Isolation and primary culture methods of chicken small intestinal epithelial cells
A technology for small intestinal epithelial cells and primary culture, which is applied in cell dissociation methods, cell culture active agents, gastrointestinal cells, etc. Good condition, low mortality rate, good cell growth condition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
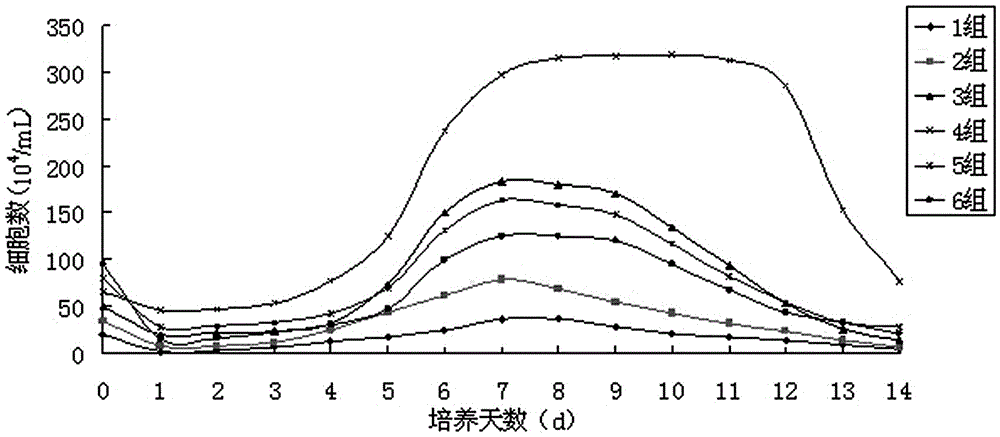
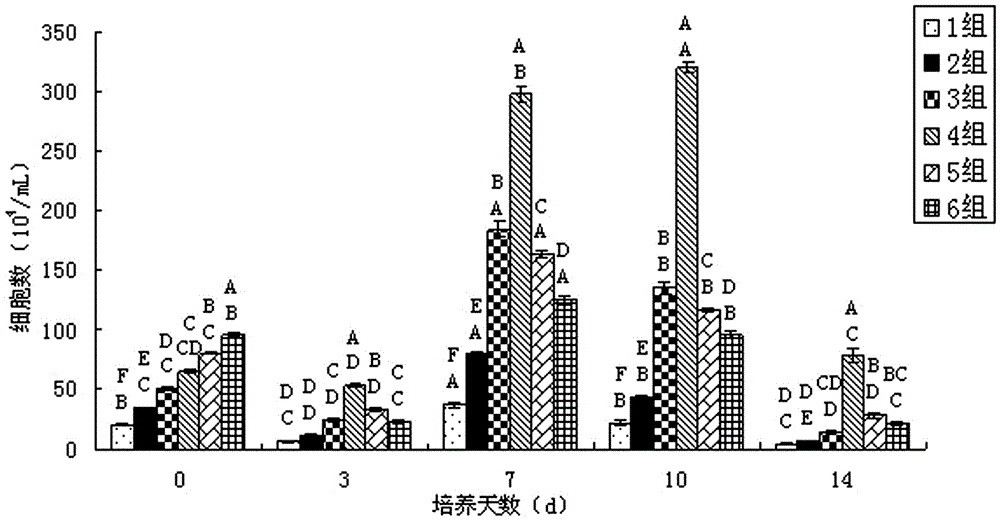
[0031] Experimental Example 1: Screening and Culture of the Optimal Cell Seeding Density of Chicken Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells
[0032] According to the number of cells per ml obtained by cell counting, it is divided into six gradients, as shown in Table 1. The above-mentioned diluted cell mass dilutions were inoculated into 6-well cell culture plates according to the data of different gradients, and each gradient was repeated 3 times. , placed at 40°C, 7%CO 2 Cultivate in the incubator for 36 hours, observe the growth state of the cells, and calculate the cell attachment rate. After 48 hours, the culture medium was replaced, and the growth and adhesion of the cells were observed every day. The number of living cells was counted by trypan blue staining, and the observation was continued for 14 days. The growth curve of chicken small intestinal epithelial cells was made with the culture time of chicken small intestinal cells as the abscissa and the number of viable cell...
