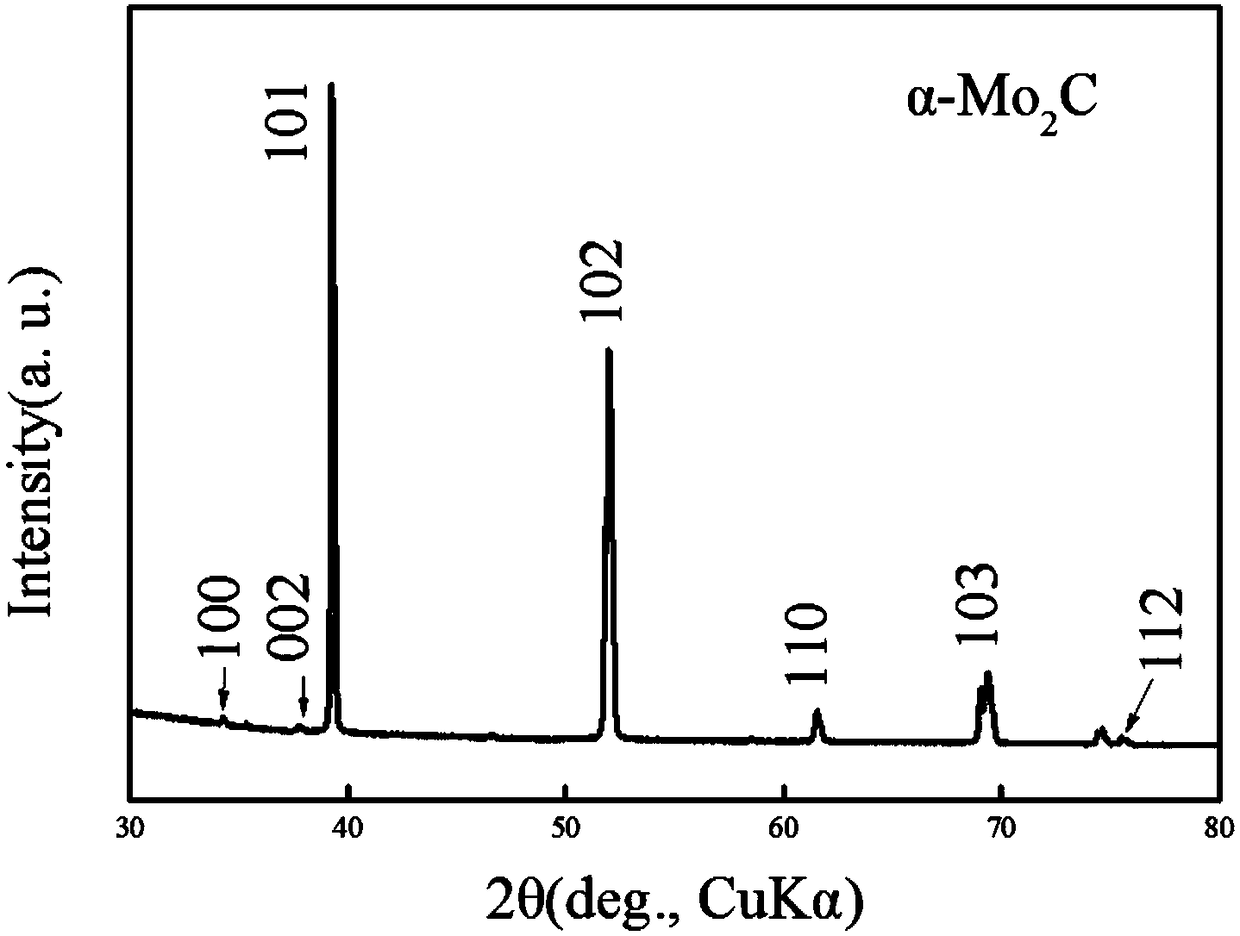
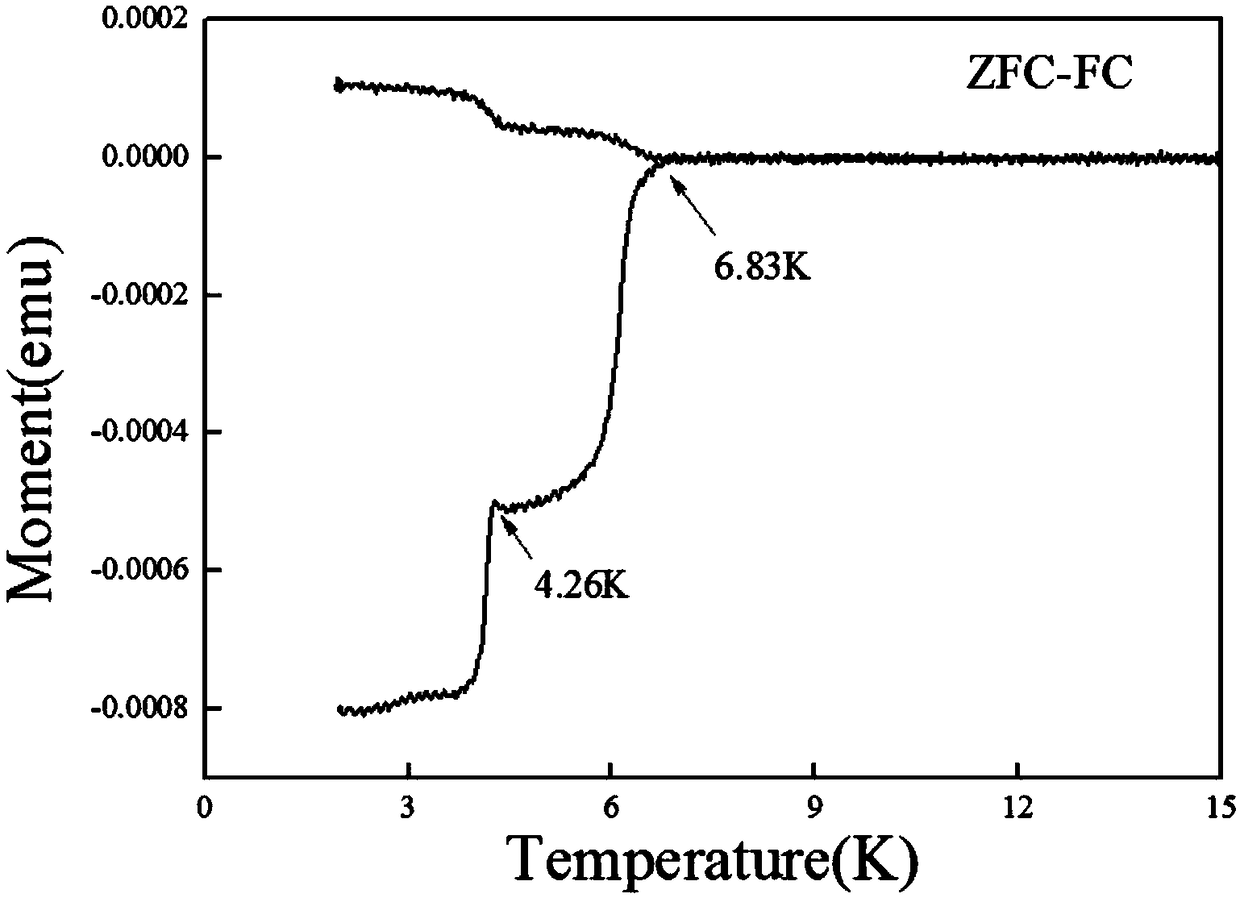
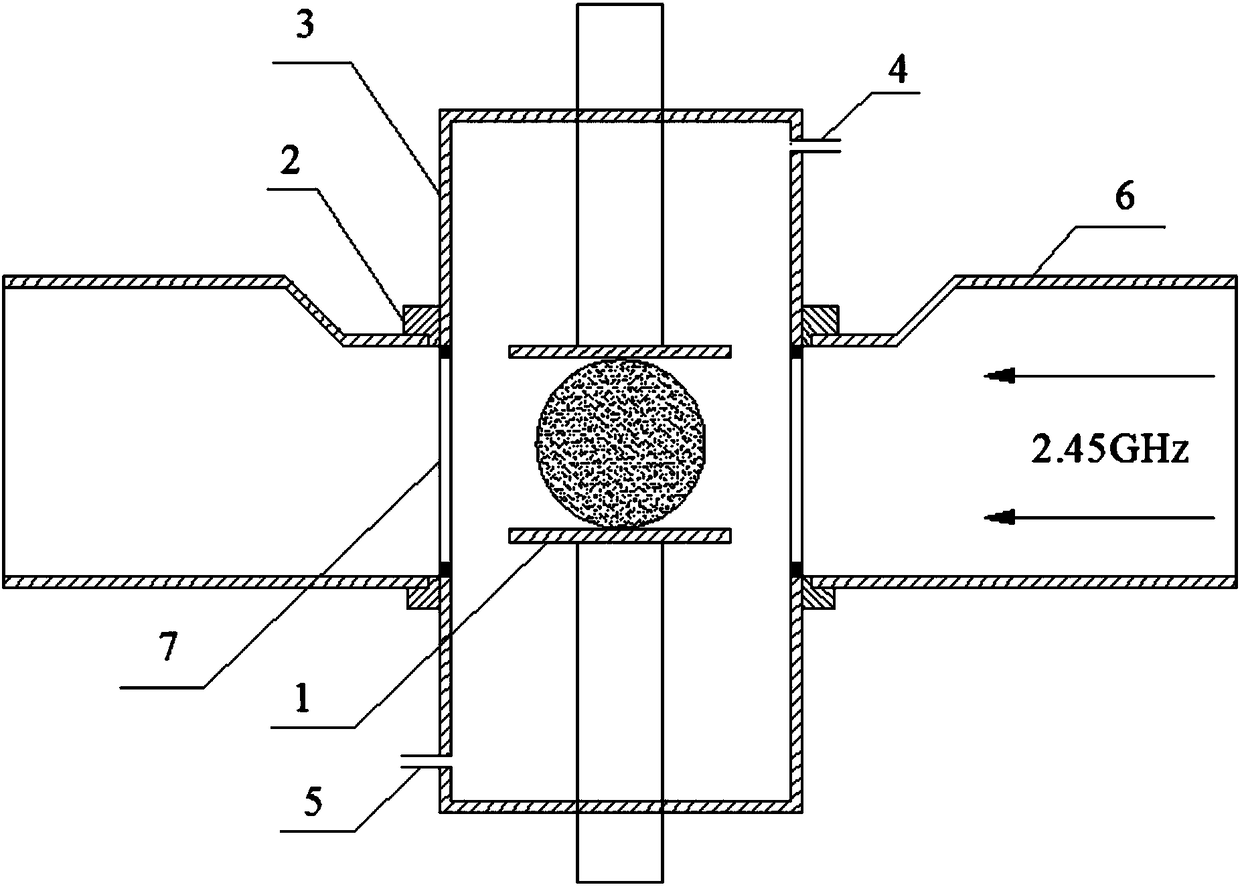
A method for preparing α-phase molybdenum carbide crystals by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition
A technology of chemical vapor deposition and microwave plasma, which is applied in the direction of gaseous chemical plating, metal material coating process, coating, etc., can solve the problems of different research results, affecting the performance and content of molybdenum carbide, and achieve energy density Large, deposition-promoting, easily dissociated effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Using ethanol and acetone solutions in sequence to ultrasonically clean the silicon substrate to remove surface impurities. Subsequently, the silicon wafer is placed in the center above the substrate stage, the metal flange is sealed, and the cavity is evacuated.
[0025] (2) Pass hydrogen into the chamber, adjust the microwave power, hydrogen flow and pressure, and the gas absorbs microwave energy to excite plasma. The process parameters used are: hydrogen flow 200 sccm, working pressure 10kPa, microwave power 800W.
