Method for preparing doped graphene or graphene-like compound
A technology of graphene and heteroatoms, which is applied in the field of preparation of doped graphene or graphene-like, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining large-area, thick graphene, complex surface structure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The nano-silica and hexamethylenediamine are prepared into a solution according to the mass ratio of 0.1, and after stirring to obtain a uniform suspension liquid, the mixture is heated to 150° C. and kept for 24 hours. After centrifugal separation, the obtained solid product is dried, and then sintered by microwave heating. The sintering temperature is 900° C., and the sintering time is 30 minutes.
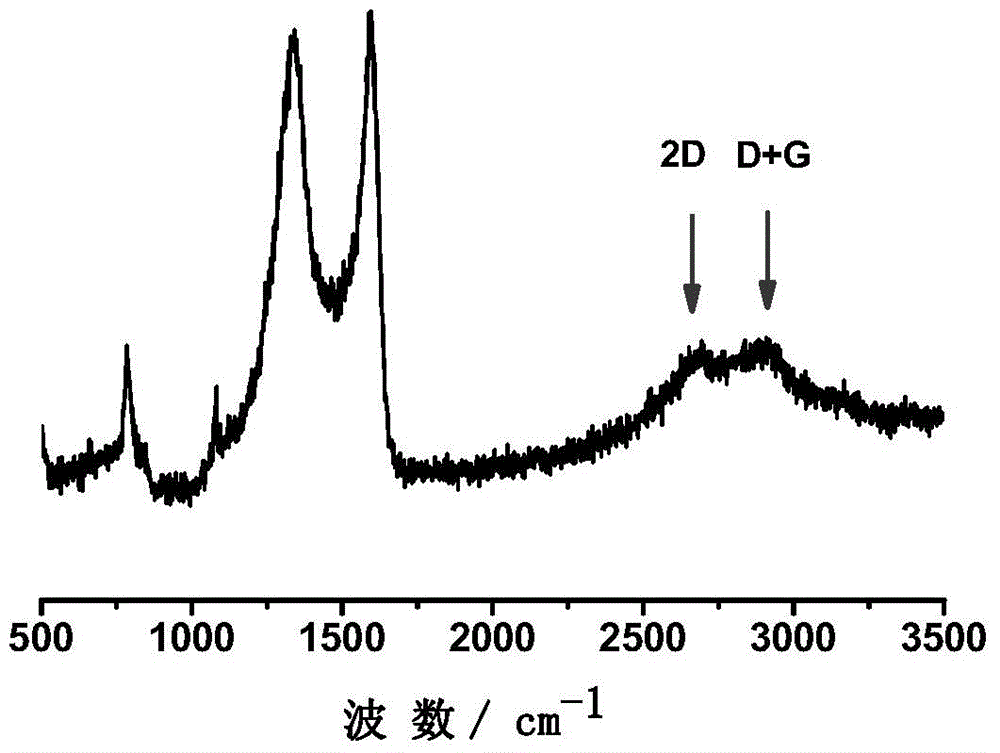
[0036] The nitrogen-doped graphene that present embodiment obtains, its Raman spectrum is as follows figure 1 shown. The Raman spectrum of nitrogen-doped graphene has strong D and G peaks, and the intensity of the G peak is higher than that of the D peak, indicating that graphite-structured carbon is formed, and the 2D and D+G peaks appear at the same time, and the peak intensity is weak , indicating that there are more layers of graphitic carbon.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Prepare nano-silica and hexamethylenediamine into a solution with a mass ratio of 0.1, and add CoCl 2 , where CoCl 2 The molar ratio to hexamethylenediamine is 0.01. After stirring to obtain a uniform suspension liquid, heat it to 150°C and keep it warm for 24 hours. After centrifugal separation, the obtained solid product was dried, and then sintered by microwave heating under nitrogen atmosphere, the sintering temperature was 650° C., and the sintering time was 60 minutes.
