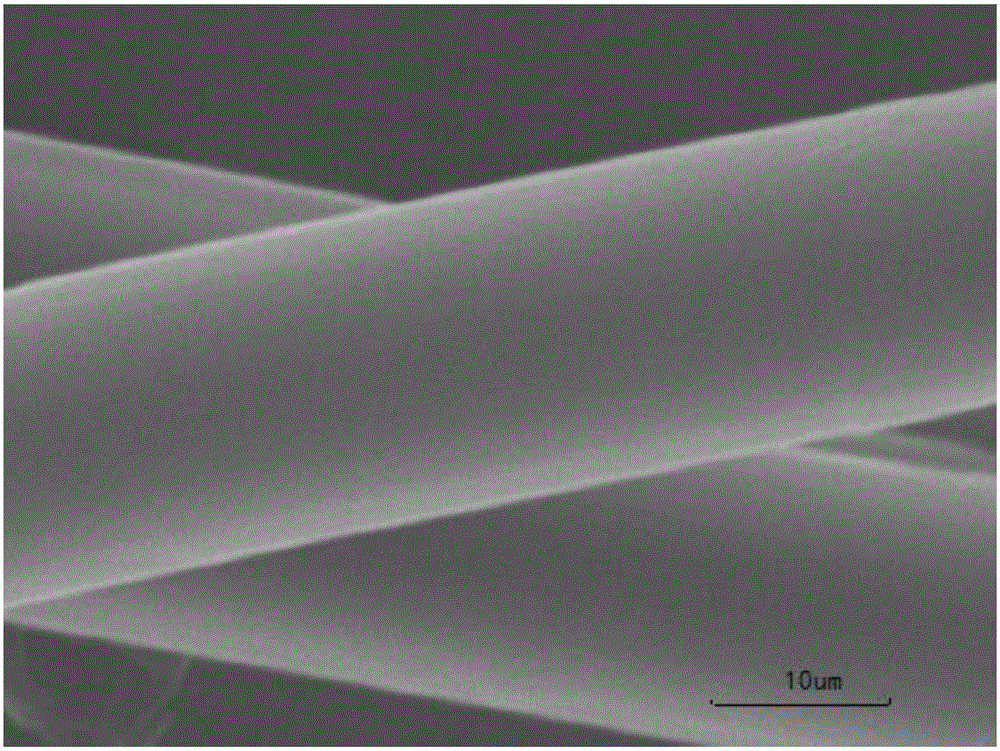
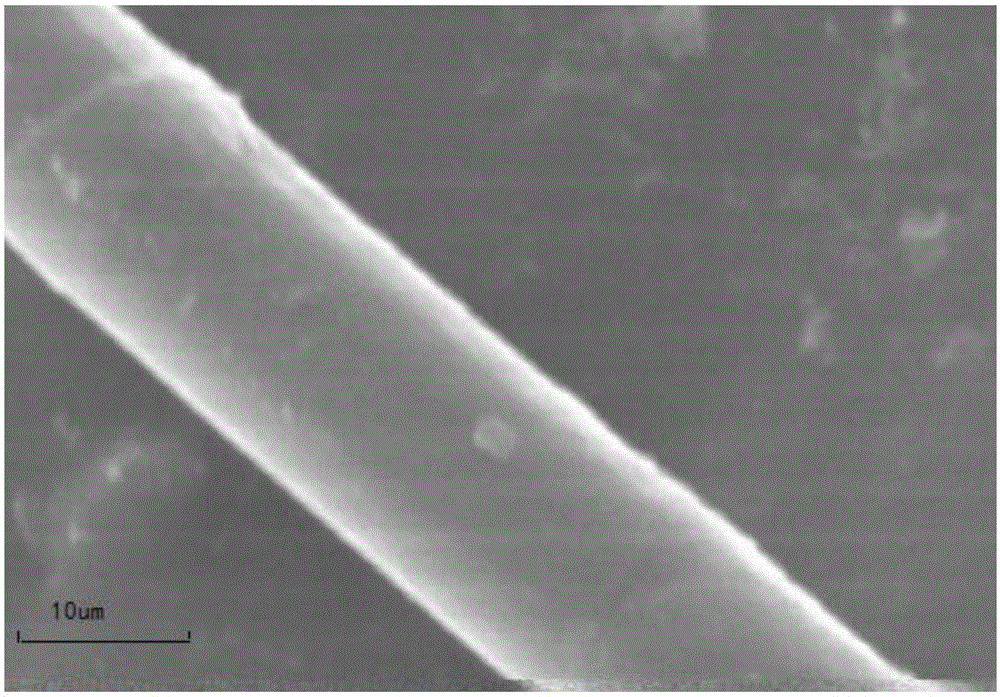
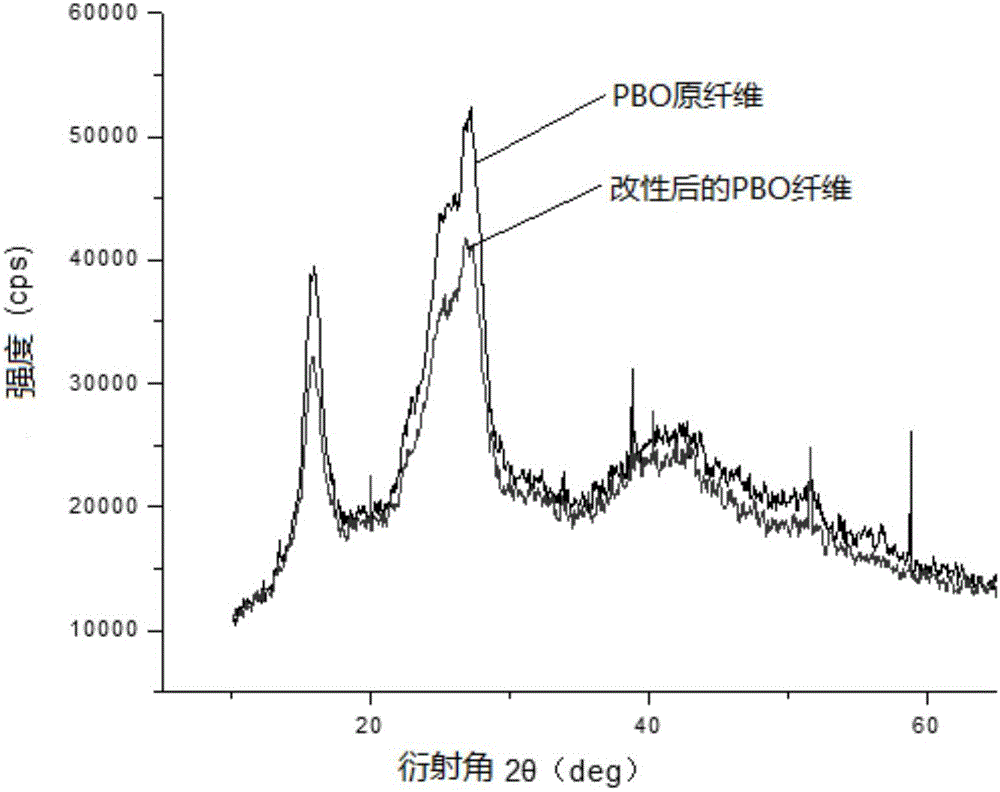
PBO (poly-p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fiber molecular structure modification method
A molecular structure and fiber technology, which is applied in the field of PBO fiber molecular structure modification, can solve the problems of fiber strength reduction, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing mutual attraction, reducing interaction energy, and improving interface bonding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Step 1, prepare multi-component compound acid finishing agent:
[0040] Weigh the following raw materials according to mass percentage: 5% polyphosphoric acid, 3.5% non-oxidative inorganic acid, 0.5% non-ionic surfactant, 0.1% stabilizer, and the balance is deionized water. The sum of the mass percentages of the above components is 100%; Mix the weighed raw materials at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to make them evenly combined to obtain a multi-component composite acid finishing agent.
[0041] Among them, the polyphosphoric acid is polyphosphoric acid; the non-oxidizing inorganic acid is boric acid; the nonionic surfactant is Tween; the stabilizer is phosphite.
[0042] Step 2, surface treatment of PBO fiber with multi-component compound acid finishing agent:
[0043] 2.1 Use alcohol and deionized water to remove impurities on the surface of the PBO fiber and dry it;
[0044] 2.2 Dilute the multi-component composite acid finishing agent prepared in step 1. The d...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Step 1, prepare multi-component compound acid finishing agent:
