A method for preparing nanometer zero-valent iron based on liquid-phase complexation reduction method
A nano-zero-valent iron and reduction method, applied in nanotechnology and other directions, can solve the problems of uneven particle shape, size, and particle agglomeration, and achieve the effects of simple equipment, uniform distribution, and convenient operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Measure 10mL 0.1mol·L respectively -1 FeCl 3 solution and 0.1mol·L -1 NaH 2 PO 4 Solution, adjust the pH value of the system to 4 after mixing, then add 20mL of tetrahydrofuran, stir to make it fully mixed. Weigh 0.32gNaBH 4 Dissolve in 10mL of tetrahydrofuran and water (volume ratio: 1:1) mixture, and finally drop the sodium borohydride solution into the complex iron salt solution at a rate of 2-3 drops / second, and control the reaction after the addition is complete The time is 15 min. After washing the nano-iron particles with anaerobic deionized water and absolute ethanol three times respectively, the nano-iron particles are stored in absolute ethanol.
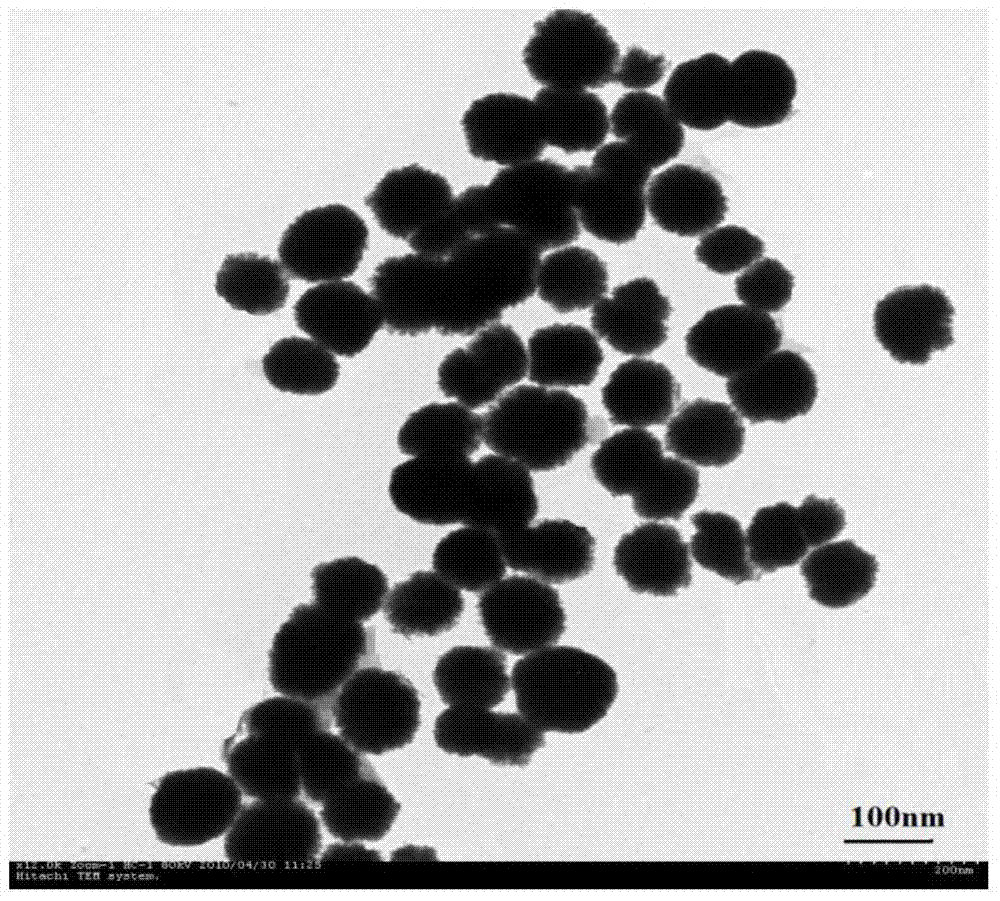
[0041] The test result of TEM shows that the range of particle size is about 50-80m, and the average particle size is 66nm.
