Method using abnormally-activated-cell detection to test for malignant tumors and abnormally-activated-cell apheresis-therapy apparatus
A technology for activating cells and malignant tumors, which is used in the field of removing abnormal activated cells and returning blood circulation to the treatment device, which can solve the problems of increased indirect bilirubin concentration and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] (Example 1) Blood circulation reinfusion treatment device for removing abnormally activated cells
[0125] like Figure 5 As shown, the blood circulation reinfusion treatment device for removing abnormal activated cells is composed of the following: a blood collection pipeline 10 with a puncture needle (not shown) for blood collection at one end; blood samples supplied from the blood collection pipeline 10 A centrifugal separator 20 for separating white blood cells; a cell sorter 30 for removing abnormally activated cells such as leukemia cells from the white blood cells separated by the centrifugal separator 20; The normal white blood cell part of the activated cell is irradiated with light of a predetermined wavelength by the light irradiator 40; the blood is reinfused into the blood circulation composed of plasma components other than the white blood cell part separated by the centrifugal separator 20, red blood cell part and platelet part, etc. Blood circulation re...
reference example 1
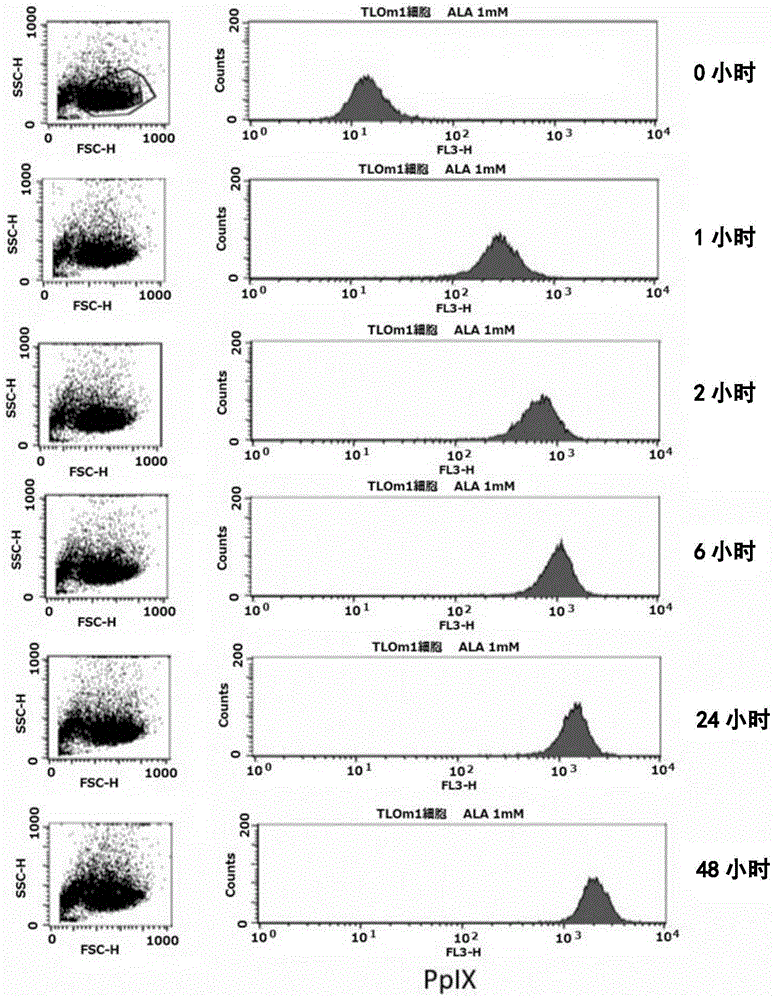
[0139] (Reference Example 1) Confirmation of accumulation of PpIX using strained cells
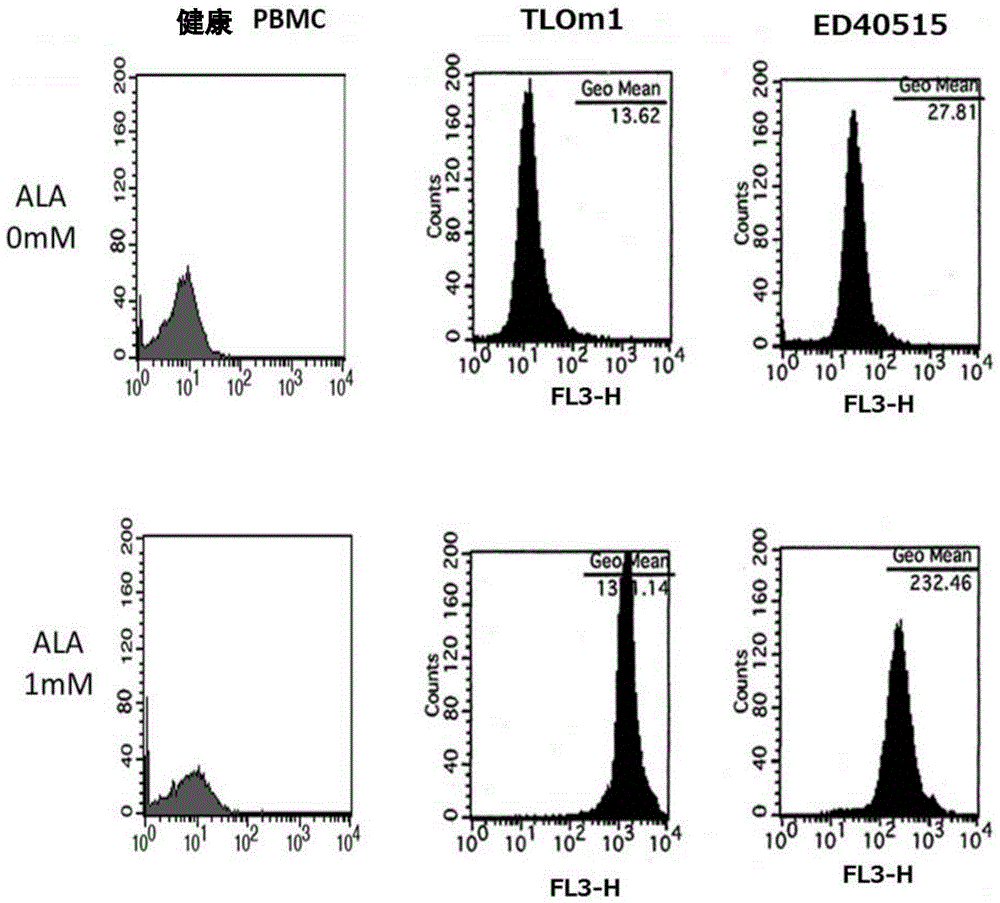
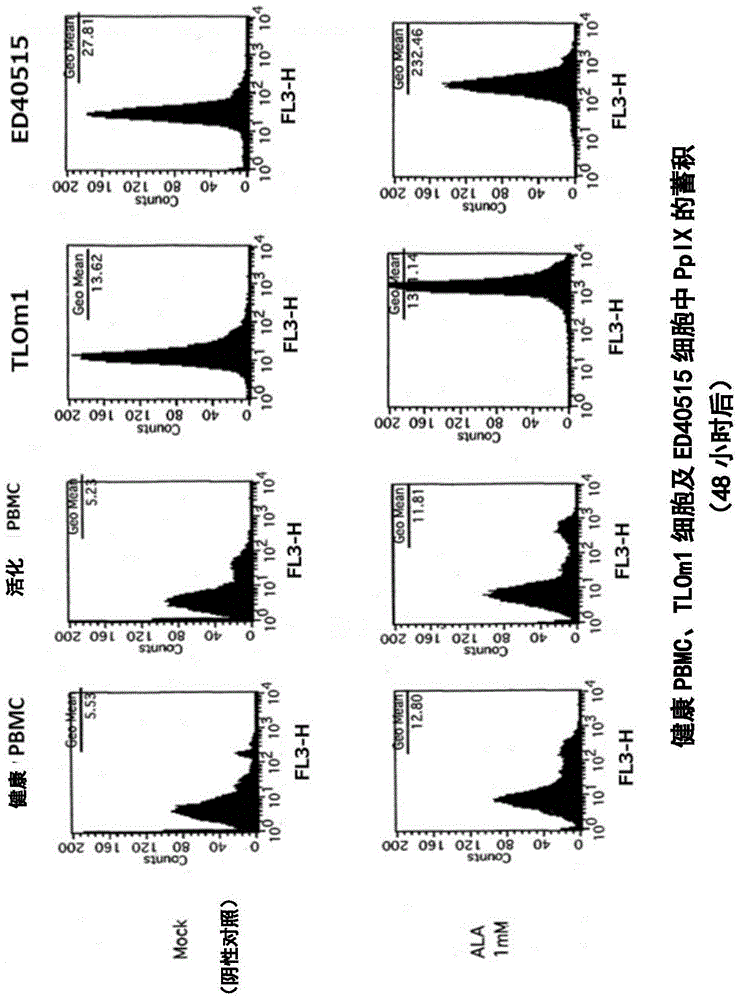
