Method and device for synergetically removing multiple heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in runoff rainwater
A technology of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals, applied in runoff/rainwater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as soil infiltration, low adsorption saturation point, soil and groundwater pollution, and achieve improved treatment Efficiency, low cost, increased removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
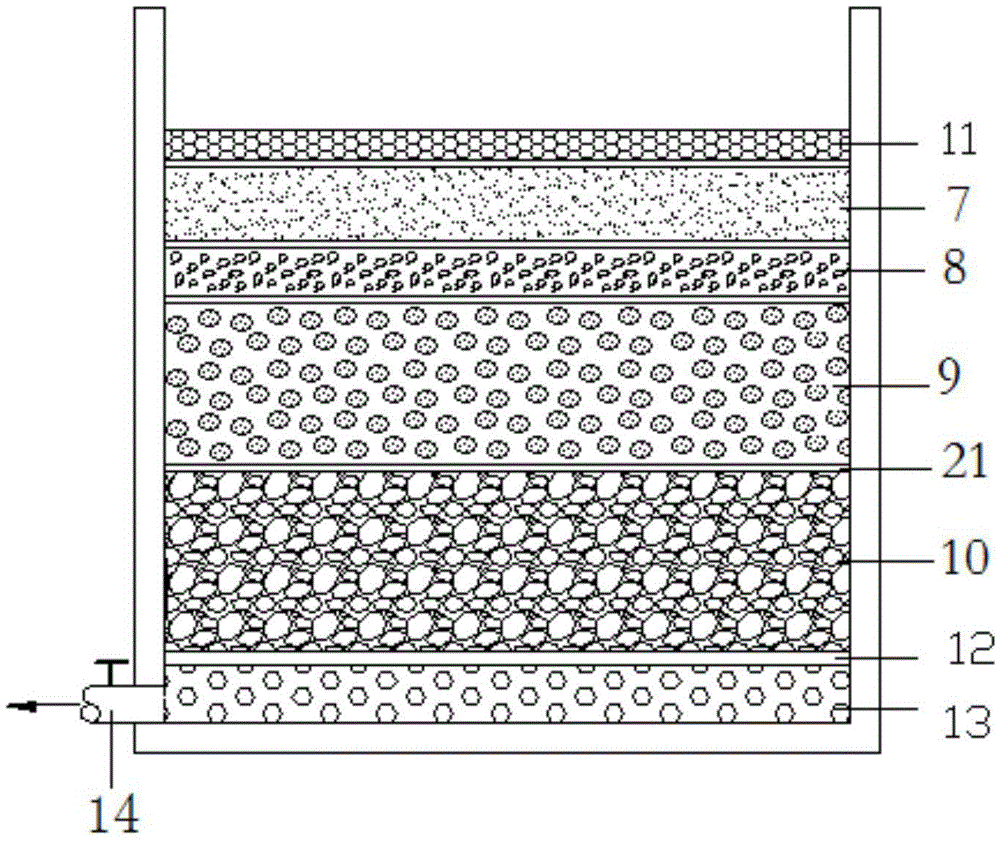
[0081] A method for the synergistic removal of various heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in runoff rainwater, the method uses a filler, and the filler includes a layer of zero-valent iron balls.
[0082]The zero-valent iron ball layer is the main removal layer for removing pollutants. Through the adsorption, redox and catalytic reduction of zero-valent iron, most of the heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are removed. Zero-valent iron balls can simultaneously remove various heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The setting of the new material layer of zero-valent iron balls actively increases the removal effect of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals by using the large specific surface of zero-valent iron balls, and improves the treatment efficiency. It solves the problem that the removal ability of traditional filter materials (natural sand, sandstone, gravel, etc.) to heavy metals is not as good as that of conventional...
Embodiment 2
[0084] A method for the synergistic removal of multiple heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in runoff rainwater, the method uses fillers, the fillers include zero-valent iron ball layers, and the fillers also include sand layers, sawdust layers, pumice layers and fine particles. The gravel layer includes the zero-valent iron ball layer, the sand layer, the sawdust layer, the pumice layer and the fine gravel layer in sequence according to the direction in which runoff rainwater enters.
[0085] The thickness ratio of the zero-valent iron ball layer, the sand layer, the sawdust layer, the pumice layer and the fine gravel layer is 1:2.5:1:6:6.
[0086] The filter material of the zero-valent iron ball layer includes zero-valent iron balls, and the diameter of the zero-valent iron balls is 6-10±0.5mm.
[0087] The raw material for preparing the zero-valent iron balls includes nano-zero-valent iron powder, and the diameter of the nano-zero-valent iron powder is 336.6 n...
Embodiment 3
[0107] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 2 only lies in:
[0108] The thickness ratio of the zero-valent iron ball layer, the sand layer, the sawdust layer, the pumice layer and the fine gravel layer is 1:2:1:5:5.
[0109] The raw material for preparing the zero-valent iron ball includes nano-zero-valent iron powder, and the diameter of the nano-zero-valent iron powder is 336nm.