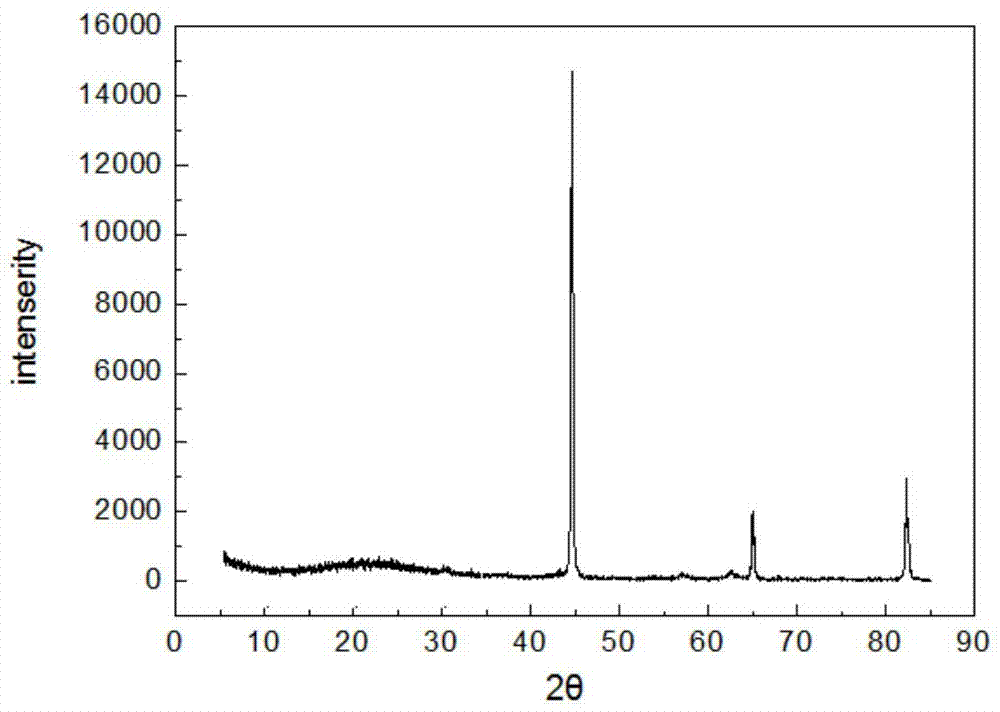
[0042] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle 2θ is 30°~100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 45.4453°, 65.0265°, and 82.1369°, wh...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Add 10mL 0.1mol·L respectively -1 FeCl 3 solution and 0.3mol·L -1 NaH 2 PO 4 Solution, adjust the pH value of the system to 5, then add 20mL of tetrahydrofuran, stir to make it fully mixed. Weigh 0.32gNaBH 4 Dissolve in 10mL of tetrahydrofuran and water (volume ratio: 1:1) mixture, and finally drop the sodium borohydride solution into the complex iron salt solution at a rate of 2-3 drops / second, and control the reaction after the addition is complete The time is 15 min. After washing the nano-iron particles with anaerobic deionized water and absolute ethanol three times respectively, the nano-iron particles are stored in absolute ethanol.
[0046] TEM test results show that: the range of particle size is about 50-80m, and the average particle size is 64nm.
[0047] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle 2θ is 30°~100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 45.1269°, 65.7531°, and 82.1568°, respectively, and compare...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Add 10 mL of 0.1 mol L to 28 mL of distilled water -1 Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 solution and 0.2mol·L - 1 NaH 2 PO 4 Solution, adjust the pH value of the system to 6, then add 12mL of tetrahydrofuran, stir to make it fully mixed. Weigh 0.32gNaBH 4 Dissolve in 10mL of tetrahydrofuran and water (volume ratio: 1:4) mixture, and finally drop the sodium borohydride solution into the complex iron salt at a rate of 2-3 drops / second, and control the reaction time after the addition is complete After 20 min, the nano-iron particles were washed three times with anaerobic deionized water and absolute ethanol, and then the nano-iron particles were stored in absolute ethanol.
[0051] The test result of TEM shows that the range of particle size is about 50-80m, and the average particle size is 63nm.
[0052] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle 2θ is 30°~100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 45.2568°, 65.1237°, and 82.5648°, re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com