Polymerization method used for reducing vinyl chloride/vinyl acetate copolymer blending resin glass transition temperature
A technology of glass transition temperature and resin blending, which is applied in the polymerization field of reducing the glass transition temperature of vinyl acetate copolymer blending resin, can solve the problems of low plasticity, difficult to meet the industrial sector, poor processing rheology, etc., and achieves high plasticity and easy processing. Adhesion to metal surface, low molding temperature effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
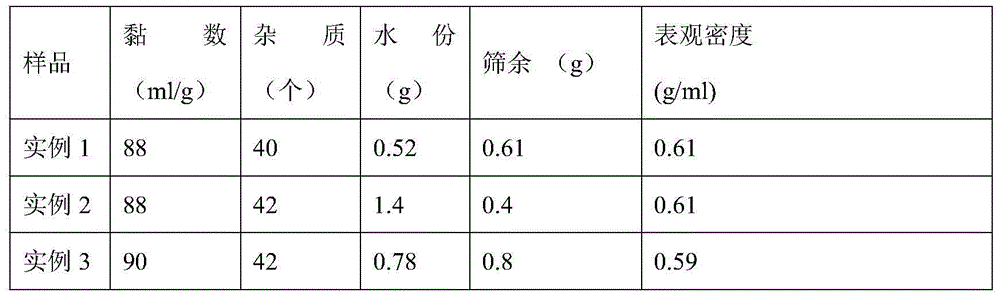
[0024] Put 10.2kg vinyl chloride, 1.08kg vinyl acetate, 0.008kg initiator azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.006kg sodium bicarbonate, 0.0005kg sodium carbonate, 0.03kg hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and 16kg water into the polymerization kettle , the temperature was raised to 52°C and maintained for 1 hour, and then the temperature was naturally raised to 60°C. When the reaction pressure dropped by 300KPa, 0.04kg of terminator acetone thiosemicarbazone and 0.001kg of defoamer organosiloxane were added to terminate the reaction to obtain vinyl chloride- The slurry emulsion of vinyl acetate copolymer blended resin is discharged into the discharge tank, and 0.15 kg of lye with a weight concentration of 32.5% is added for treatment, and then stripped, centrifugally dehydrated, and air-dried to obtain a finished product. The obtained finished product was tested according to the GB5761-93 standard, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0025] The glass transition temperature (Tg) is 70-75°...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Put 11.5kg of vinyl chloride, 0.9kg of vinyl acetate, 0.009kg of azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.006kg of ammonium bicarbonate, 0.0005kg of sodium carbonate, 0.03kg of dispersant polyvinyl alcohol and 16kg of water in a polymerization kettle and heat up to 48°C Maintain for 1 hour, then naturally raise the temperature to 65°C, and when the reaction pressure drops by 200KPa, add 0.04kg of terminator acetone thiosemicarbazone and 0.001kg of defoamer silicone ether copolymer to end the reaction to obtain vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer blend The slurry emulsion of the resin is discharged into the discharge tank, treated by adding 0.15kg of 32.5% lye, and then subjected to steam stripping, centrifugal dehydration and air drying to obtain the finished product. The obtained finished product was tested according to the GB5761-93 standard, and the results are shown in Table 1. The glass transition temperature (Tg) is 70-75°C;
Embodiment 3
[0029] Put 9.1kg of vinyl chloride, 2.2kg of vinyl acetate, 0.008kg of azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.006kg of sodium bicarbonate, 0.0005kg of sodium carbonate, 0.03kg of dispersant gelatin and 16kg of water in a polymerization kettle, and raise the temperature to 51°C to maintain After 1.5 hours, the temperature was naturally raised to 64°C. When the reaction pressure dropped by 250KPa, the reaction was completed, and 0.04kg of terminator acetone thiosemicarbazone and 0.001kg of defoamer polyether were added to complete the reaction, and a vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer blend was obtained. The slurry emulsion of the resin is discharged into the discharge tank, treated by adding 0.15kg of 32.5% lye, and then subjected to steam stripping, centrifugal dehydration and air drying to obtain the finished product. The glass transition temperature (Tg) is 70-75°C; the obtained finished product is tested according to the GB5761-93 standard, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com