Method for reducing hexavalent chromium through micromolecular diketone-ultraviolet light
A technology of hexavalent chromium and small molecules, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of complex pollution sources of hexavalent chromium and lack of prevention and control technology, and achieve the effects of wide pH range, simple operation and high industrial application prospect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
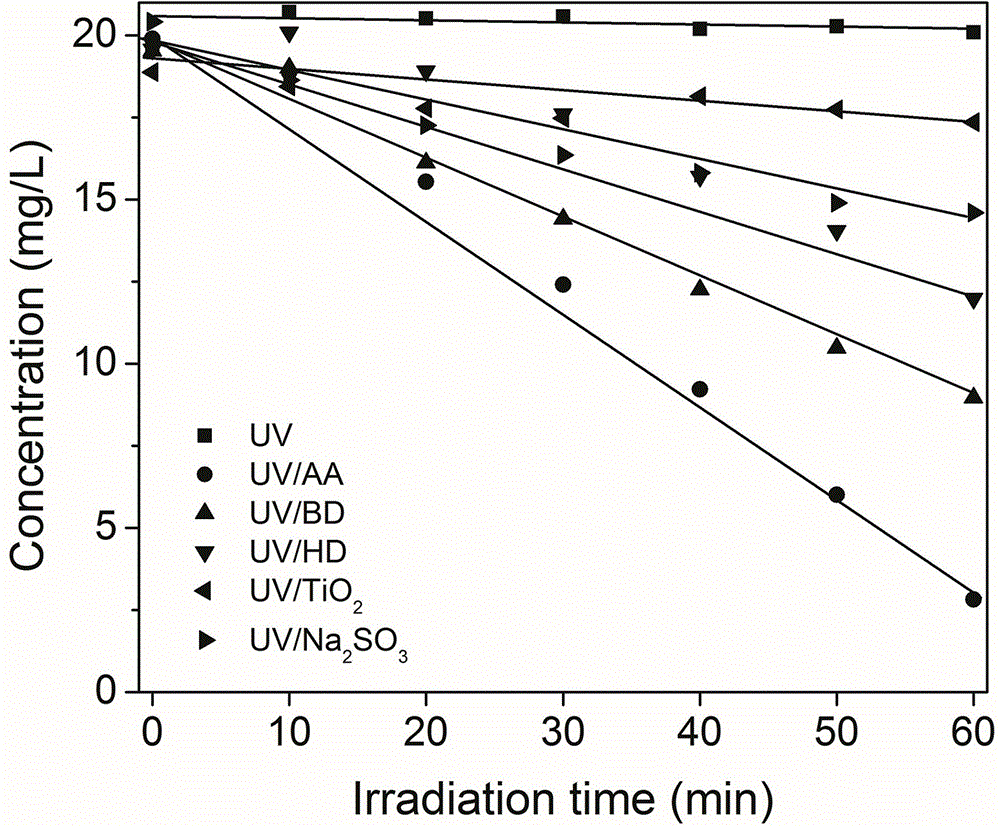
[0023] Embodiment 1UV / diketone is to Cr (VI) reducing effect experiment
[0024] Add the Cr(VI) stock solution into several 25mL colorimetric tubes, and then add the small molecule diketones AA, BD, HD, Na 2 SO 3 and TiO 2 , the final concentration of Cr(VI) (in units of K 2 CrO 7 In Cr(VI))) diluted to 20mg / L, and small molecular diketones AA, BD, HD, and reducing agent Na in the colorimetric tube 2 SO 3 The final concentration is 1.0mM, TiO 2 The final concentration was 1g / L, and then poured into the 25mL reaction tube of the light reaction device.
[0025] The photochemical device used in this implementation case is attached to the specification of the patent CN102491450B figure 1 , 2 As shown, the instrument operation steps are the same as those in Example 1 of this patent.
[0026] This embodiment uses a 300W medium pressure mercury lamp, and the light intensity at the reaction solution is 5mW / cm 2 , light irradiation reaction 60min, sampling once every 10min to...