[0026] (3) Adjust the height of the substrate stage so that the plasma wraps the silicon wafer and heats the silicon substrate (the temperature is 600°C-800°C, and the temperature is determined by the heat generated by microwave energy). Adjust the vacuum trimmer valve to keep the air pressure in the chamber at about 11kPa.
[0027] (4) When the plasma state is stable, feed methane and molybdenum hexafluoride successively to adjust the gas flow and r...
Embodiment 2
[0031] (1) Using ethanol and acetone solutions in sequence to ultrasonically clean the silicon substrate to remove surface impurities. Subsequently, the silicon wafer is placed in the center above the substrate stage, the metal flange is sealed, and the cavity is evacuated.
[0032] (2) Pass hydrogen into the cavity, adjust the microwave power, hydrogen flow and air pressure, and the gas absorbs microwave energy to excite and generate plasma. The process parameters used are: hydrogen flow 300 sccm, working pressure 10kPa, microwave power 1000W.
[0033] (3) Adjust the height of the substrate table so that the plasma wraps the silicon wafer and heats the silicon substrate (the temperature is 600°C-800°C). Adjust the vacuum trimmer valve to keep the air pressure in the chamber at about 15kPa.
[0034] (4) When the plasma state is stable, feed methane and molybdenum hexafluoride successively to adjust the gas flow and ratio (the volume ratio of methane and molybdenum hexafluorid...
Embodiment 3
[0037] (1) Using ethanol and acetone solutions in sequence to ultrasonically clean the silicon substrate to remove surface impurities. Subsequently, the silicon wafer is placed in the center above the substrate stage, the metal flange is sealed, and the cavity is evacuated.
[0038] (2) Pass hydrogen into the cavity, adjust the microwave power, hydrogen flow and pressure, and the gas absorbs microwave energy to excite plasma. The process parameters used are: hydrogen flow 300sccm, working pressure 10kPa, microwave power 1200W.
[0039] (3) Adjust the height of the substrate table so that the plasma wraps the silicon wafer and heats the silicon substrate (the temperature is 600°C-800°C). Adjust the vacuum trimmer valve to keep the air pressure in the chamber at about 20kPa.
[0040] (4) When the plasma state is stable, feed methane and molybdenum hexafluoride successively to adjust the gas flow and ratio (the volume ratio of methane and molybdenum hexafluoride is CH 4 :MoF 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com