[0110] The filter material of the sand layer includes zeolite.
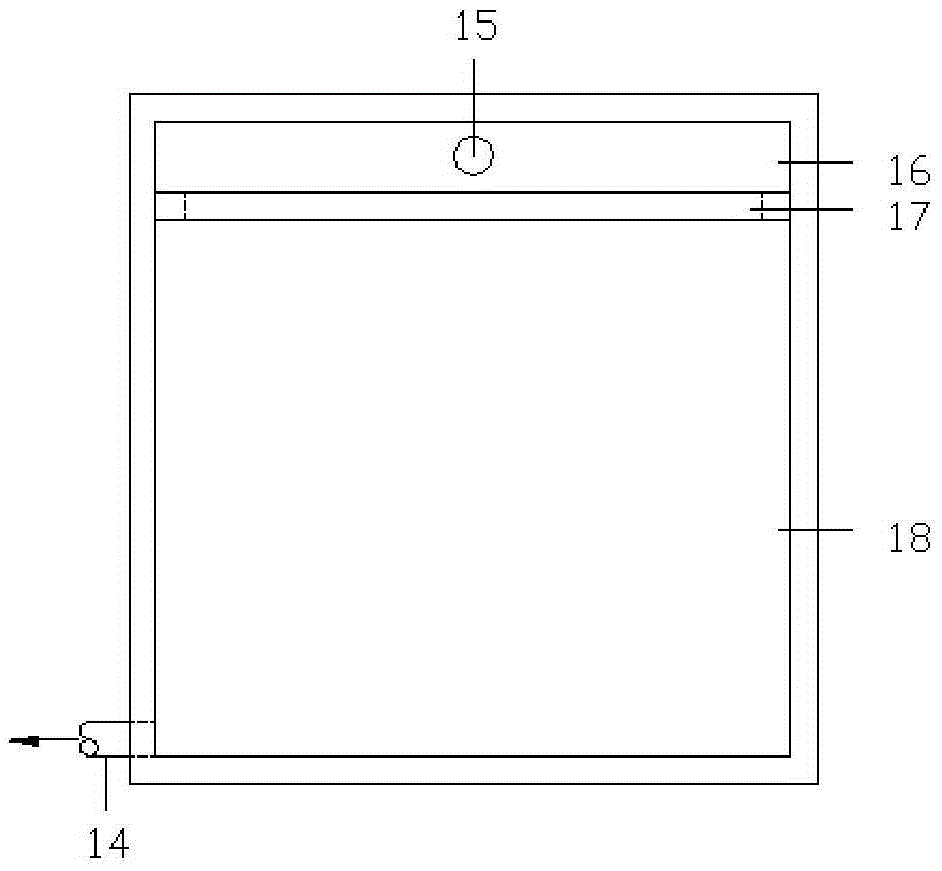
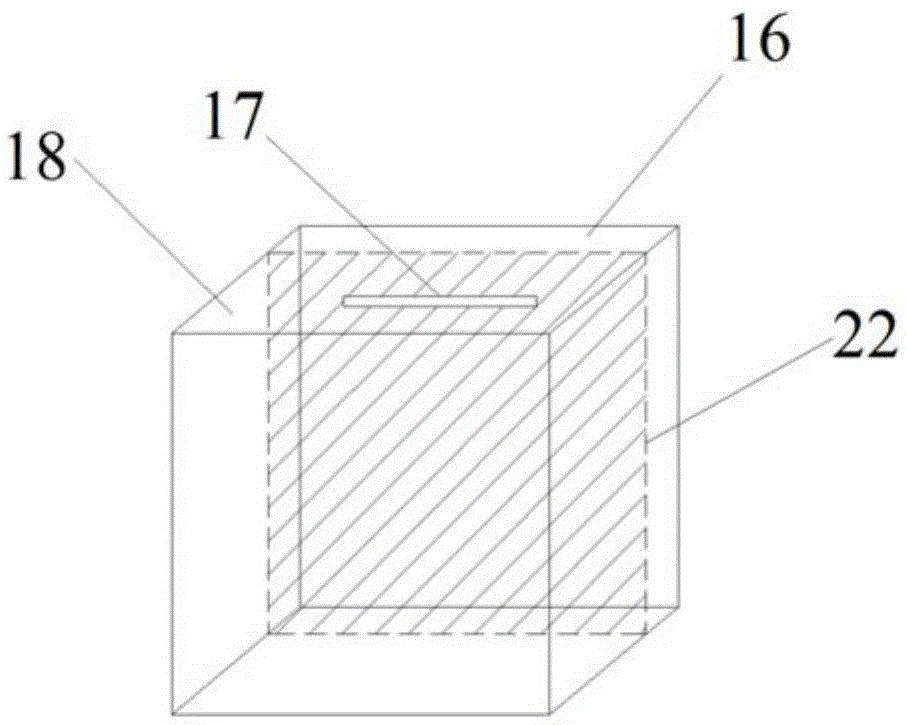
[0111] The thickness ratio of the zero-valent iron ball layer to the supporting layer is 1:1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com