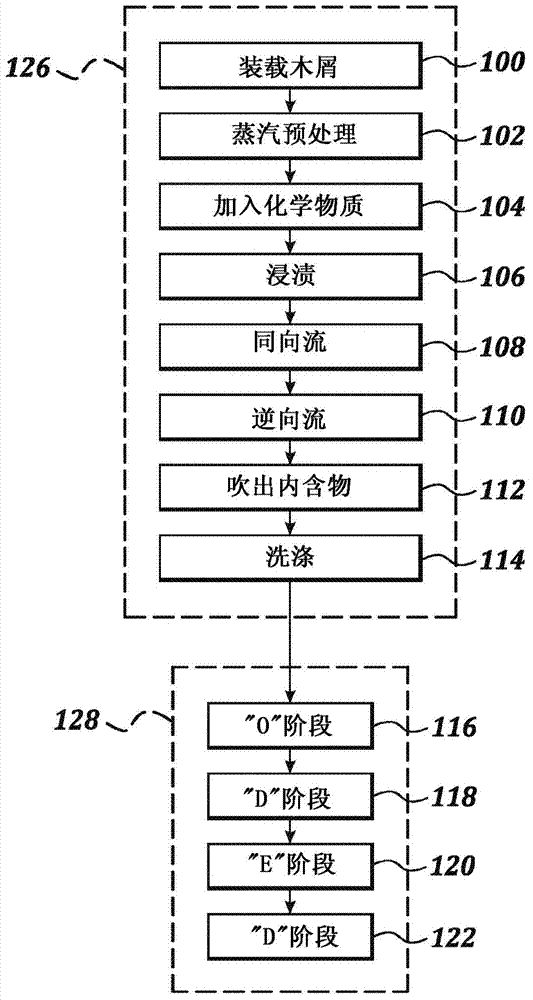
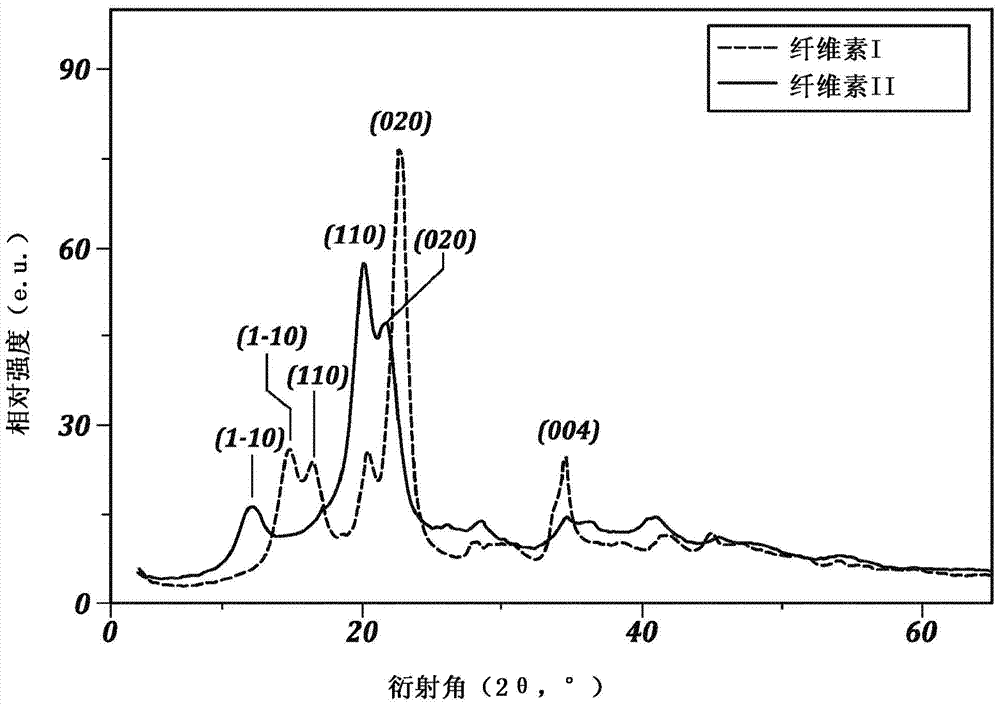
Treated kraft pulp compositions and methods of making the same
A technology of sulfate and pulp, applied in the direction of pulping with acid salts/acid anhydrides, pulping with halogen compounds, fiber raw material treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost of rayon fibers, and achieve the effect of improving reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0115] Example 1: Protocol for Standard Reactivity Test
[0116] In this example, the protocol for the standard reactivity test (based on the Chinese national standard test FZ / T50010.13) is described.
[0117]Weigh 7.7 grams of pulp (oven dry weight) and place the pulp in a Teflon bottle (250 mL). Add 180.5 mL of 13.7% NaOH to the bottle. A stirrer with a fitted lid was inserted and the pulp suspension was stirred at 2000 RPM for 5 minutes. Cap the bottle. Shake by hand to disperse possible fiber bundles at the bottom of the bottle (invert the bottle several times). The pulp suspension was then stirred for an additional 2 minutes at 2000 RPM.
[0118] Remove the stirrer with the fitted lid and transfer the bottle to a fume hood. Add 4.0 mL of carbon disulfide (CS 2 ). Cap the bottle (on timer: zero hour). crank.
[0119] The bottle was clamped to a Burrell wrist action shaker with 4 clamps (can handle 4 vials simultaneously) and the lever arm set to 7.5, and the bot...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Example 2: Protocol for Modified Responsiveness Test (MRT)
[0122] Since treated kraft pulp is not a dissolving pulp, its reactivity is generally low to moderate compared to dissolving pulp. To assess its suitability for viscose applications a modified reactivity test was used. The procedure for improving reactivity was the same as the laboratory reactivity test described in Example 1, except that 10 mL of CS 2 And there is no ripening time after 4 hours shaking. Modified reactivity was defined as the adulterant volume in mL that flowed through the filter within the first 1 minute. The volume may range from 0 to about 200 mL.
Embodiment 3
[0123] Embodiment 3: SEM fiber segment test
[0124] After performing the MRT test, the filter was placed in water to diffuse out residual solvent before drying the filter in air, exposing possible undissolved fiber segments. Observe the filter drier with fiber segments under SEM (scanning electron microscope) at magnifications of 100, 500 and 2000, observe the area with the most fiber segments and count the fiber segments (from 100 magnification) to calculate the units area of fiber segments. Samples with high reactivity may not have residual fibers on the filter. Samples with poor reactivity may have more than 11 or 20 fiber segments on the filter. In all experiments, undissolved fiber segments remaining on the filter were identified as latewood. Thus, poorly processed latewood is mainly responsible for the poor reactivity.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Falling ball viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com