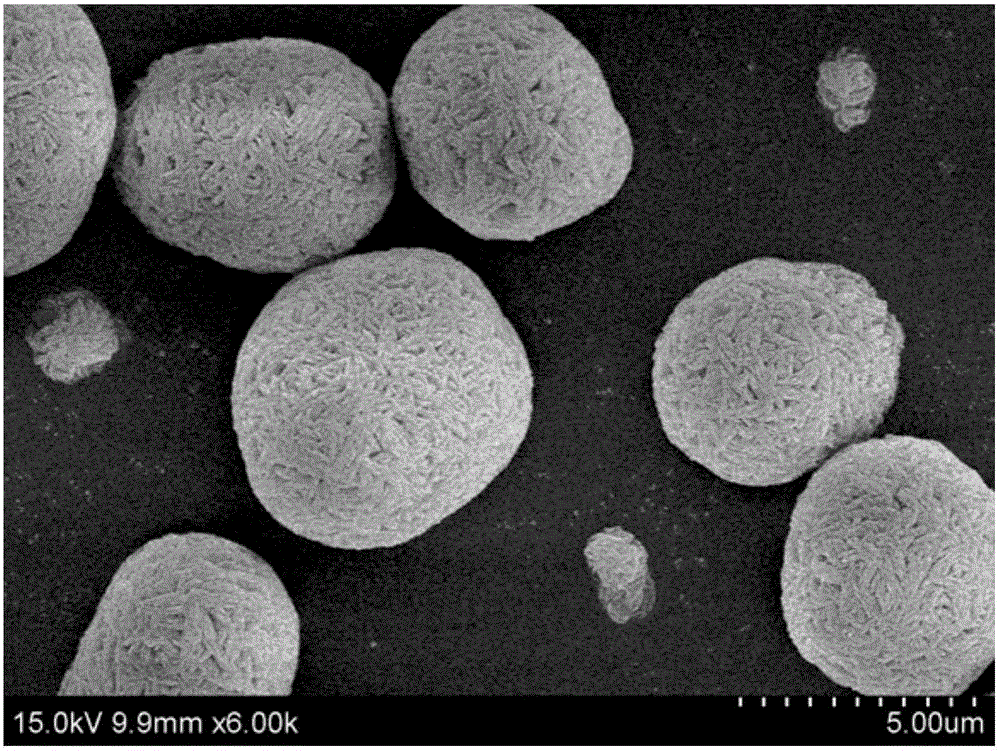
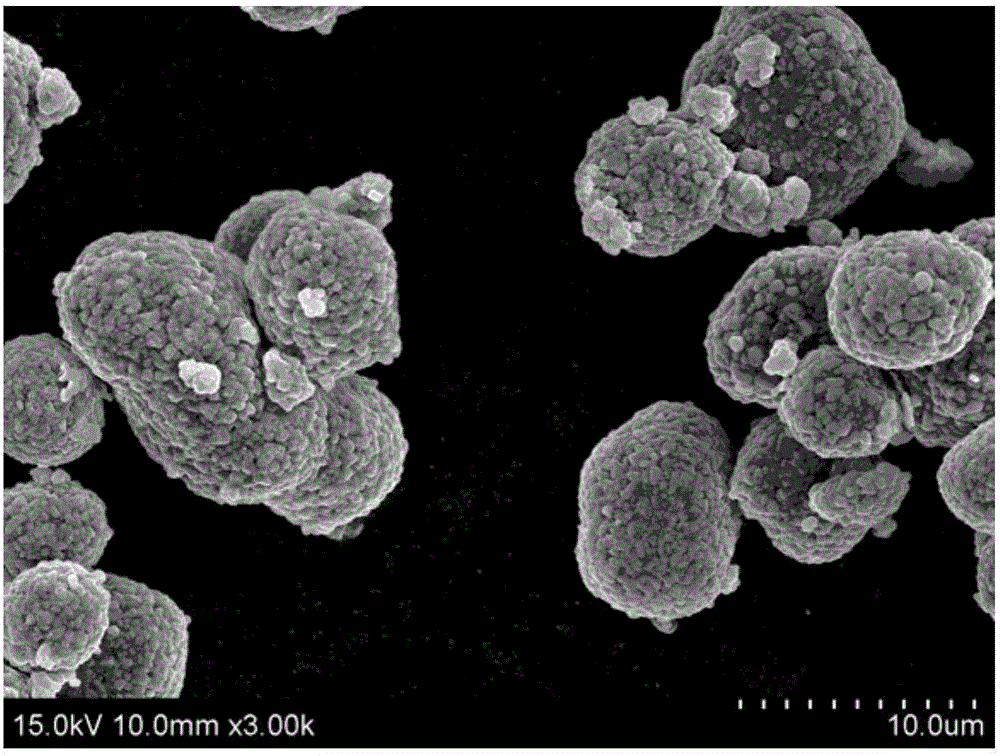
Preparation method of lithium-ion-battery anode material with bulk-phase-doped metal elements
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and positive electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory electrochemical performance, few types of doping elements, complex doping process, etc., and achieve ideal electrochemical performance , good doping effect, avoiding the effect of limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific Embodiment 1: The preparation method of the lithium-ion battery positive electrode material doped with metal elements in bulk according to the present embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0023] 1. First prepare the precursor of the positive electrode material of lithium-ion battery by hydrothermal method, co-precipitation method or chemical synthesis method;
[0024]2. Preparation of organometallic salt derivative solution: use ethanol as solvent, add organic chelating agent and organic metal salt to react to generate new organometallic salt derivatives, and prepare organometallic salt with a concentration of 0.5mol / L~3mol / L Derivative solution; the molar ratio of the organic chelating agent to the organometallic salt is (0.1-2): 1, stirred in an oil bath at 50-60°C until the solution is uniform and transparent, and an organometallic salt derivative solution is obtained;
[0025] 3. Vacuum impregnation method to prepare the precursor o...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the organic metal salt is Ni, Co, Mn, Mg, Al, Ca, Zn, Cu, Cr, Zr, Ti, Fe, V, Mo metal alkoxide, phenoxide or a combination of one or more of the above metals and alkoxy, phenoxy, etheroxy, ketooxy, aldehydeoxy, esteroxy, amine groups organometallic salts. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0028] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the organic chelating agent is acetic acid, glutaric acid, amino acid, ethyl propionate, butyl hydroxypropionate, o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, acetylacetone, One of benzoylacetone, dimethyl malonate, monoethyl malonate, ethyl butyryl acetate, ethyl levulinate, methyl methoxyacetate, methyl succinic acid, propionic anhydride or a mixture of several. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com