Determination method for activity of phospholipase D alpha
A technology of phospholipase and activity, which is applied in the field of determination of phospholipase Dα activity, can solve the problems of physical injury to operators, high measurement sensitivity, and time-consuming operation, and achieve the effect of easy operation, high sensitivity and fast method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0021] Additional experimental example 1 Determination of protein content
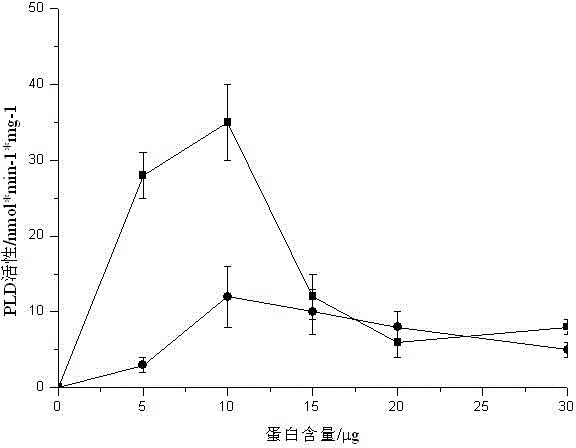
[0022] At 4°C, take 7 g of peach fruit and use HEPES buffer solution (pH 7.0, containing 0.32 mol / L sucrose, dithiothreitol, phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and EGTA each 1 mmol / L) to make 20 % homogenate, centrifuged at 12,000g for 45min, and the supernatant was centrifuged at 105,000g for 1 hour. The precipitated part was the membrane component of the cell membrane, which was dissolved in 100mmol / L DMG at pH6.5 to obtain the crude enzyme extract of PLDα, and the protein was determined by the Coomassie brilliant blue method content. Take the protein content as the abscissa and the activity of phospholipase Dα as the abscissa figure 2 .
[0023] exist figure 2 Among them, BA represents the peach fruit soaked in n-butanol and stored at 4°C for 28 days, and CK represents the peach fruit without any treatment and stored at 4°C for 28 days.
[0024] From figure 2 It can be seen that in the 200μl rea...
experiment example 2
[0025] Additional experimental example 2 Ca 2+ Determination of concentration
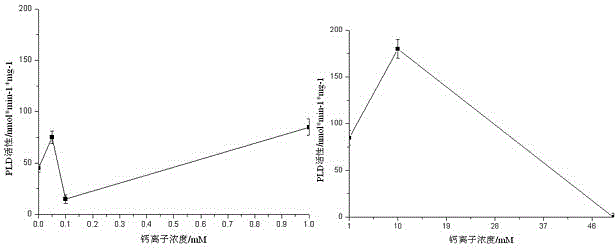
[0026] In the 200μl reaction system, the final concentrations of calcium ions added were 0, 0.05mM, 0.1mM, 1mM, 10mM, and 50mM. The final concentration of calcium ions was taken as the abscissa, and the activity of phospholipase Dα was taken as the ordinate. image 3 .
[0027] From image 3 It can be seen that the activity of phospholipase Dα increases with Ca 2+ The increase of the concentration presents a fluctuating growth trend, when the Ca 2+ When the concentration reaches 10mM, phospholipase Dα shows the maximum activity, see image 3 . Determination of Ca in Peach Fruit Phospholipase Dα Activity 2+ The concentration is preferably 10mM.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com