Embodiment 2
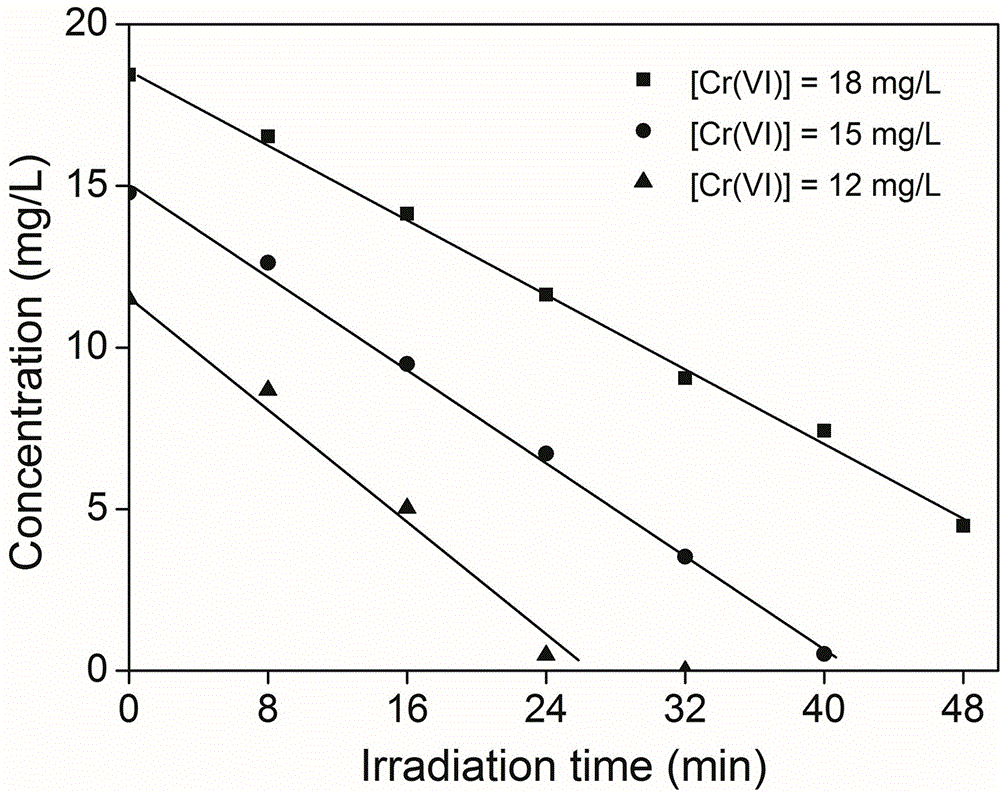
[0028] Example 2 Different initial concentrations of Cr (VI) affect the UV / AA reduction treatment effect test
[0029] The illumination device and illumination conditions of the present embodiment are the same as the implementation case 1, but the hexavalent chromium concentration added in the colorimetric tube is 12-18mg / L, and the AA concentration is 0.1mM, and the reaction result is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0030] Depend on figure 2 The photoreduction effect can be seen. When the concentration of AA is constant, the lower the concentration of Cr(VI) is, the shorter the time required for photoreduction to trivalent chromium is, and the 100% reduction of Cr(VI) can be completed within half an hour, but at different concentrations The photoreduction rate of Cr(VI) changed little, that is, UV / AA had better reduction effect on different initial concentrations of Cr(VI).
Embodiment 3
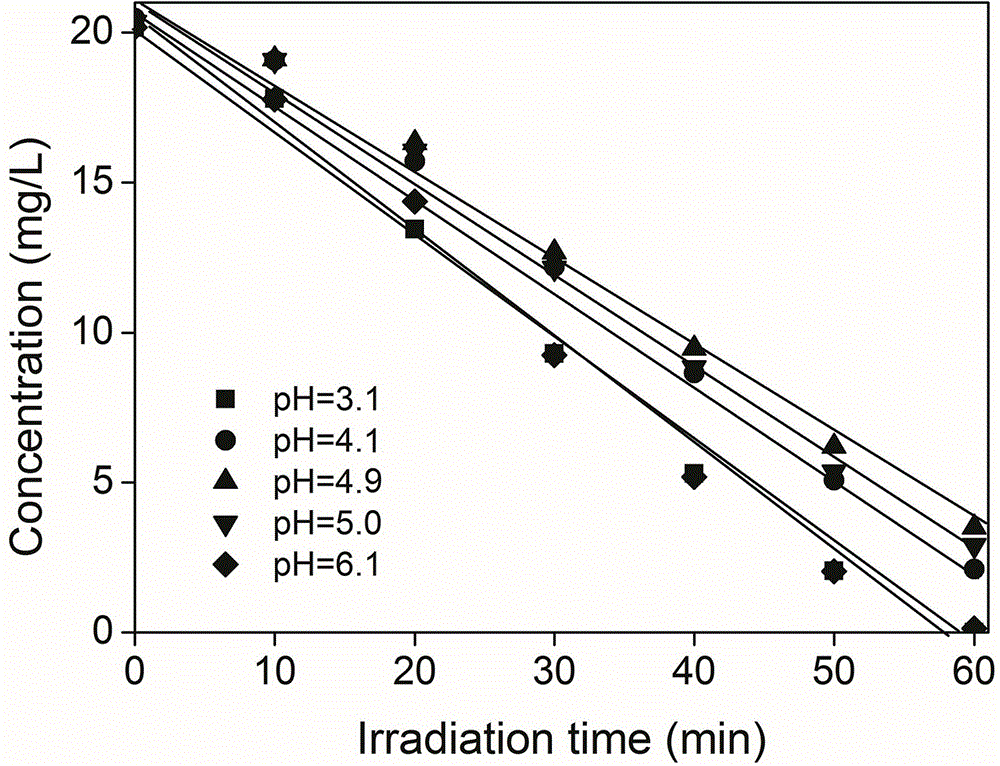
[0031] Example 3 Different initial pH effects test on the effect of UV / AA reduction treatment
[0032] The illumination device and illumination conditions of this embodiment are the same as those in Example 1, but the concentration of Cr(VI) added is 20 mg / L, and the concentration of AA is 0.1 mM. In addition, the pH of the solution is adjusted to 3.1 and 4.1 in sequence with perchloric acid and sodium hydroxide. , 5.0 and 6.1, the reaction results are shown in 3.
[0033] Depend on image 3 It can be seen that under moderately acidic conditions, UV / AA has a faster photoreduction effect on hexavalent chromium, and the reduction efficiency is less affected by pH, and, as the light reaction proceeds, the pH in the solution gradually increases. After UV60min, the pH of the solution is 1-2 higher than the initial pH (such as Figure 4 shown), which indicates that the hydrogen ions in the solution will be consumed in the process of UV / AA photoreduction of hexavalent chromium, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com