A kind of preparation method of cross-linked acrylamide type profile control agent
A technology of acrylamide and profile control agent, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, drilling compositions, etc., can solve the problems of pollution, poor temperature and salt resistance, etc., and achieve reduced production costs, good environmental protection, and good stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A preparation method of cross-linked acrylamide profile control agent, the preparation steps are as follows:
[0024] After 0.1g of chitosan is completely dissolved in 100mL of glacial acetic acid with a volume fraction of 2%, add 0.2g of potassium persulfate at 60°C and pass N 2 An inert environment is formed. After 10 minutes, 50 mL of a mixed solution of 10 g of acrylamide and 1 g of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid is added, and radical polymerization is carried out to form the first product. Then, the product of the first step was placed at 110°C for nucleophilic addition reaction, and the reaction was conducted for 3 hours to obtain a polymer gel.
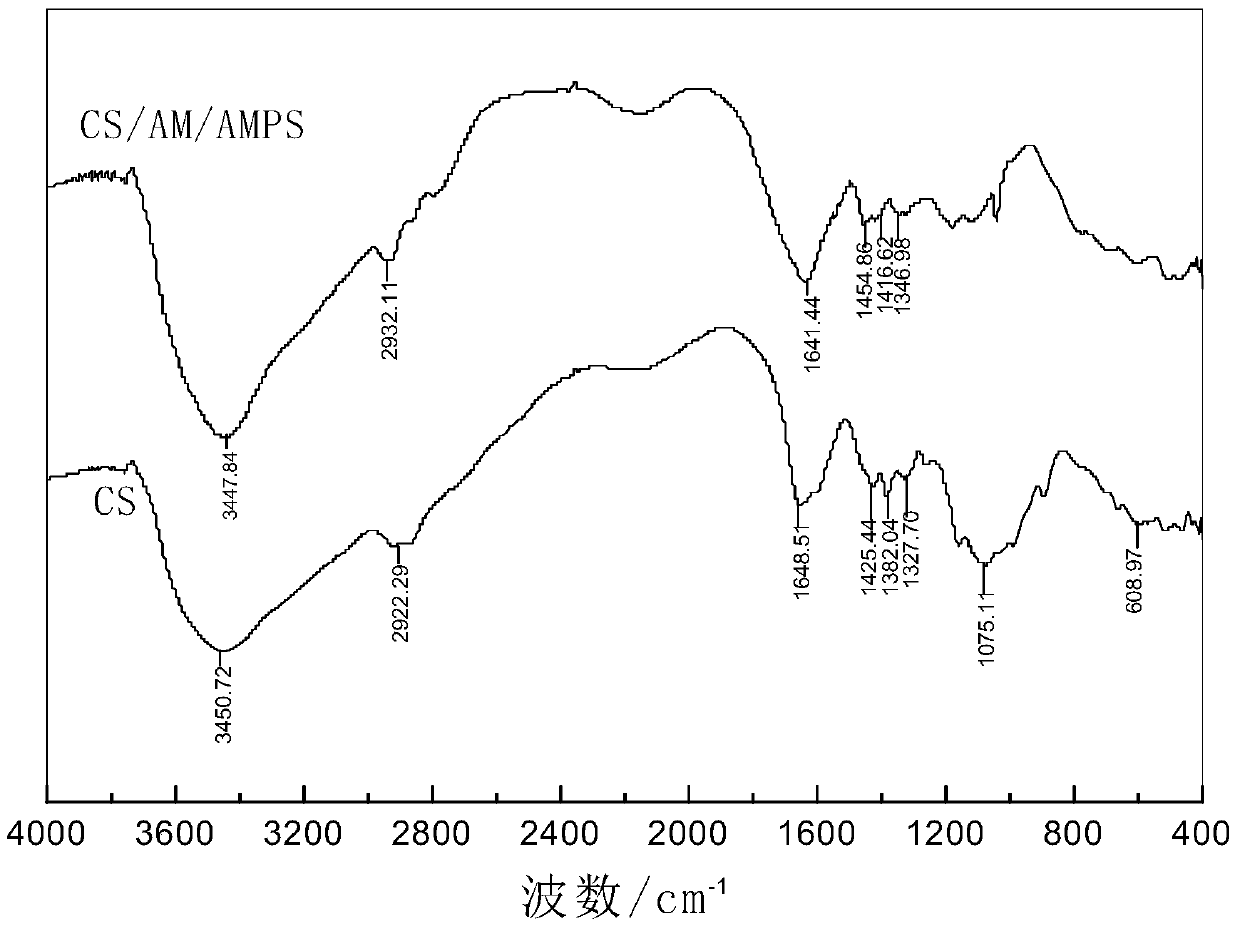
[0025] After purifying and drying the polymer gel profile control agent and the cross-linking agent chitosan, perform an infrared test to obtain an infrared spectrum, as attached figure 1 As shown, the results of the spectrogram analysis are shown in Table 1.
