A kind of production technology of medicinal gelatin
A production process and process technology, which is applied in the field of pharmaceutical gelatin production process, can solve the problems of high viscosity reduction rate, high production cost, low product viscosity, etc., and achieve the goals of reducing waste and contamination, saving energy, and improving the color of gelatin Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
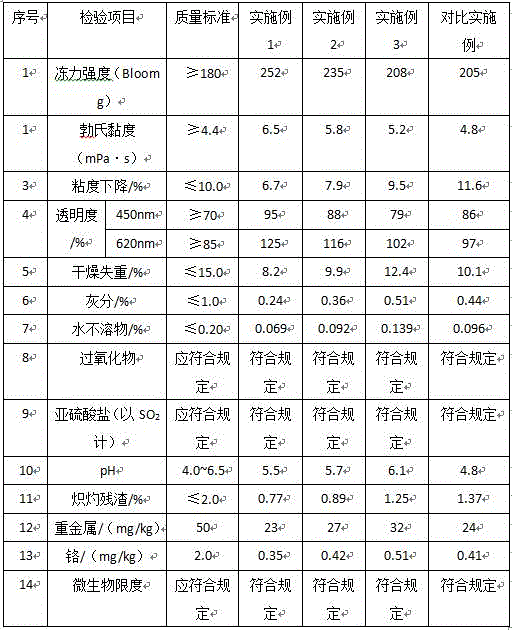
[0031] In this embodiment, 1 kg of pigskin (the collagen content of which is measured to be 256.4 g) is used for processing through the pretreatment process of the present invention, including the following steps:
[0032] (a) Skin cutting: use a leather cutter to cut the leather into strips, and transfer it to the washing tank with a delivery pump;
[0033] (b) Alkali treatment: add water to the leather, add 1.0% liquid caustic soda sodium hydroxide, and soak for 2 hours;
[0034] (c) Hydrogen peroxide pretreatment: add hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 10% to the lye in (b) to treat the raw skin,
[0035] Soak at room temperature for 6 days;
[0036] (d) Separation: Use a separation system to separate skin water and recover liquid alkali;
[0037] (e) Water washing: wash the leather in the washing tank until the pH value of the solution is 6.5;
[0038] (f) Pickling: Add sulfuric acid to make the pH of the solution reach 2.1, and the soaking time is 18 hours;
[...
Embodiment 2
[0052] In this embodiment, 1 kg of cowhide (278.2 g of collagen content was measured) was used to carry out the process through the pretreatment process of the present invention.
[0053] row processing, including the following steps:
[0054] (a) Skin cutting: use a leather cutter to cut the leather into strips, and transfer it to the washing tank with a delivery pump;
[0055] (b) Alkali treatment: Add water to the leather, add 0.8% liquid caustic soda sodium hydroxide, and soak for 2 hours;
[0056] (c) Hydrogen peroxide pretreatment: add hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 5% to the lye in (b) to treat the raw skin,
[0057] Soak at room temperature for 8 days;
[0058] (d) Separation: Use a separation system to separate skin water and recover liquid alkali;
[0059] (e) Water washing: wash the leather in the washing tank until the pH value of the solution is 7.2;
[0060] (f) Pickling: add sulfuric acid to make the pH of the solution reach 2.4, and the soaking t...
Embodiment 3
[0067] In this embodiment, 1 kg of cowhide (278.2 g of collagen content was measured) was used to carry out the process through the pretreatment process of the present invention.
[0068] row processing, including the following steps:
[0069] (a) Skin cutting: use a leather cutter to cut the leather into strips, and transfer it to the washing tank with a delivery pump;
[0070] (b) Alkali treatment: add water to the leather, add 0.9% liquid caustic soda sodium hydroxide, and soak for 2 hours;
[0071] (c) Hydrogen peroxide pretreatment: add hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 20% to the lye in (b) to treat the raw skin,
[0072] Soak for 5 days at room temperature;
[0073] (d) Separation: Use a separation system to separate skin water and recover liquid alkali;
[0074] (e) Water washing: wash the leather in the washing tank until the pH value of the solution is 6.8;
[0075] (f) Pickling: Add sulfuric acid to make the pH of the solution reach 1.8, and the soaking ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com