Device for treating and recycling aluminum electrolysis solid waste
A technology for solid waste and aluminum recycling, applied in the field of metallurgical environment, can solve the problems of affecting cement, separation, secondary pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
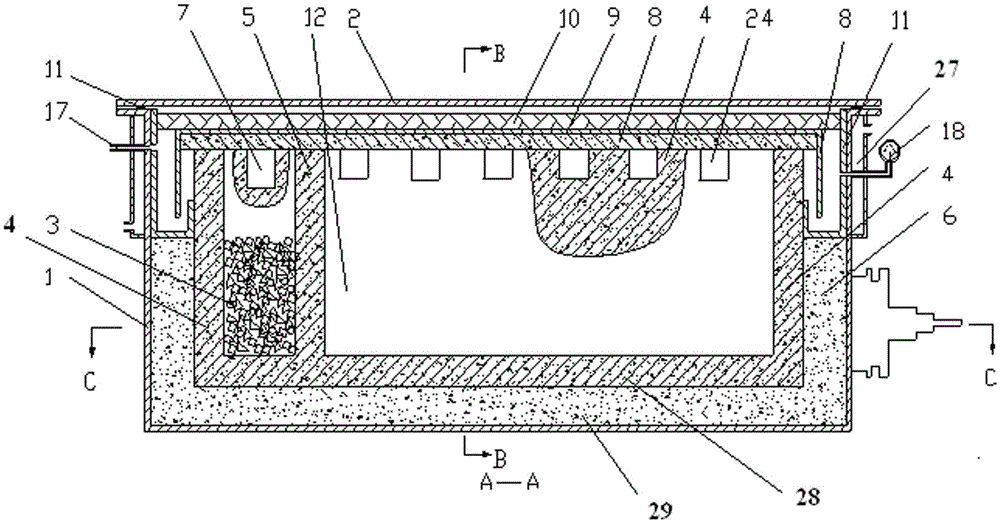
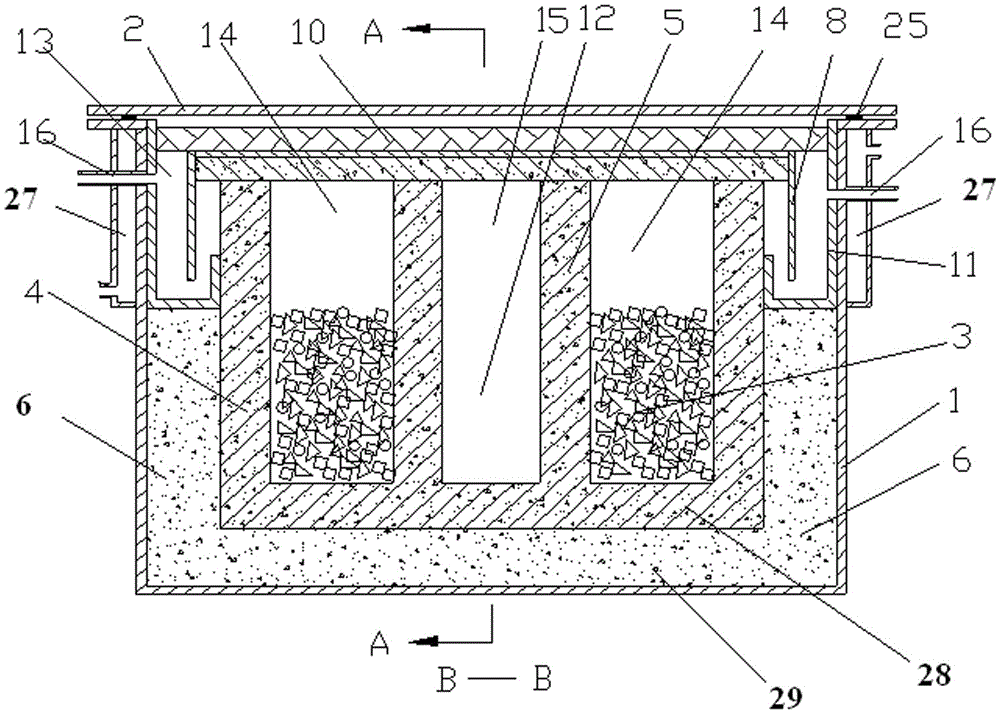
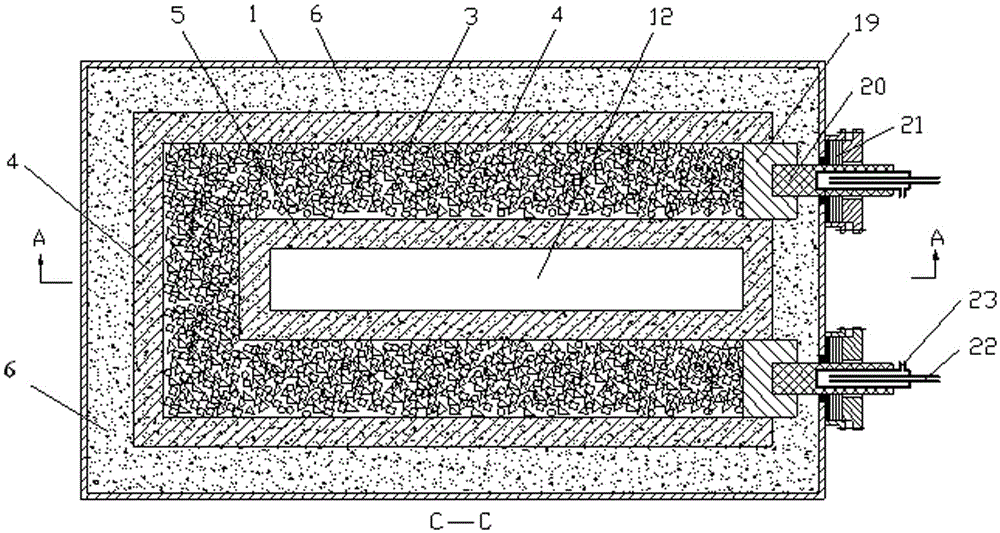
[0052] The structure of the device for processing and recycling solid waste from aluminum electrolytic cells is as follows: figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 Shown; resistance heating element is П-type design;
[0053] Including furnace shell 1, furnace cover 2, furnace lining, furnace wall refractory wall 4, resistance heating element 3, refractory wall 5 in the middle of the furnace, alkali metal crystallizer 11, heat insulation cover plate 8, metal cover 9. Electrode, auxiliary material chamber 12, electrolyte crystallization chamber and alkali metal crystallization chamber 13;
[0054] The furnace shell 1 is a box-type metal shell made of steel metal material; the outer edge of the top of the furnace shell 1 has a flange structure, and the outer wall of a section of the furnace shell 1 under the flange structure is provided with a cooling water jacket 27, The furnace shell 1 at the lower part of the flange structure is welded with a vacuum exhaust pipe 16; the lower edg...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Figure 4 C-C sectional view of the U-shaped resistance heating element and electrode structure when the resistance heating element of the present invention is a U-shaped design;
[0078] The difference between device structure and embodiment 1 is:
[0079] (1) The resistance heating element is a U-shaped structure design;