[0048] Weigh the following raw materials according to mass percentage: 7% polyphosphoric acid, 5.5% non-oxidative inorganic acid, 0.75% non-ionic surfactant, 0.3% stabilizer, and the balance is deionized water. The sum of the mass percentages of the above components is 100%; Mix the weighed raw materials at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to make them evenly combined to obtain a multi-component composite acid finishing agent.
[0049] Among them, the polyphosphoric acid polyphosphoric acid; the non-oxidizing inorganic acid is glacial acetic acid; the nonionic surfactant is fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether; the stabilizer is epoxy resin.
[0050] Step 2, surface treatment of PBO fiber with multi-component compound acid finishing agent:
[0051] 2.1 Use alcohol and deionized water to remove impurities on the surface of the PBO fiber and dry it;
[0052]2.2 Dilute the multi-component composite acid fin...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Step 1, prepare multi-component compound acid finishing agent:
[0056] Weigh the following raw materials according to mass percentage: 10% of polyphosphoric acid, 7% of non-oxidizing inorganic acid, 1% of nonionic surfactant, 0.5% of stabilizer, and the balance is deionized water. The sum of the mass percentages of the above components is 100%; Mix the weighed raw materials at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to make them evenly combined to obtain a multi-component composite acid finishing agent.
[0057] Wherein, the polybasic phosphoric acid is pyrophosphoric acid; the non-oxidizing inorganic acid is commercially available analytically pure hydrochloric acid (mass fraction is 36-38%); the nonionic surfactant is polyoxyethylene ester; the stabilizer is ethanolamine.
[0058] Step 2, surface treatment of PBO fiber with multi-component compound acid finishing agent:
[0059] 2.1 Use alcohol and deionized water to remove impurities on the surface of the PBO fiber and d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| friction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com