Aptamer for recognizing adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells as well as screening method and application of aptamer
A breast cancer cell and nucleic acid aptamer technology, which is applied in the field of identifying adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cell nucleic acid aptamers and its screening, can solve the problems of cumbersome steps, high cost, and long time consumption, and achieve high affinity and high specificity sex, increase the success rate of chemotherapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
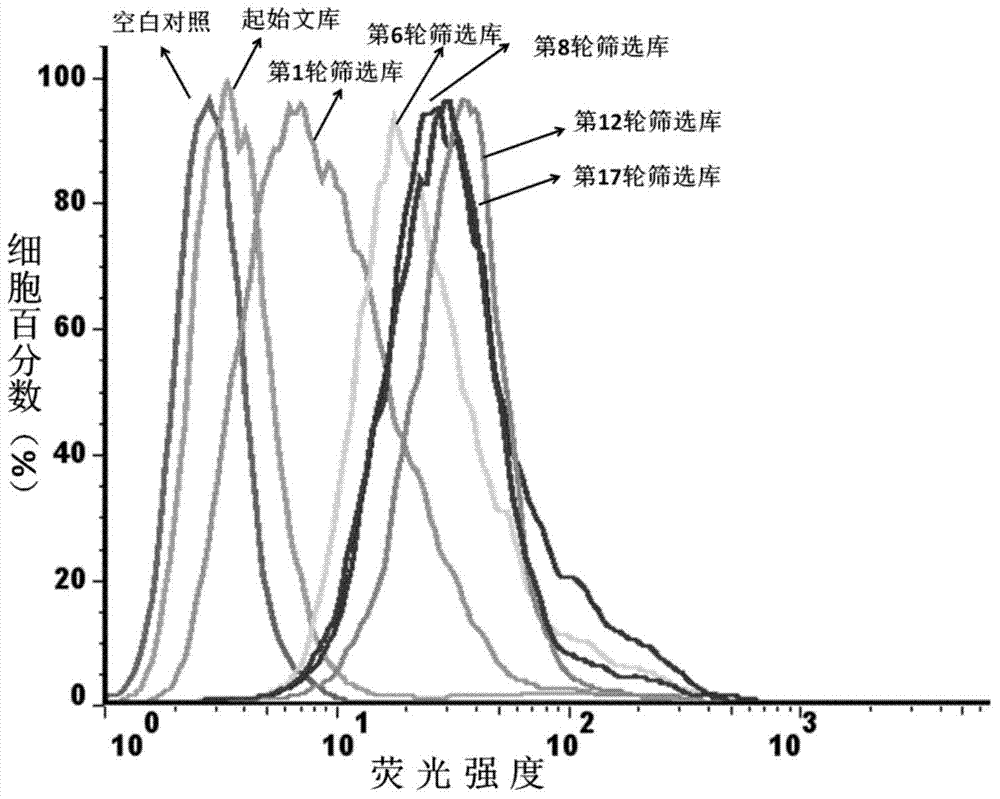
[0054] Example 1, Screening and Preparation of Nucleic Aptamers
[0055] 1. Culture of doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells and sensitive breast cancer cells
[0056] Doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells (MCF-7 / Adr) (purchased from Shanghai Aiyan Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) were treated with RPMI 1640 (containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin / streptomycin) supplemented with 1 μg / mL doxorubicin prime) culture, inoculated into doxorubicin-free medium before use and cultivated for one generation;
[0057] Sensitive breast cancer cells (MCF-7) (purchased from Shanghai Cell Bank, Chinese Academy of Sciences) were cultured in DMEM (containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin / streptomycin). All cells were routinely cultured in an incubator (37°C, 5% CO 2 ), passaged every two days.
[0058] 2. Design of Random Nucleic Acid Library
[0059] Design a random nucleic acid library with 20 fixed nucleotides at both ends and 45 nucleotides in the middle: 5'-AAGGAGCAG...
