Preprocessing method and device for image recognition of DNA sequence
A DNA sequencing and image recognition technology, applied in the field of DNA sequencing analysis, can solve problems affecting base types, difficult identification of targets and backgrounds, and misidentification of targets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
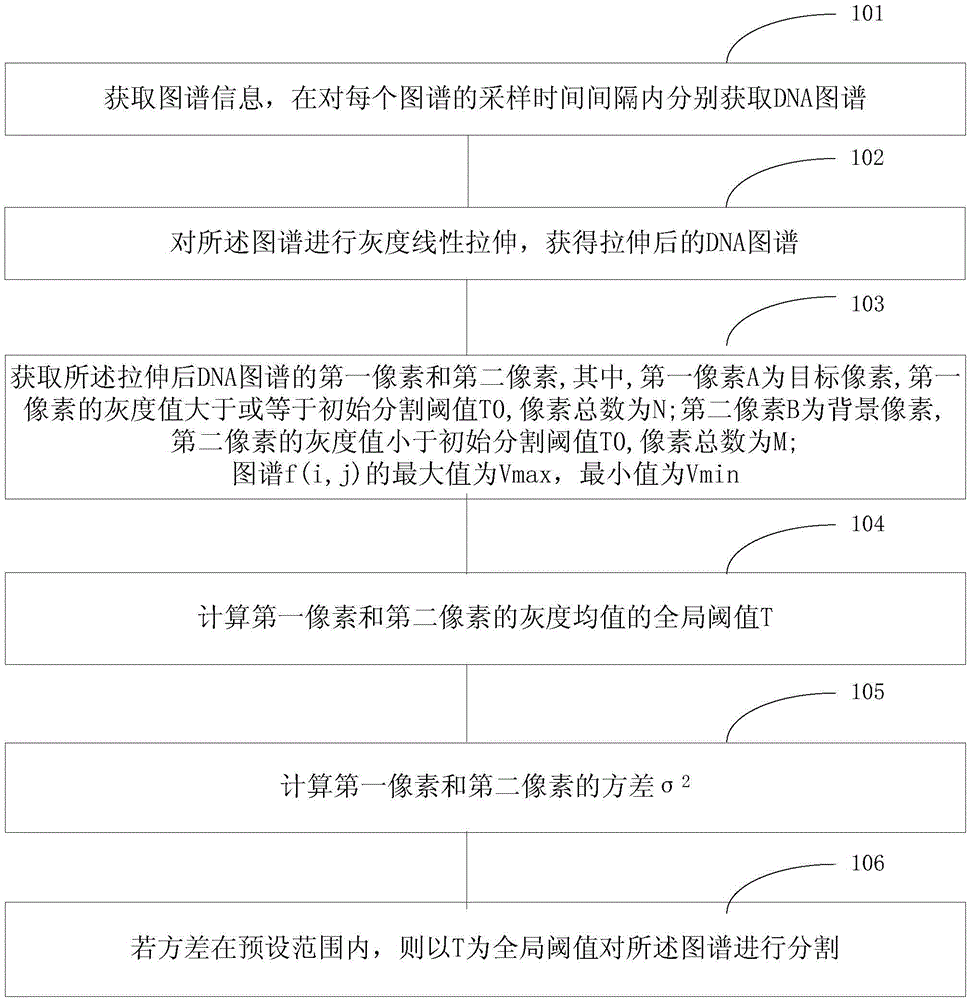
[0066] see figure 1 As shown, it is a flow chart of the image recognition preprocessing method for DNA sequencing provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention, including:
[0067] Step 101, obtain the spectrum information, and obtain the DNA spectrum within the sampling time interval of each spectrum;
[0068] Specifically, the acquisition of the DNA map can be achieved in the following ways:
[0069] The reaction solution enters the reaction chip of the DNA sequencer for a chemical reaction to generate visible light; the CCD camera takes pictures of the visible light information generated in the reaction chip at the appropriate photographing position to collect the DNA spectrum.
[0070] More specifically, when obtaining the map information, for the signal waveform, in each continuous K cycle, select n sampling points at preset moments in each cycle, and each interval time T 0 Sampling once, continuous sampling M times; in order to ensure the referenceability and accur...
