Transmitting-interference-resistant wireless communication link adaptive method
A technology of link adaptation and transmission interference, applied in the research field of wireless communication link transmission, can solve the problems of increasing frame length, difficult to estimate synchronization interference, insufficient estimation of synchronization interference, etc., and achieves low overhead and high throughput. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
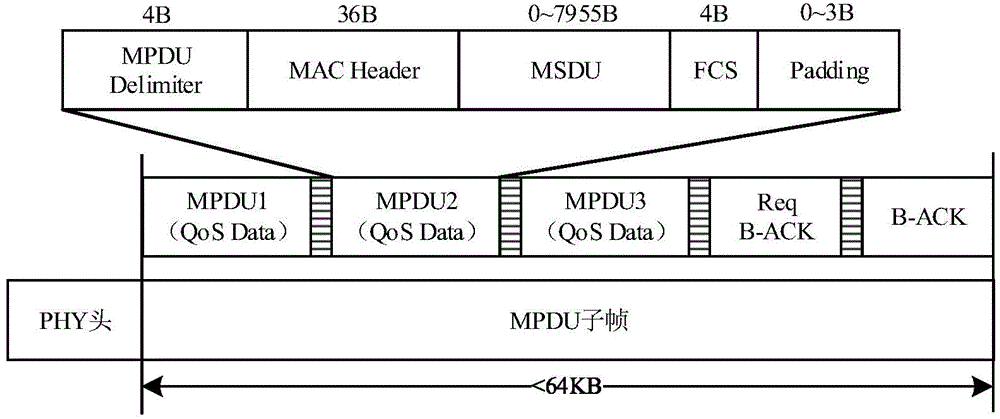
[0049] This embodiment uses the frame aggregation technology in the IEEE 802.11n protocol to fragment and aggregate data according to the A-MPDU aggregation frame format, see figure 1 , A-MPDU aggregates multiple MPDU subframes containing data, and shares the same PHY header for transmission in the link. In the figure, 4B, 36B, 64KB, etc. are the byte lengths occupied by each part. In addition, the QoS system in the IEEE 802.11e protocol is combined with the block acknowledgment mechanism (B-ACK) to perform a one-time acknowledgment of continuously received MPDU subframes. The B-ACK frame can be used to attach link condition information, adjust the frame transmission strategy, and select the MPDU subframe that fails to be retransmitted.
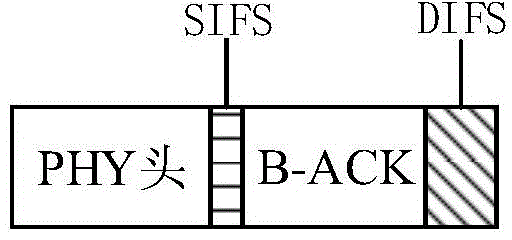
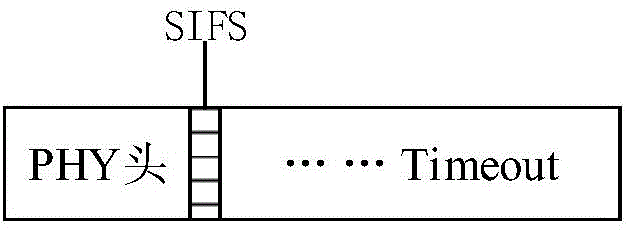
[0050] A-MPDU frame transmission combines frame aggregation and block acknowledgment technology, including PHY header transmission and MPDU subframe transmission. For PHY header transmission, see Figure 2(a) and (b). In the figure, SIFS means sh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com