[0080] (2) The resistance heating element is 10cm higher than the graphite conductor;
[0081] The difference between method and embodiment 1 is:
[0082] (1) The briquetting material is made by mixing and pressing the grinding powder of the waste refractory lining of the electrolytic cell and aluminum ash; the Na in the grinding powder of the waste refractory lining of the electrolytic cell 2 The O component is 5%, the electrolyte component is 10%; the elemental aluminum in the aluminum ash is 15%, and the ingredients are based on the added aluminum ash. The aluminum in the aluminum ash can reduce the Na in the waste refractory lining. 2 O is c...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Figure 5 It is a C-C sectional view when the resistance heating element of the present embodiment is designed as two independent and parallel linear shapes;
[0088] The difference with embodiment 2 is:
[0089] (1) The resistance heating element is designed as two independent and parallel linear structures. The two electrodes of each independent resistance heating element are respectively located on the two sides of the electric furnace; at this time, the two electrodes on the same side are connected to the power supply Power connection, the two electrodes on the other side are connected with metal conductors;
[0090] (2) The resistance heating element is 20cm higher than the graphite conductor;
[0091] The difference between method and embodiment 2 is:
[0092] (1) The briquetting material is made by mixing and pressing the grinding powder of the waste refractory lining of the electrolytic cell and Al-Fe alloy powder. The aluminum content in the Al-Fe alloy is 6...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com