[0026] Table 1 Infrared spectrogram analysis results of ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] After 0.1 g of chitosan is completely dissolved in 100 mL of glacial acetic acid with a volume fraction of 2%, add 0.2 g of potassium persulfate-sodium sulfite (the molar ratio of the two is 1:1) at 50°C, and pass N 2 An inert environment is formed. After 10 minutes, 50 mL of a mixed solution of 10 g of acrylamide and 1 g of 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid is added, and radical polymerization is carried out to form the first product. Then, the product of the first step was placed at 110°C for nucleophilic addition reaction, and the reaction was conducted for 3 hours to obtain a polymer gel.
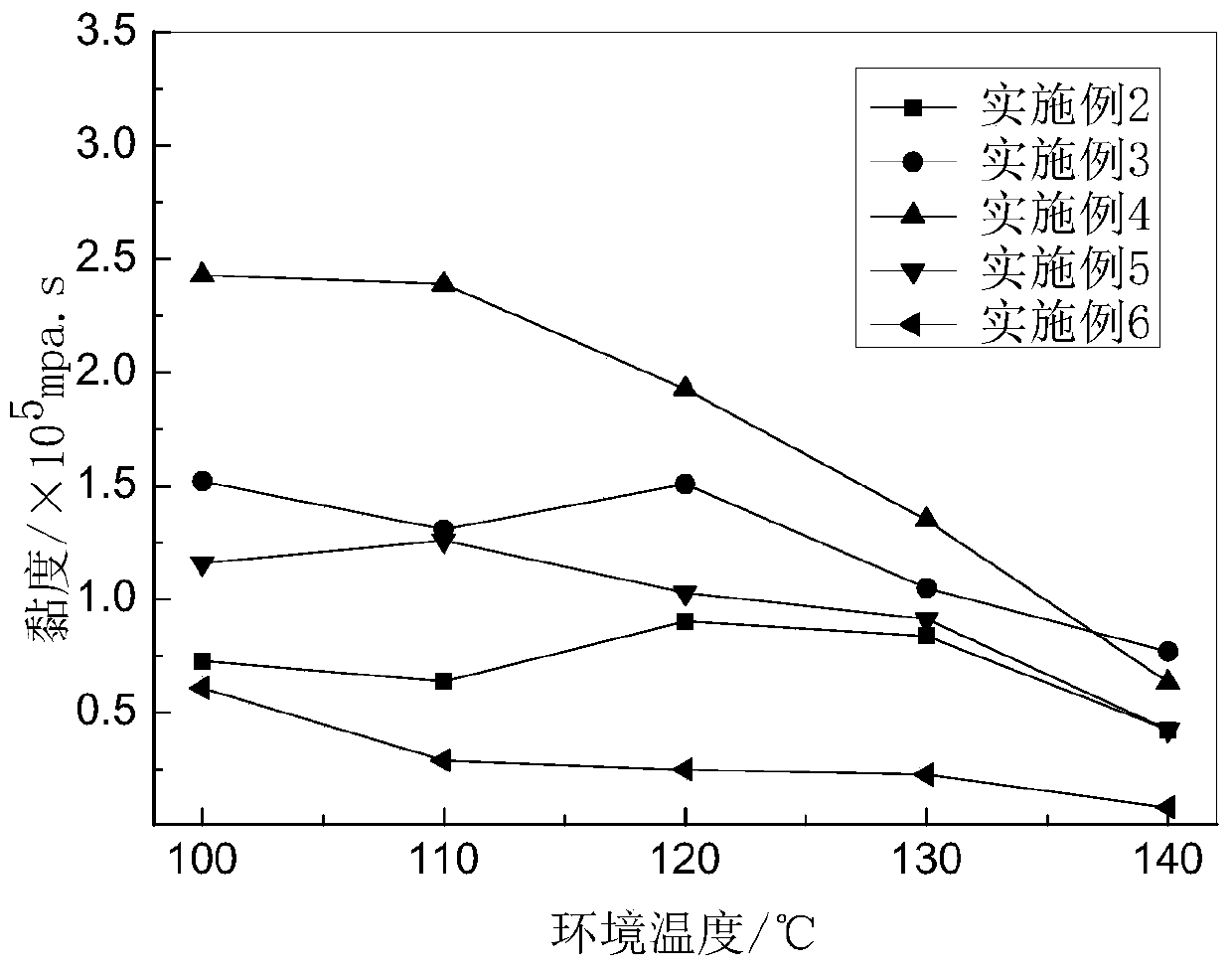
[0032] During the test, use NDJ-8S viscometer to measure the viscosity of the gel. figure 2 And image 3 As shown, the temperature resistance range is 100~140℃; the applicable coarse salt concentration range: 0~25×10 4 mg / L.
Embodiment 3
[0034] After 0.1g of chitosan is completely dissolved in 100mL of glacial acetic acid with a volume fraction of 2%, add 0.2g of potassium persulfate at 55°C and pass N 2 An inert environment is formed. After 10 minutes, 50 mL of a mixed solution of 10 g of acrylamide and 1 g of styrene sulfonic acid is added to carry out free radical polymerization to form the first step product. Then, the product of the first step was placed at 110°C for nucleophilic addition reaction, and the reaction was conducted for 3 hours to obtain a polymer gel.
[0035] During the test, use NDJ-8S viscometer to measure the viscosity of the gel. figure 2 And image 3 As shown, the temperature resistance range is 100~140℃; the applicable coarse salt concentration range: 0~25×10 4 mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com