Method for preventing and curing Bradysia odoriphaga by jointly applying entomopathogenic nematodes and chemical pesticides
A technology of entomopathogenic nematodes and chemical pesticides, which is applied in the field of biological control and chemical control, can solve the problems of instability, slow killing of entomopathogenic nematodes, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of use, improving the control effect, and safe leek maggots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
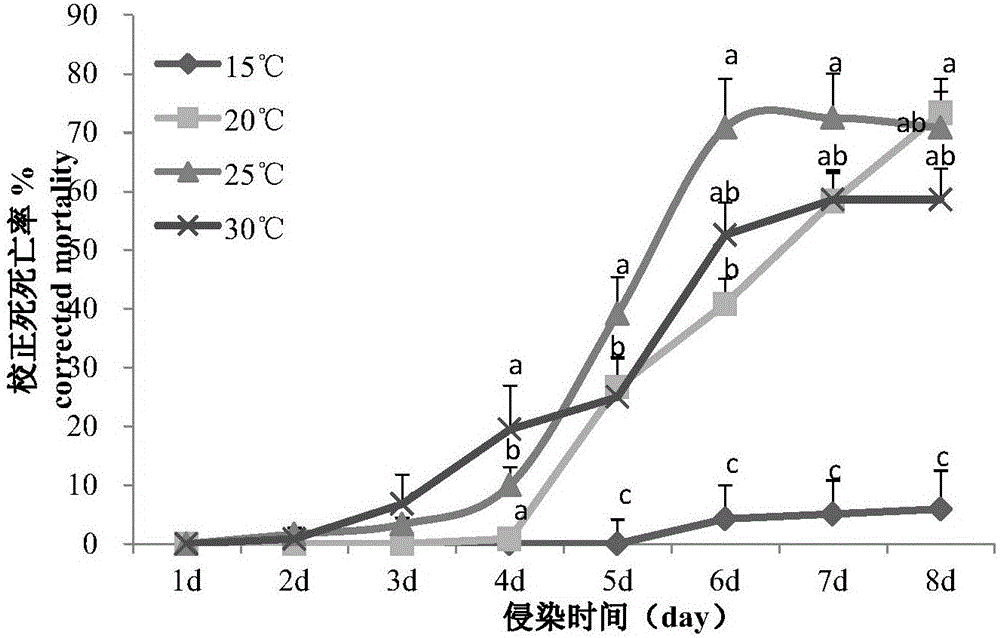
[0023] The impact of embodiment 1 chemical pesticide on entomopathogenic nematode survival
[0024] Heterorhabditis bacteriophora Cangzhou strain (CZ for short) was collected and isolated from the peanut planting area in Cangzhou, Hebei Province, and was propagated live with Galleria mellonella to obtain infective juvenile stages (IJs). The larvae of Mellonella mellonella used in the experiment were artificially reared indoors in our laboratory. All the tested pesticides were provided by the Pesticide Laboratory of the Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
[0025] Select 70% imidacloprid (Imidacloprid), 40% chlorpyrifos (Chlorpyrifos), 35% phoxim (Phoxim) and 25% thiamethoxam (Thiamethoxam) commonly used in the leek field as test chemical pesticides. , RD) is diluted 4000 times, and the recommended dosage of each pesticide is diluted 1 / 2 times (referred to as 1 / 2RD), 1 / 4 times (referred to as 1 / 4RD), 1 / 8 times (referred to as 1 / 8RD) as the ...
Embodiment 2
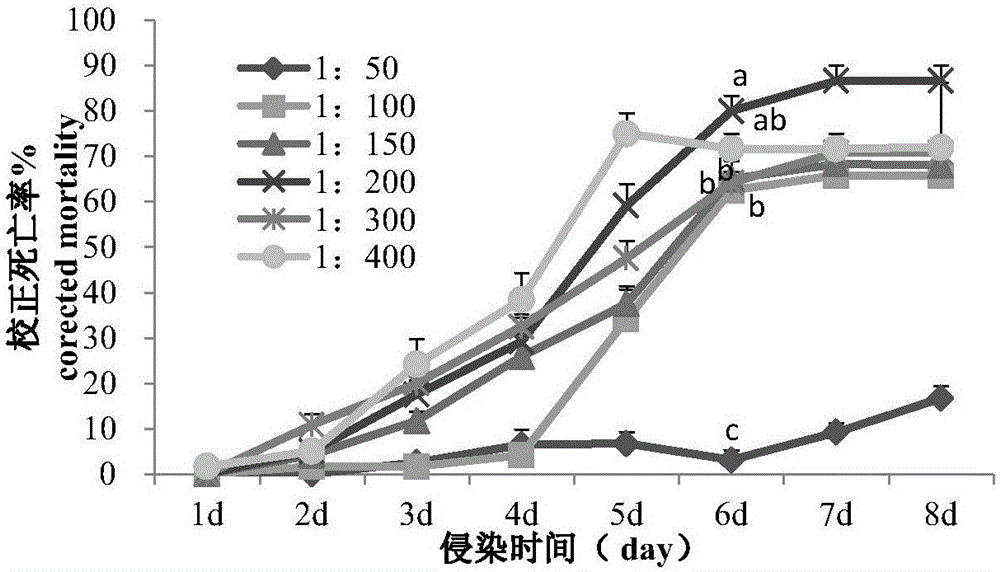
[0035] Example 2 Effect of Chemical Pesticides on Entomopathogenic Nematode Infection Ability
[0036] Shake the mixed solution of medicament and entomopathogenic nematode suspension or the mixed solution of clear water and pathogenic nematode suspension in Example 1, and evenly drop it in a petri dish (Φ=9cm) that is cushioned with two layers of medium-speed qualitative filter paper (double circle brand) Add 2mL of the mixed solution, place it in the dark at 25±1°C, and pick 5 last-instar larvae of Mellonella mellonella 24 hours later. Four replicates were set up for each treatment, and nematodes were treated alone as a control. After 72 hours of treatment, it was observed whether the larvae of Mellonella mellonella died. The dead worms treated with nematodes were taken out and placed in a clean petri dish, and dissected under a stereomicroscope to observe whether there were nematodes in the dead S. mellonella moth, and record the number of S. mellonella moth larvae infected b...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3, the lethal effect of imidacloprid and entomopathogenic nematodes in combination on leek maggots
[0042] The dosage of imidacloprid and the suspension of entomopathogenic nematodes are the same as in Example 1. The leek maggots (Bradysiaodoriphaga Yanget Zhang) for the test were provided by the Institute of Plant Protection, Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences (long-term artificial rearing after collection in local leek fields in Tianjin).
[0043] Put a piece of medium-speed filter paper in a petri dish (Φ=9cm) equipped with 2.5% agar, add 0.6 mL of distilled water dropwise, and put 20 4th-instar tardyophthora larvae and appropriate amount of chive stems. Add 0.1mL of nematode solution (2000IJs) and 0.1mL of different doses of imidacloprid liquid respectively, and set imidacloprid and entomopathogenic nematode single-use treatment, and distilled water treatment as control. Place them in a constant temperature incubator at (22±1°C), check and record ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com