Embodiment 2
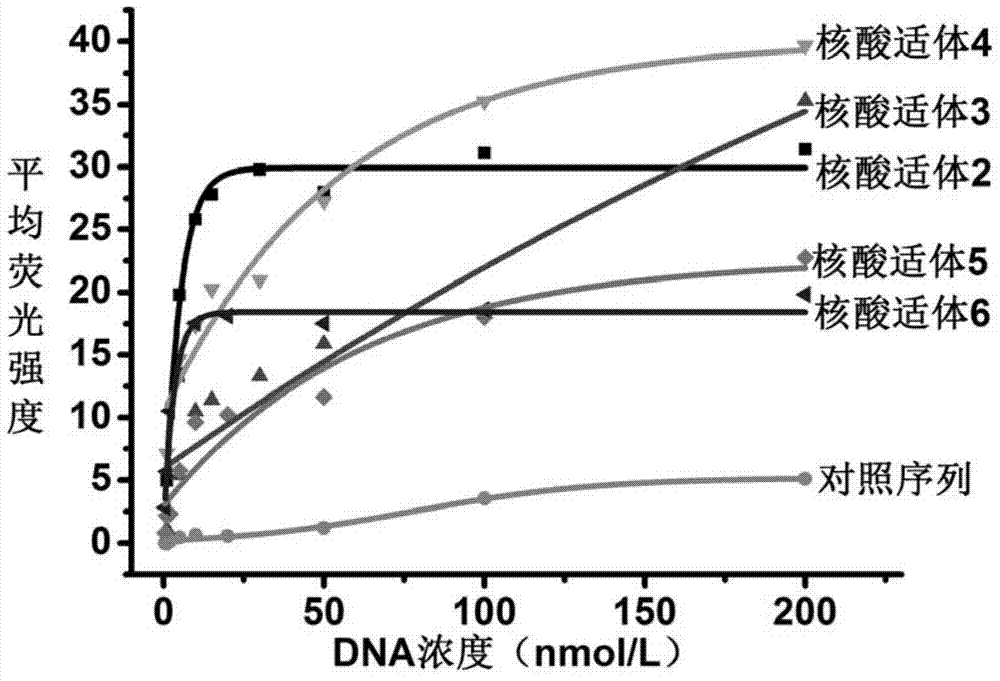
[0080] Example 2, flow cytometric analysis to detect the binding ability of nucleic acid aptamers to doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells MCF-7 / Adr
[0081] The obtained nucleic acid aptamer 2 to nucleic acid aptamer 6 and the control sequence (SEQ ID No. 7) were labeled with a fluorescein (FAM) molecule at the 5' end. Each single-stranded DNA was dissolved with binding buffer, and the concentration was calibrated according to ultraviolet absorption, heated at 95°C for 5 minutes, placed on ice for 10 minutes, and left at room temperature for 30 minutes. The denatured-refolded DNA is diluted with binding buffer to a DNA solution with a concentration gradient of 1nmol / L, 2nmol / L, 5nmol / L, 10nmol / L, 20nmol / L, 50nmol / L, 100nmol / L and 200nmol / L . Take a plate of doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells in the logarithmic growth phase, digest them with 0.2% EDTA into a monodisperse cell suspension, divide them into several parts, incubate with the above DNA solution on ice fo...
Embodiment 3
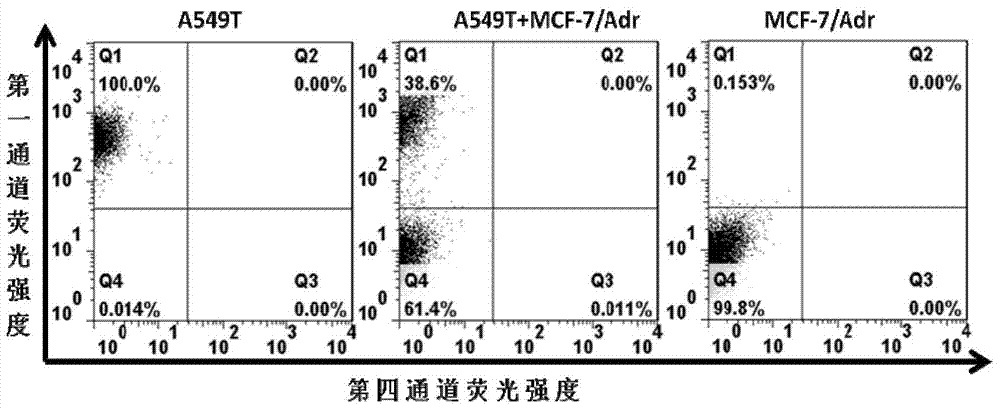
[0083] Embodiment 3, the specificity of nucleic acid aptamer detection by flow cytometry
[0084] 1. Nucleic acid aptamer probe pretreatment
[0085] Dissolve the synthesized fluorescein (6-FAM)-labeled aptamer 2, aptamer 3, aptamer 4, aptamer 5 and aptamer 6 and the control sequence (SEQ ID No.7) in A 20 μM DNA solution was obtained in the binding buffer, denatured by heating at 95° C. for 5 minutes, placed on ice for 10 minutes, and left at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0086]2. Pretreatment of cell lines
[0087] Human doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells (MCF-7 / Adr), human breast cancer cells (MCF-7), human breast cancer cells (SK-BR-3), human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231), Human vincristine-resistant oral cancer cells (KB / VCR), human paclitaxel-resistant lung cancer cells (A549T), human paclitaxel-resistant colon cancer cells (HCT-8T), human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293), human oral cancer cells (KB) , human lung cancer cells (A549), human colon cancer c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com