Continuous production method and device for chloroformyl substituted benzenes
A chloroformyl group and a production method technology are applied in the field of continuous production methods and devices for chloroformyl substituted benzene, and can solve problems such as by-product hydrogen chloride being difficult to handle, environmental pollution, and unstable product quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
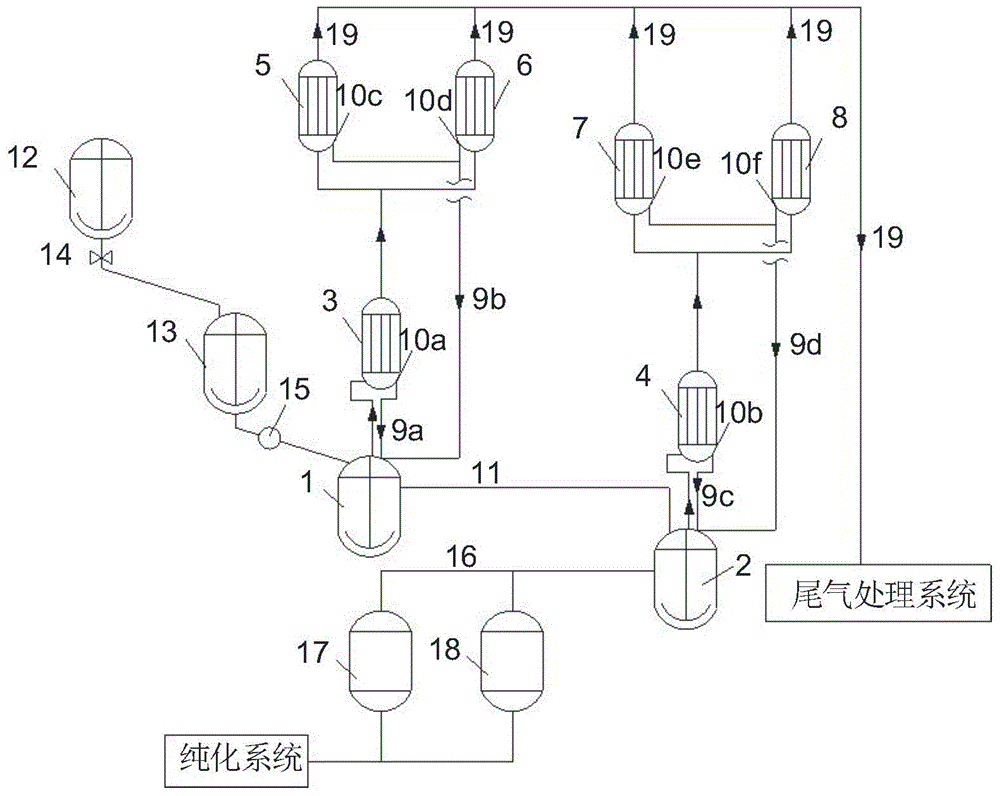
[0064] Reference attached figure 1 , using 1,4-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene as a raw material, and carrying out acyl chloride reaction with 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid, the specific steps are as follows:
[0065] (1) Ingredients: Add 43.2Kg 1,4-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene into the batching kettle 12, add 10.8Kg 1,4-bis(chloroformyl)benzene as a solvent, and raise the temperature to make 1,4 - After bis(trichloromethyl)benzene is completely dissolved, add 22.17Kg of 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid according to 1.01 times the number of moles of 1,4-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene, and then add 22.17Kg of 1,4-bis( 0.25% of trichloromethyl) benzene weight adds 0.11Kg of iron trichloride catalyst, after reaction material mixes in batching kettle 12, promptly opens valve 14, and material is conveyed continuously to batching kettle 13, closes valve after conveying finishes 14. The batching kettle 12 continues batching to ensure the continuity of batching;
[0066] (2) After the batching s...
Embodiment 2
[0071] 1,3-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene is used as raw material, and 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid is used for acyl chloride reaction.
