Method for removing trivalent arsenic
A technology for trivalent arsenic and pentavalent arsenic is applied in the field of pollutant treatment, which can solve the problems of difficult production, slow speed, and unsuitable for direct treatment of low-concentration arsenic-containing wastewater.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
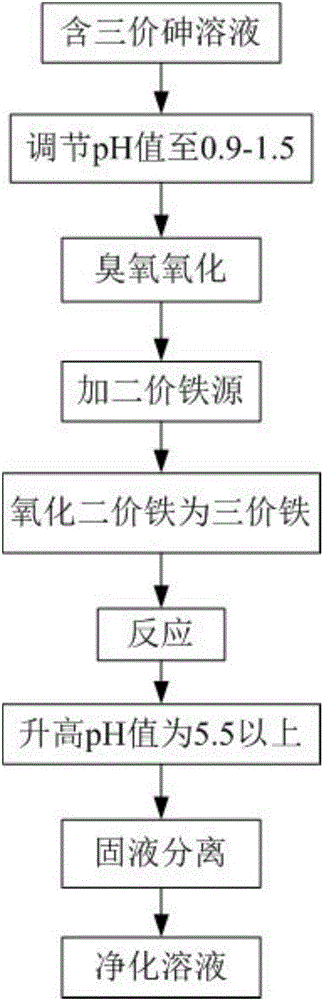
[0052] A method for removing trivalent arsenic in arsenic-containing drainage of a simulated mine, wherein the arsenic-containing drainage of the simulated mine is passed through sodium arsenite (Na 3 AsO 3 ) and iron sulfate (Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ) is dissolved in water and prepared, wherein the concentration of trivalent arsenic is 300mg / L, and the concentration of iron is 1g / L. The method comprises the following steps:
[0053] (1) Take 1000 ml of arsenic-containing drainage from the simulated mine, adjust the pH to 1.0 with sulfuric acid, and pass in ozone-containing gas (concentration about 40 mg / L) generated by the ozone generator at 20 ° C, stir and ventilate for 10-40 minutes After that, a solution containing pentavalent arsenic is obtained;
[0054] (2) Add 5g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4) to the solution containing pentavalent arsenic 4 ·7H 2 0), after stirring and dissolving, the temperature is raised to 70° C. and the air is reacted. During the reaction, sul...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A method for removing trivalent arsenic in arsenic-gold concentrate bioleaching waste liquid, said arsenic-containing gold concentrate bioleaching waste liquid contains 2.8g / L arsenic, 3.6g / L iron, and an initial pH of 2.2. The method includes the following steps:
[0058] (1) Take 1000 milliliters of arsenic-containing gold concentrate bioleaching waste liquid, adjust the pH to 1.3 with sulfuric acid, and feed the ozone-containing gas (concentration of about 40 mg / L) produced by the ozone generator at 25 ° C, and stir and ventilate After 10-40 minutes, a solution containing pentavalent arsenic was obtained;
[0059] (2) Add 10g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4) to the solution containing pentavalent arsenic 4 ·7H 2 0), after stirring and dissolving, the temperature is raised to 70° C. and the air is reacted. During the reaction, sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide are added to control the pH between 0.9-1.5. After 3 hours of reaction, the crystal precipitate contai...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A method for removing trivalent arsenic in arsenic-containing wastewater produced by zinc smelting, wherein the arsenic-containing wastewater produced by zinc smelting contains 0.5 g / L of arsenic, 1.0 g / L of iron, and an initial pH of 2.2.
[0063] (1) Take 1000 milliliters of arsenic-containing waste water produced by zinc smelting, adjust the pH to 1.3 with sulfuric acid, and feed the ozone-containing gas (concentration about 40 mg / L) produced by the ozone generator at 15°C, stir, and ventilate for 10- After 40 minutes, a solution containing pentavalent arsenic was obtained;
[0064] (2) Add 5g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4) to the solution containing pentavalent arsenic 4 ·7H 2 0), after stirring and dissolving, the temperature is raised to 70° C. and the air is reacted. During the reaction, sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide are added to control the pH between 0.9-1.5. After 3 hours of reaction, the crystal precipitate containing scorodite and goethite precip...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com