Device for automatically detecting two-dimensional shape of wafer substrate
An automatic detection and substrate technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as laser output power and wavelength instability, and achieve the effect of improving internal heat dissipation performance and enhancing stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
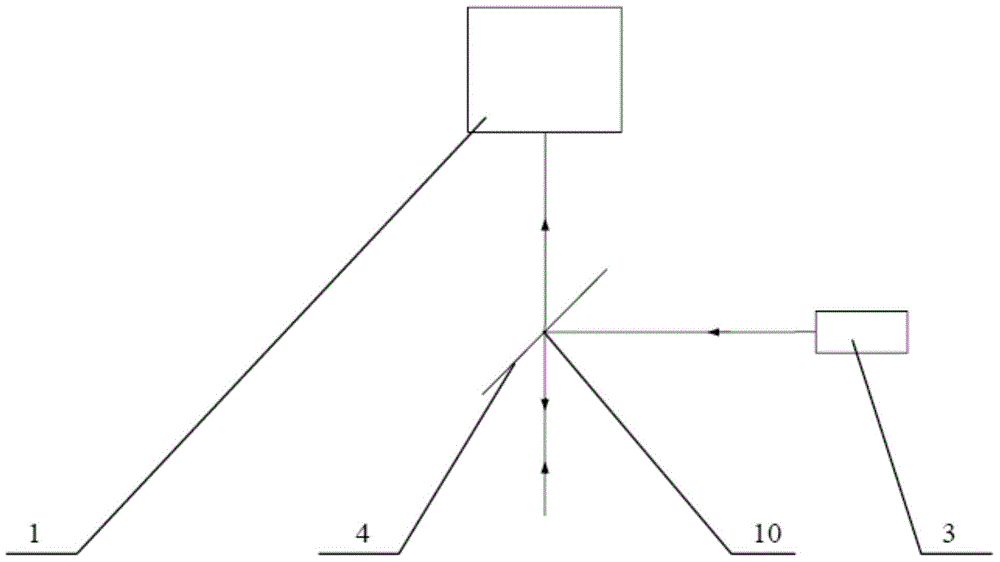
[0028] For ease of understanding, the attached figure 1 The light path diagram of only one of the spots is given.
[0029] see attached figure 1 The device for real-time and rapid detection of the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention includes N PSD1, N beams of laser light and the first light splitting element 4, and the N beams of laser light are arranged along a straight line, wherein N is a natural number greater than 3 , N PSD1s are in one-to-one correspondence with N laser beams,
[0030] N beams of laser light are first directed at positions 10 of the first light-splitting element 4, and incident light is formed after passing through the first light-splitting element 4, and the incident light is incident on the wafer substrate, and N incident points are formed radially on the wafer substrate, and the incident light N beams of the first type of reflected light beams are formed after being reflected by the su...
Embodiment 3
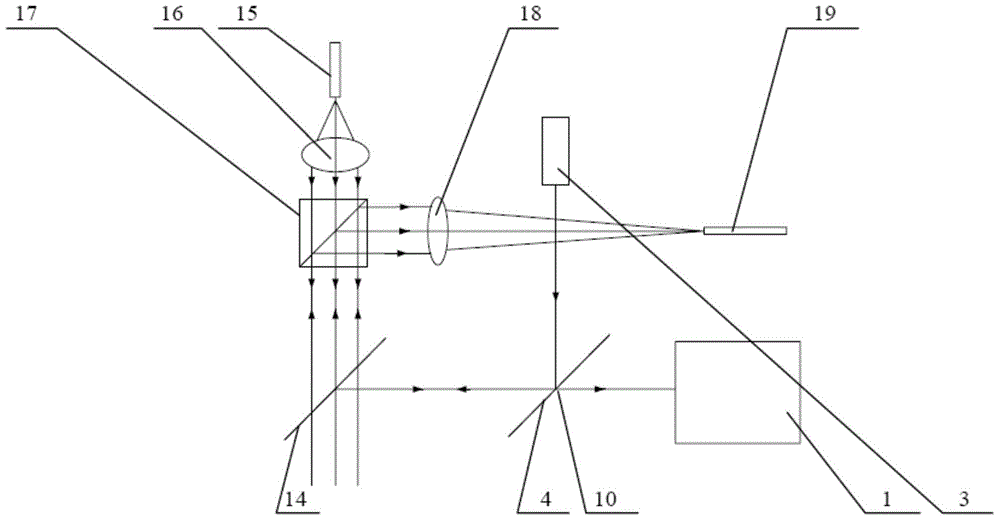
[0067] The difference between the device for real-time and rapid detection of the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided by the third embodiment of the present invention and the first and second embodiments of the present invention is that the device for the real-time rapid detection of the two-dimensional topography of the wafer substrate provided by the third embodiment of the present invention It may also include a light-passing device, which is arranged on the optical path where the incident light and the first reflected light beam pass through together. The light-passing device is provided with N light-passing holes, and the N light-passing holes correspond to the N beams of laser light one by one. , the optical holes are provided with reflective mirrors 11 at intervals, which are used to reverse the direction of the corresponding passing beam by 90°, so that the corresponding PSD can be turned to another direction, saving the placement space.
[0068] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com