Heat-stable catechol 1,2-dioxygenase derived from animal manure metagenome and coding gene thereof, and preparation method of heat-stable catechol 1,2-dioxygenase
A catechol and dioxygenase technology, applied in the field of microorganisms and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of limiting the breadth and effectiveness of screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 The acquisition of catechol 1,2-dioxygenase gene catPLCgl
[0044] 1. Construction of a metagenomic library for the fecal microorganisms of the Japanese slow loris
[0045] Microbial genomic DNA was extracted from the feces of the loris (see the patent "A method for extracting high molecular weight genomes from animal feces" for details on the extraction method, publication number: CN102586234A, application date: 2012-03-12), after fragmentation Separation by pulsed field electrophoresis and agarose gel electrophoresis to recover a DNA fragment with a size of about 40kb. The recovered DNA fragment was ligated with the fosmid vector pCC1FOS and transfected with host bacteria E.coliEPI300, and spread on an LB plate containing 12.5 μg / mL chloramphenicol Transformants were obtained by culturing overnight at 37°C, and the clone library was stored in a 96-well plate at -80°C.
[0046] 2. Extraction and sequencing of fosmid plasmid
[0047] The fosmid mixed plasmid...
Embodiment 2
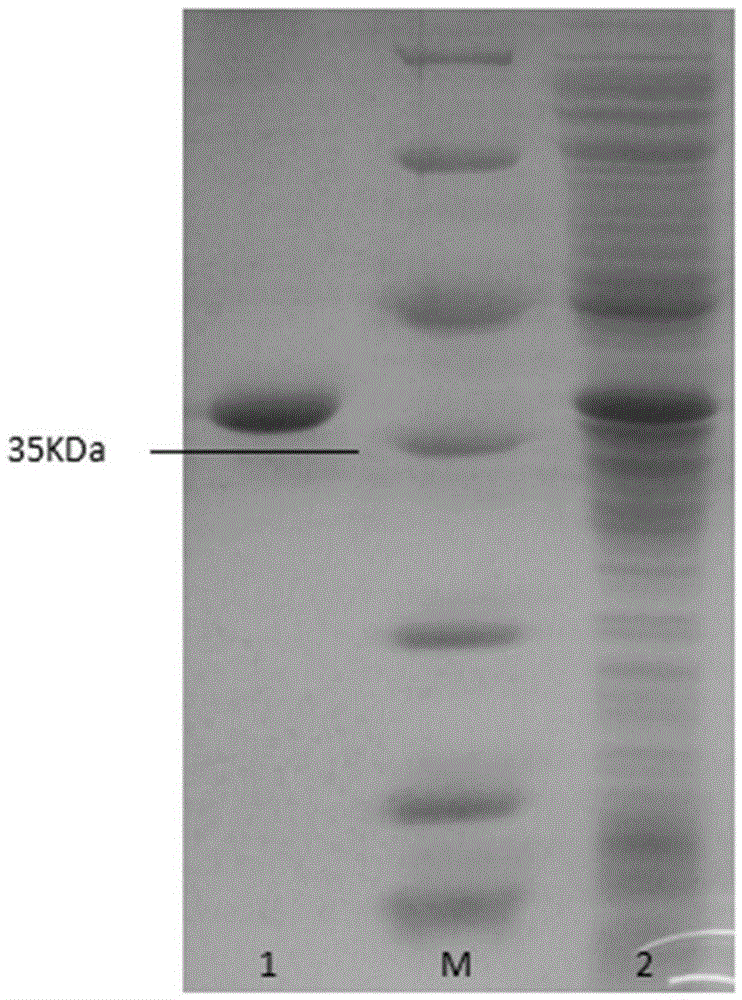
[0050] Example 2 Preparation of thermostable catechol 1,2-dioxygenase CatPLCgl
[0051] The catechol 1,2-dioxygenase gene catPLCgl prepared in Example 1 was connected to the plasmid pEasy-E2 to obtain the recombinant expression vector pEasy-E2-catPLCgl, and then transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3) / catPLCgl. Take the Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3) / catPLCgl containing the recombinant expression vector pEasy-E2-catPLCgl, and inoculate it in LB (containing 100 μg / mL Amp) culture medium with a 0.1% inoculum amount, and shake rapidly at 37°C for 16 hours. Then inoculate the activated bacterial solution into fresh LB (containing 100 μg / mL Amp) culture solution with 1% inoculum, and culture it with rapid shaking for about 2–3 hours (OD 600 After reaching 0.6–1.0), add IPTG at a final concentration of 0.7mmol / L for induction, and continue shaking culture at 20°C for about 20h. Centrifuge at 9500rpm for 5min to colle...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3 Thermostable catechol 1,2-dioxygenase CatPLCgl property determination
[0054] 1. Activity analysis of thermostable catechol 1,2-dioxygenase CatPLCgl
[0055]Enzyme activity was determined by spectrophotometry [Gouetal.BiotechnolLett, 2012,34(1):117-123]: take 10μl of 150mM catechol substrate solution (final concentration is 0.5mM) and 2.94mL of 50mM buffer solution at reaction temperature Preheat for 3 minutes, add 50 μl of appropriately diluted enzyme solution to react for 5 minutes, and measure the increase in absorbance within 5 minutes at the corresponding wavelength. The molar extinction coefficient of the catalytic product cis, cis-hexadienedioic acid at 260nm is 16800 / Mcm with catechol as the substrate. One enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme required to catalyze a substrate to produce 1 μmol of the corresponding product per minute under given conditions.