Embodiment 2
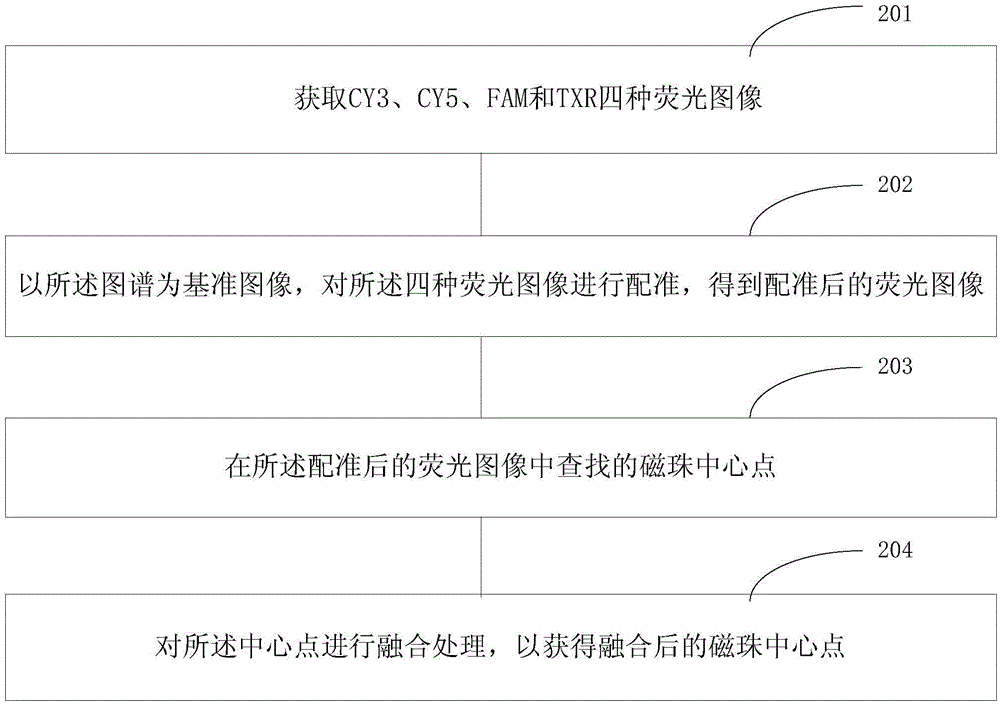
[0088] figure 2 For the flow chart of the image recognition preprocessing method for DNA sequencing provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, please refer to figure 2 On the basis of Example 1, the image recognition method for DNA sequencing provided in this example includes:
[0089] Step 201, acquiring four fluorescent images of CY3, CY5, FAM and TXR;
[0090] Specifically, when the DNA spectrum captured by the CCD camera is blurred, but the fluorescence image is clear, the magnetic bead identification can be performed by acquiring the fluorescence image.
[0091] Step 202, using the atlas as a reference image, registering the four fluorescence images to obtain a registered fluorescence image;
[0092] Step 203, finding the center point of the magnetic beads in the registered fluorescent image;
[0093] Step 204, performing fusion processing on the central point to obtain the fused central point of the magnetic bead.
[0094] Specifically, in general, one of t...
Embodiment 3
[0097] image 3 For the flow chart of the image recognition preprocessing method for DNA sequencing provided in Example 3 of the present invention, please refer to image 3 , this embodiment is further limited on the basis of embodiment two, in this embodiment,
[0098] The center point of the magnetic bead searched in the registered fluorescent image specifically includes:
[0099] Step 301, identify the magnetic bead pixels on the spectrum, if the absolute value of the minimum value of f(i,j) min(i,j) difference is greater than or equal to T 0 , it is identified as a magnetic bead, otherwise, it is a background pixel.
[0100] Preferably, it can also include:
[0101] Step 302, traversing the pixels of the magnetic bead to obtain the central pixel of the magnetic bead, wherein the central pixel of the magnetic bead is, the gray value of the current point is equal to the maximum gray value in the 4*4 pixel area centered on the current point, and The four neighbors of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com