[0140] In this reference example, the accumulation of intracellular PpIX after adding 1 mM 5-ALA to the culture solution of TLOm1 (ATLL leukemia cell line) was confirmed over time. It was confirmed that, as a result, after 5-ALA was added, PpIX was still sufficiently present in the cells after 48 hours ( figure 1 ). Moreover, CD3 / CD28 immune beads (CD3 / CD28, immuno-bead, Dynabeads) for peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of healthy normal people (R) humanT-cellactivatorCD3 / CD28 (Invitrogen)) stimulated cells, and activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), TLOm1 and ED-40515 (ATLL leukemia cell line), administered 1mM 5- The accumulation of PpIX in cells at 48 hours after ALA was analyzed. As a result, specific accumulation of PpIX in activated T cells and tumor cells was confirmed ( figure 2 , image 3 ).
Embodiment 2
[0141] (Example 2) Confirmation of flow cytometry patterns of monocytes
[0142] In this example, the confirmation of the flow cytometry pattern was performed on the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) isolated from the peripheral blood of healthy normal people, HTLV-I carriers or ATLL patients. 1 mM 5-ALA was added to the culture medium containing each peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) and cultured for 48 hours. For these cells, the accumulation of PpIX and the expression of TSLCI were confirmed, and the cell distribution pattern was analyzed by flow cytometry. analysis. As a result, for (1) healthy normal people, (2) low-risk HTLV-I carriers, (3) medium-risk HTLV-I carriers, (4) high-risk HTLV-I carriers, ( 5) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from patients with smoldering ATLL, (6) patients with chronic ATLL and (7) patients with acute ATLL confirmed their unique cell distribution patterns ( Figure 4 ). Although the lifetime risk of ATLL for HTLV-I ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com