experiment example 2
[0041] Experimental Example 2: Screening of the Best Serum for Chicken Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells
[0042]Add different concentrations of fetal bovine serum and chicken serum to the culture medium, observe the growth of the cells, divide the two serums into group A (fetal bovine serum) and group B (chicken serum), and divide the serum into 0% , 5%, 10% different concentrations. Before the adherence difference, both groups A and B were cultured with 10% serum concentration medium to culture enzyme-digested cells, which was helpful for the adherent growth of non-intestinal epithelial cells such as fibroblasts. After poor adherence, culture the purified chicken small intestinal epithelial cells with a culture medium with a serum concentration of 5%, and change the medium every two to three days. Proliferation, cells by approximately 6.5×10 5 / mL inoculated into 6-well culture plates, with 3 replicates in each group, placed at 40°C, 7% CO 2 Culture in the incubator for 1...
experiment example 3
[0049] Experimental Example 3: Identification of Chicken Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells
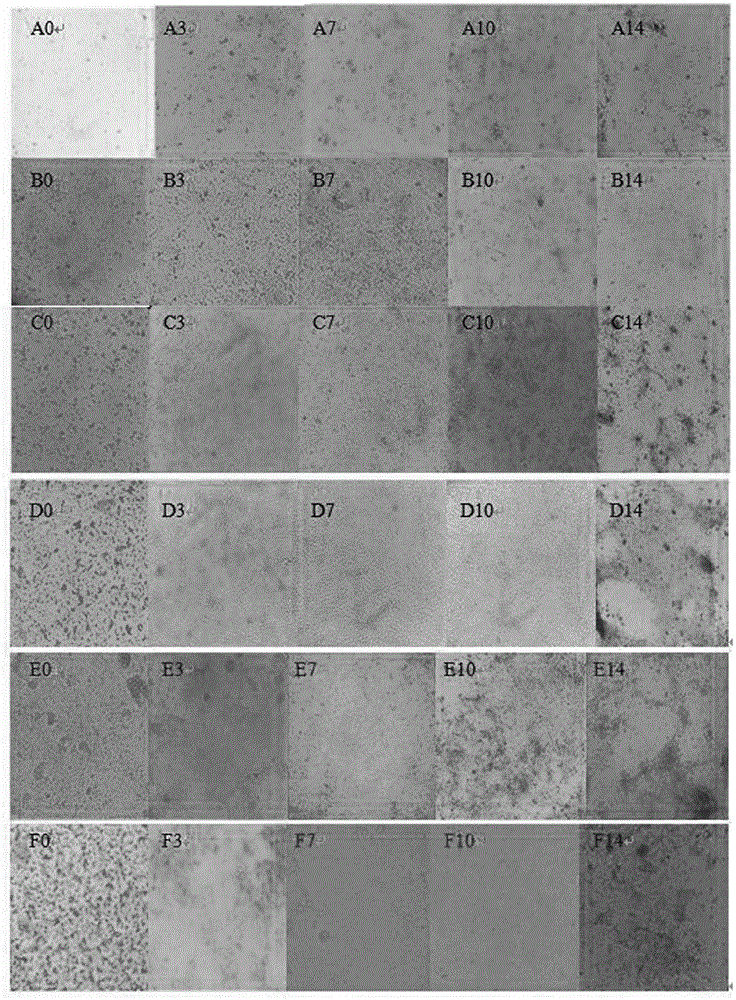
[0050] (1) Morphological identification of cells: After the primary culture of chicken intestinal epithelial cells started, live cells were directly observed through an inverted phase-contrast microscope, mainly to observe the growth and proliferation of cells attached to the wall, including the changes in cell shape and size at different times.
[0051] Cells that have just been digested from the small intestine of chickens are inoculated into cell culture plates, and the cells are observed under a microscope as Figure 7 As shown, most of them are different in size, round in shape, and transparent, and most of them digested are cell clusters. 2 Within 24 hours of culture, the cells began to adhere to the wall. Most of the newly adhered cells were distributed in the shape of islands, and some of them were scattered in the shape of flat irregular polygons and spindles. Most of the cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com