[0072] When batching, add 12.65Kg of 1,3-di(chloroformyl)benzene as a solvent.
[0073] The molar ratio of 1,3-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene to 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid is 1:1.03, and then add trichloride according to 0.28% of the weight of 1,3-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene Iron catalyst 0.14Kg
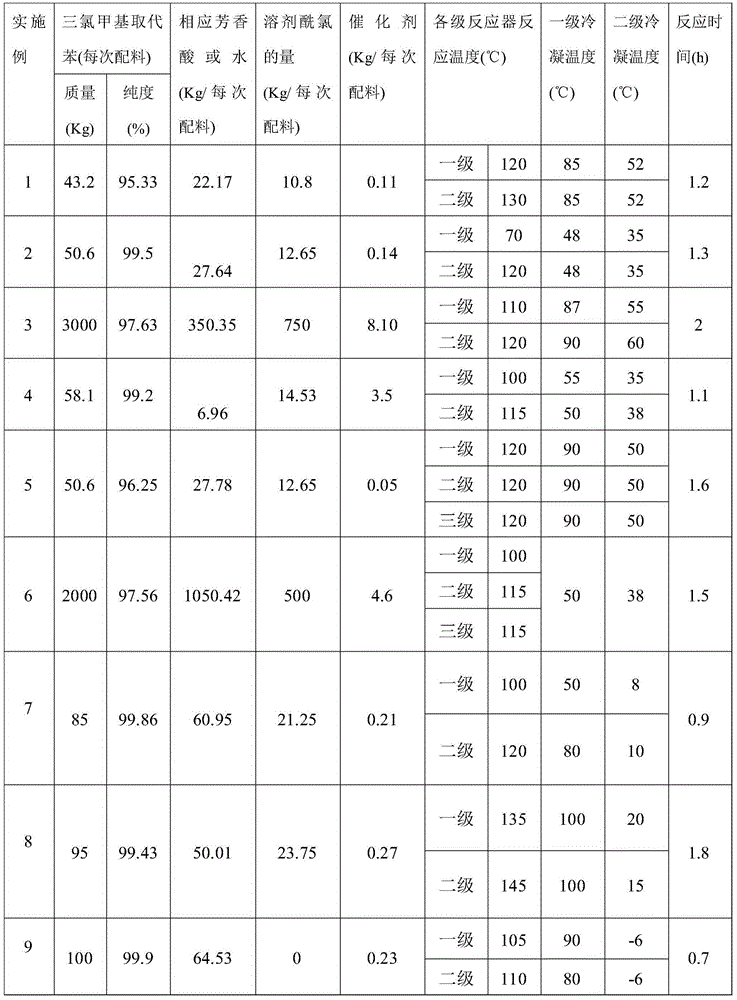
[0074] The amount of reactants and the operating process are shown in Table 1. The specific operation process is the same as in Example 1.
[0075] The crude product of 1,3-bis(chloroformyl)benzene obtained from the reaction was purified by rectification to obtain polymer grade 1,3-bis(chloroformyl)benzene with a purity of 99.95%. The rate is 96.1%.
Embodiment 3
[0077] Using 1,4-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene as raw material, and carrying out acyl chloride reaction with water;
[0078] When batching, add 750Kg of 1,4-di(chloroformyl)benzene as a solvent.
[0079] The molar ratio of 1,4-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene to water is 1:2.08, and 8.1Kg of ferric chloride catalyst is added according to 0.27% of the weight of 1,4-bis(trichloromethyl)benzene.
[0080] The amount of reactants and the operating process are shown in Table 1. The specific operation process is the same as in Example 1.
[0081] The crude product of 1,4-bis(chloroformyl)benzene obtained by the reaction was rectified to obtain polymer grade 1,4-bis(chloroformyl)benzene with a purity of 99.96%. ) Benzene yield is 95.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com