Method of making a mycoplasma vaccine
A technology for mycoplasma and mycoplasma infection, applied in vaccines, methods based on microorganisms, methods using microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of cost-intensive cultivation of mycoplasma bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1 The cultivation of mycoplasma bacteria in MDCK cells or McCoy cells respectively.
[0100] A. Cultivation of M. hyorhina, M. hyosynovium and M. hyopneumoniae in MDCK cells
[0101] Mycoplasma hyorhinosum:
[0102] MDCK cells from confluent T75 flasks were trypsinized and subcultured into 5 T150 flasks (1:10 split) using MEM+5% FBS. Place the flask at 37 °C + 5% CO 2 Incubation was continued until approximately 95-100% confluent monolayers were observed. Pour off the medium and rinse the flask twice with 1X PBS. Then 4-5 ml of M. hyorhina was added to each flask (MOI = 10-100). Flasks were infected under the same incubation conditions as above for no more than 2 hours. Following the infection period, sufficient infection medium (MEM + 2% FBS) warmed to approximately 37°C was added to each flask to a total volume of 60 ml in each flask. The flasks were then incubated until CPE >90% (approximately 3-7 days). Cell suspensions were then collected from eac...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Embodiment 3 is to the evaluation of vaccine effectiveness
[0123] Following administration in pigs, vaccine efficacy was assessed based on the ability to induce antibody responses (and titers by ELISA).
[0124] animal care
[0125] Animals were in good health and nutritional status before starting the study. Health checks are implemented prior to the randomization procedure. Unmedicated feed was used throughout the study period. Feeding amounts were appropriate for the age, condition, and species of test animals according to facility standard operating procedures. Water was provided ad libitum throughout the study.
[0126] Evaluation of the effectiveness of the M. hyorhina and M. hyopneumoniae vaccines after administration in pigs.
[0127] Mycoplasma hyorhinosum:
[0128] 2 ml doses (7.1-7.3 log10 CCU / dose) of M. hyorhini vaccine were administered intramuscularly to all animals of 6 weeks±5 days old conventional piglets on DO and on D21. M. hyorhinis w...
Embodiment 4
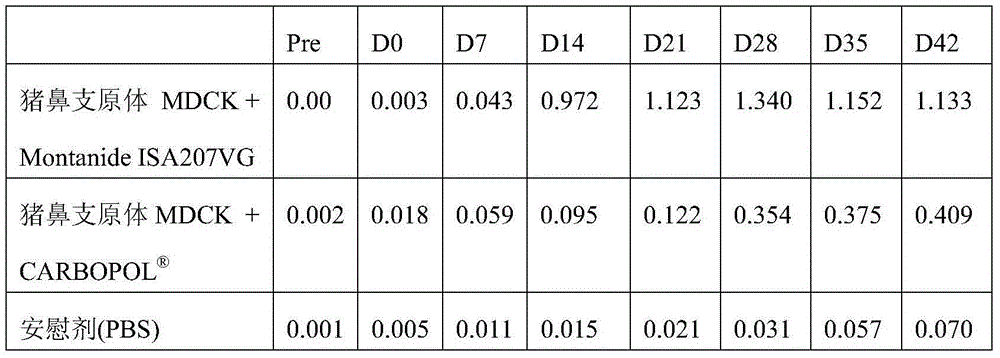
[0139] Example 4 Vaccines obtained from Mycoplasma bacterium cultivated in eukaryotic cell lines compared to free bacteria-free Effectiveness of vaccines obtained from Mycoplasma bacteria cultured in cellular systems
[0140] Fifty-four CD / CD animals aged 8 weeks±5 days were divided into six groups. Groups V1 and V2 each received pig nose cultured in MDCK cells and CM (complex medium; e.g. interstitial peptone-based medium containing porcine serum and yeast extract, or Friis-based medium), respectively. Inactivated MHRN001 isolate of Mycoplasma; Groups V3 and V4 received inactivated MHRN002 isolate of M. hyorhini cultured in MDCK cells and CM, respectively. All vaccines were adjuvanted with Montanide ISA207VG; dose and route were 2 x 2 ml doses intramuscularly, with one dose given on D0 and a second dose given on D21. Group CC (control group) received antigen-free placebo (PBS) in the same manner. Group SC (strict control) received no treatment throughout the study and w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com