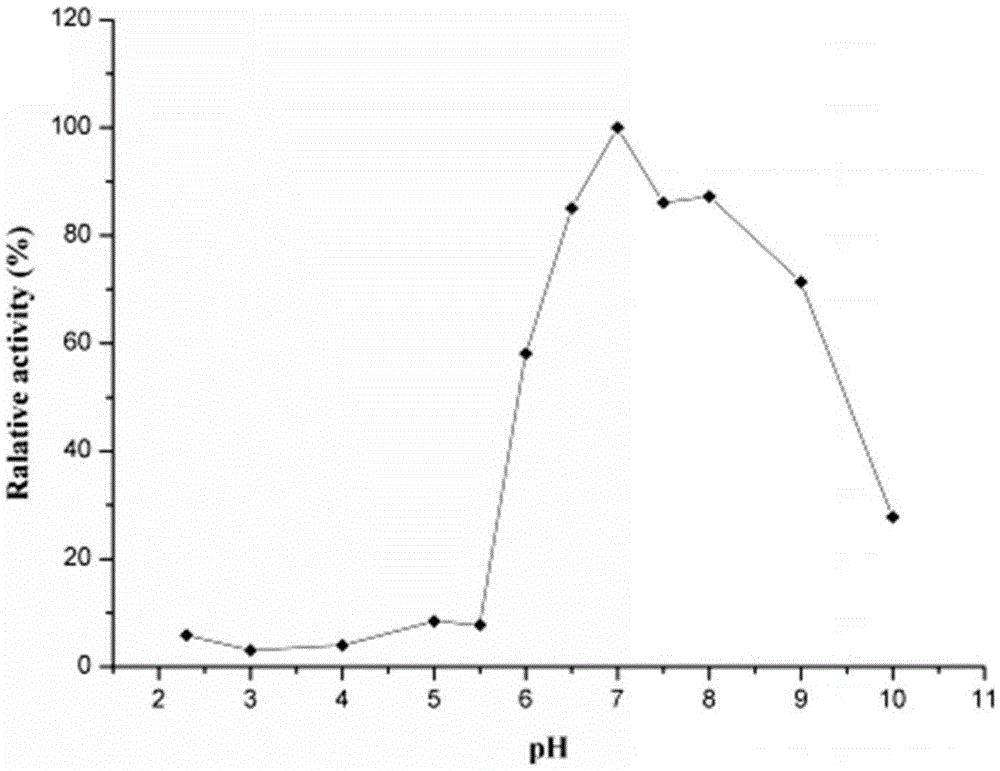
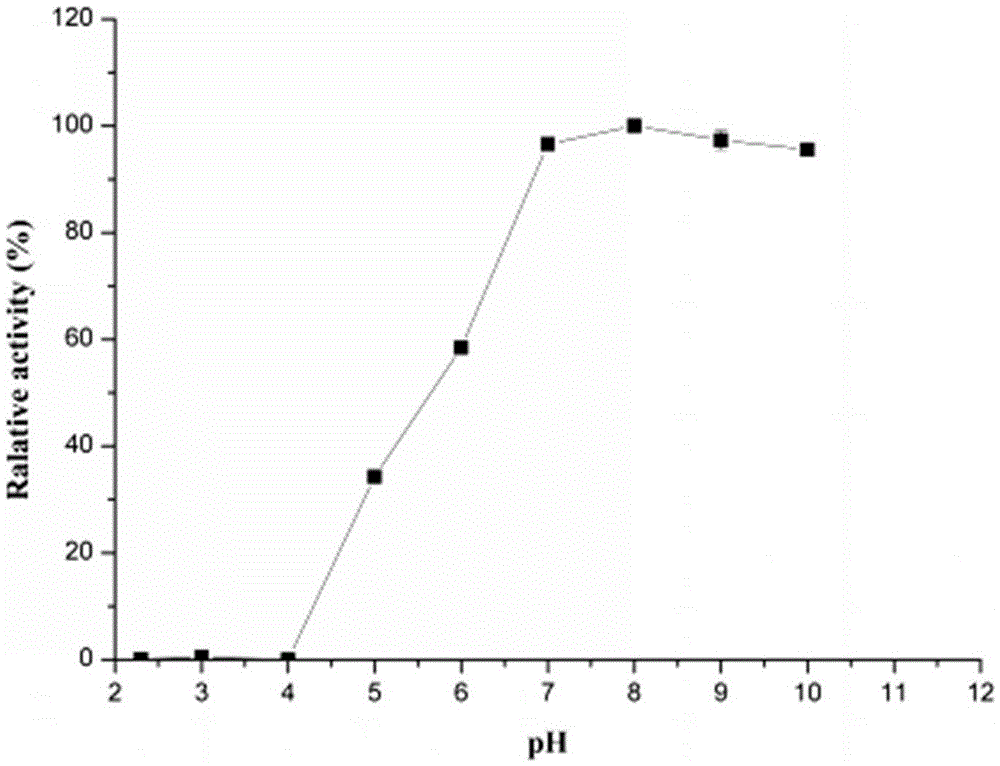
[0056] 2. Determination of optimum pH and pH stability of thermosta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com