Injectable drug-loaded xanthan gum/methyl cellulose composite solution and preparation method thereof
A technology of methyl cellulose and composite solution, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problem of no injectable drug-loaded hydrogel and achieve good mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1. Preparation of XG / MC composite solution. Add 15 mL of phosphate buffer (10 mmol / L pH 7.4 phosphate buffer + 0.15 mol / L NaCl) into a 50 mL beaker and preheat it in a water bath at 80°C for 5 minutes, then add 2.5 g of methylcellulose ( MC) powder was slowly added to the phosphate buffer at 80°C and kept stirring rapidly. After the methylcellulose powder was completely infiltrated, the solution was cooled to room temperature, and 10 mL of phosphate buffer was added and stirred evenly, and then the solution was transferred to a 4°C refrigerator and continued to stir overnight to fully dissolve the methylcellulose. Add 0.5 g xanthan gum (XG) powder to the above methylcellulose solution, stir rapidly overnight at 4°C to fully dissolve the xanthan gum, then stir gently at 4°C for 24 hours and then centrifuge at low speed to remove the system The bubbles in the xanthan gum / methylcellulose (XG2 / MC10) composite solution were obtained. A series of xanthan gum / methy...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2. Preparation of XG / MC complex solution. Add 15 mL of phosphate buffer solution into a 50 mL beaker and preheat it in a water bath at 80°C for 5 minutes, then slowly add 2.5 g of MC powder into the phosphate buffer solution at 80°C and keep stirring rapidly until the MC powder is completely soaked Cool the solution to room temperature, add 10 mL of phosphate buffer again, then add 0.5 g of XG powder to the above MC dispersion, stir at room temperature until the viscosity of the blended solution is very high, then transfer the solution to a 4°C refrigerator to cool, Then stir at 4°C for 24 hours to fully dissolve XG and MC, and finally remove the air bubbles in the system by low-speed centrifugation to obtain a xanthan gum / methylcellulose (XG2 / MC10) complex solution. A series of XG / MC complex solutions with different concentrations shown in Table 1 can also be prepared by using this method.
Embodiment 3
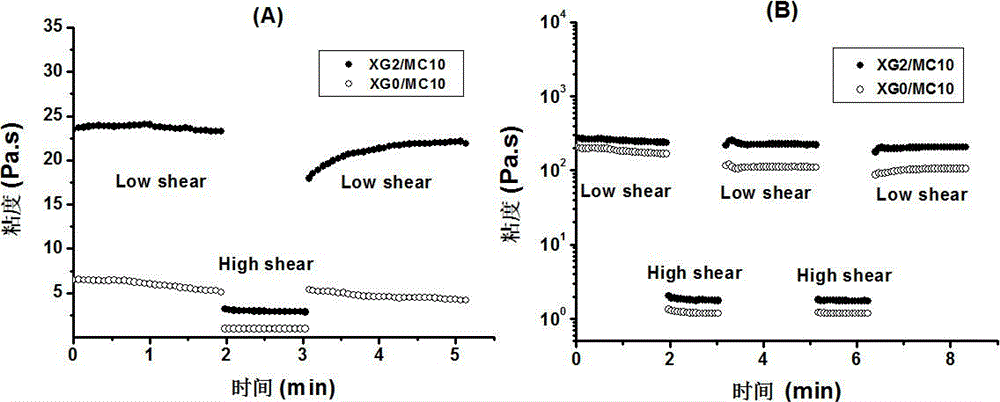
[0025] Example 3. The injectable properties of XG / MC composite solution and XG / MC composite hydrogel were studied by rotational rheometer. A multi-step thixotropic rate scan was performed on the XG / MC composite solution at 23°C (room temperature condition) and the XG / MC composite hydrogel at 37°C (human body temperature condition) to characterize the thixotropic recovery performance before and after shearing, figure 1 for the experimental results. Among them, the low shear rate (low shear) at room temperature is 0.1 s -1 , hold time is 2 minutes (min), high shear rate (high shear) is 10 s -1 , hold time 1 min; low shear rate 0.5 s at body temperature -1 , with a hold time of 2 min and a high shear rate of 500 s -1 , and the hold time is 1 min. figure 1 The experimental results show that the XG / MC complex solution has high viscosity properties at room temperature and is a hydrogel at body temperature. Both of them have good shear thinning properties and fast recovery pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com