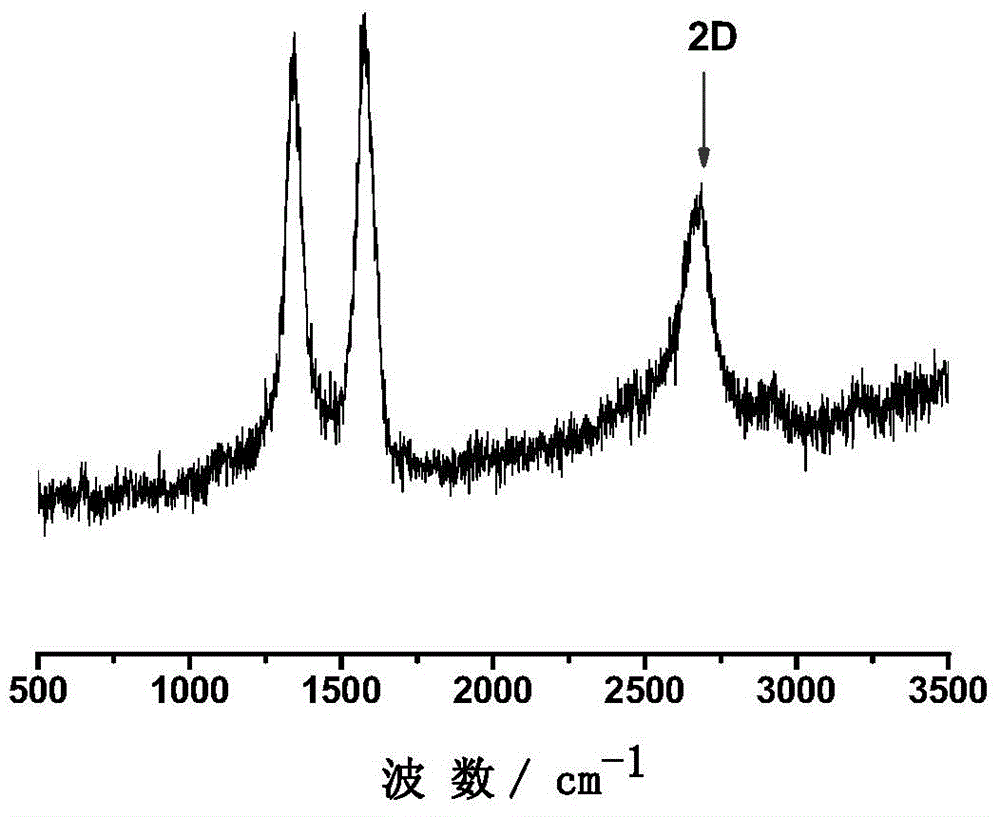
[0039] The nitrogen-doped graphene that present embodiment obtains, its Raman spectrum is as follows figure 2 shown. The Raman spectrum of nitrogen-doped graphene has sharp D and G peaks, and the intensity of G peak is higher than that of D peak, indicating that graphite structure carbon is formed. At the same time, sharp and symmetrical 2D peaks appear, and their intensity is significantly enhanced, indicating that Graphite carbon has fewer layers, forming a few-layer graphene structure. XPS...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Prepare nano-silica and hexamethylenediamine into a solution with a mass ratio of 0.1, and add CoCl 2 , where CoCl 2 The molar ratio to hexamethylenediamine is 0.01. After stirring to obtain a uniform suspension liquid, heat it to 150°C and keep it warm for 24 hours. After the centrifuged solid product is dried, it is sintered by microwave heating under a nitrogen atmosphere, the sintering temperature is 900° C., and the sintering time is 30 minutes.
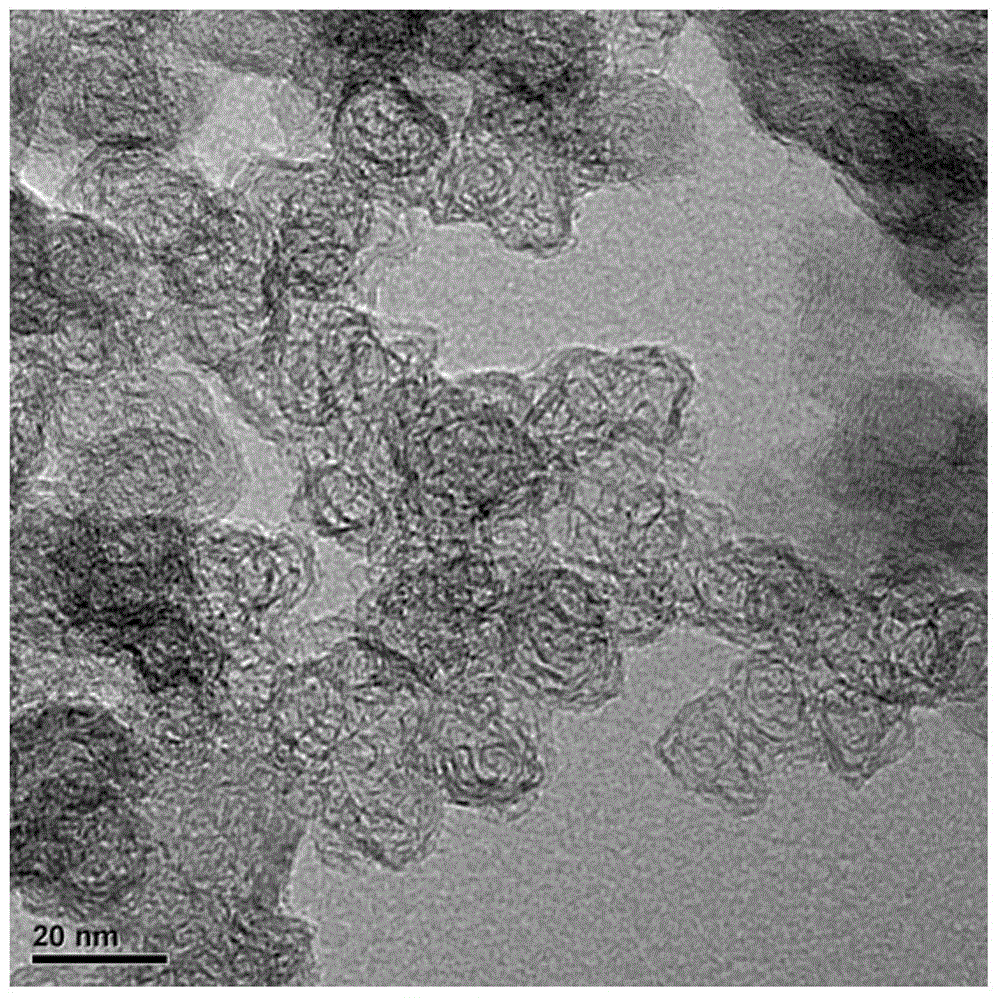
[0042] The nitrogen-doped graphene that present embodiment obtains, its Raman spectrum is as follows Figure 4 shown. The Raman spectrum of nitrogen-doped graphene has strong D and G peaks, and the intensity of G peak is higher than that of D peak, indicating that a better graphite structure carbon is formed, and a broad 2D peak appears at the same time, and the peak intensity is weaker, indicating that Graphite carbon has many layers. XPS results showed that the atomic ratio of N / C was 8%. After washing silica with ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com