Method for efficiently extracting midge larva DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
A high-efficiency technology for chironomus larvae, applied in DNA preparation, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as poor results, and achieve low cost, good quality, and high success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: DNA extraction from chironomid larvae
[0042] Preparation of lysate (100ml):
[0043] CTAB2g final concentration 2%
[0044] SDS0.5g final concentration 0.5%
[0045] 0.5 MEDTA 6ml final concentration 0.03M
[0046] 1MTris-HCl10ml final concentration 0.1M
[0047] 5MNaCl20ml final concentration 1M
[0048] PVP1g final concentration 1%
[0049] β-mercaptoethanol 0.1ml final concentration 0.1%
[0050] Make up to 100ml with distilled water.
[0051] (1) Pretreatment:
[0052] a. Take a single chironomid larva and mount the head shell, use a dissecting needle to pull out all the intestines and discard them as much as possible to prevent the digestion in the intestine from interfering with subsequent experiments.
[0053] b. Soak the insect body with distilled water, and change the distilled water every 5 minutes for a total of 15 minutes to remove impurities on the insect body. Finally, use absorbent paper to absorb the distilled water on the surface of the insect body.
[0054...
Embodiment 2
[0063] PCR amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase subunit I gene (COI gene)
[0064] (1) PCR reaction system:
[0065] Total system 25ul: ddH 2 O16.2ul, 10ⅹPCRBuffer 2.5ul, dNTPs (2.5mmol / L) 2ul, universal primer LCO and HCO (10umol / L) each 1ul, Taq enzyme (500U, 2.5U / ul) 0.3ul, DNA template 2ul.
[0066] (2) PCR reaction conditions:
[0067] Pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5min; denaturation at 94°C for 40s; annealing at 56°C for 40s; extension at 72°C for 1 min; 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 5 min; storage at 4°C.
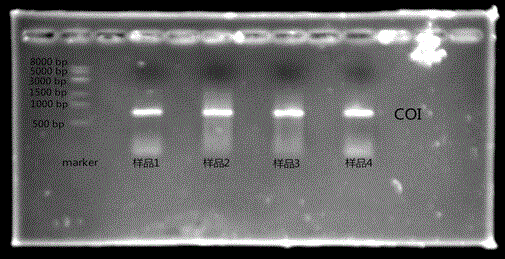
[0068] (3) Configure 1% agarose gel for electrophoresis detection, see attached picture.
[0069] Explanation of results:
[0070] (1) The first lane of the electrophoresis graph is 8KpMarker, and the second lanes 2, 3, 4, and 5 are the PCR results of a single red chironomid larva after DNA extraction.
[0071] (2) The COI gene is about 698bp, between the first and second bands of the Marker, and the result is in line with expectations.
Embodiment 3
[0073] Comparative Test
[0074]
[0075] Conclusion: Compared with conventional methods, the method of the present invention has higher DNA concentration and higher purity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com