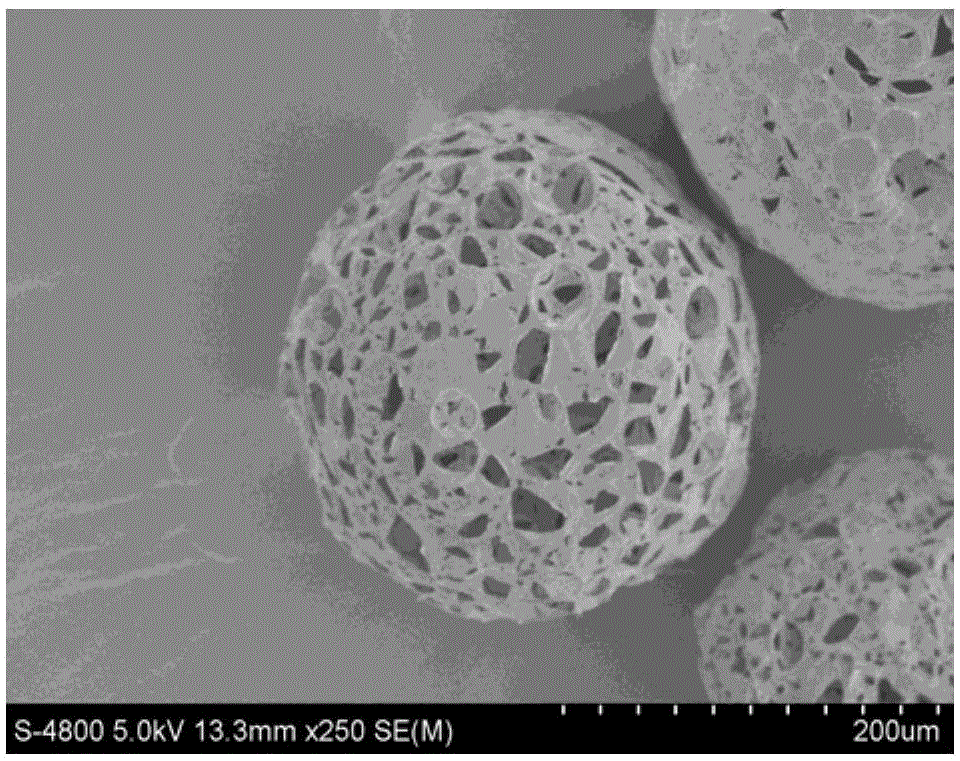
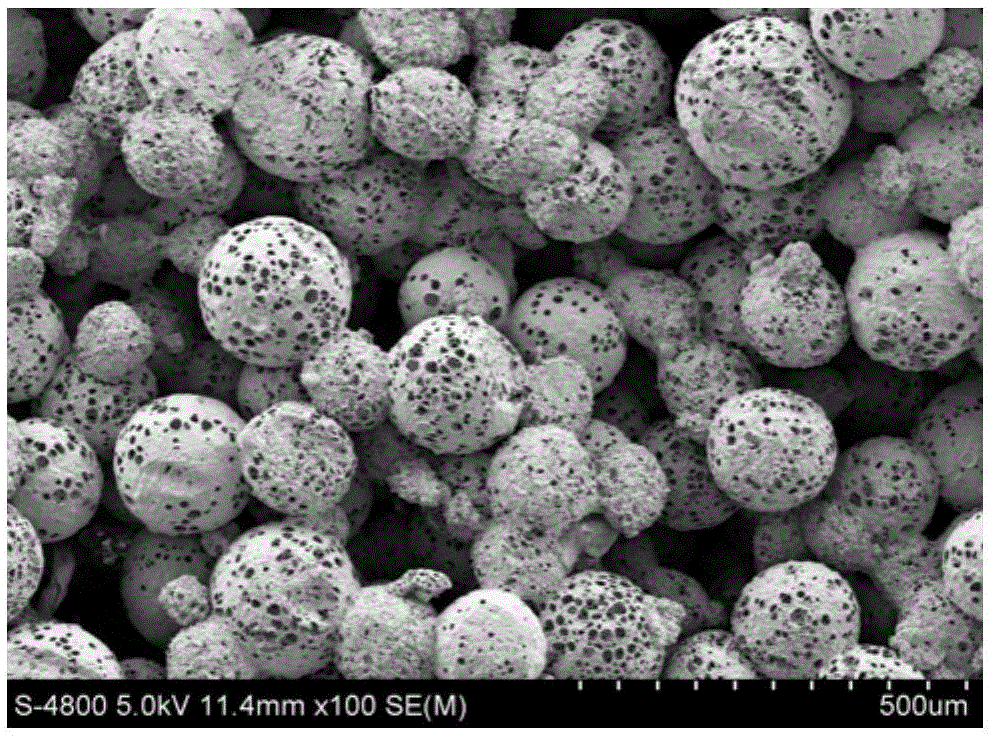
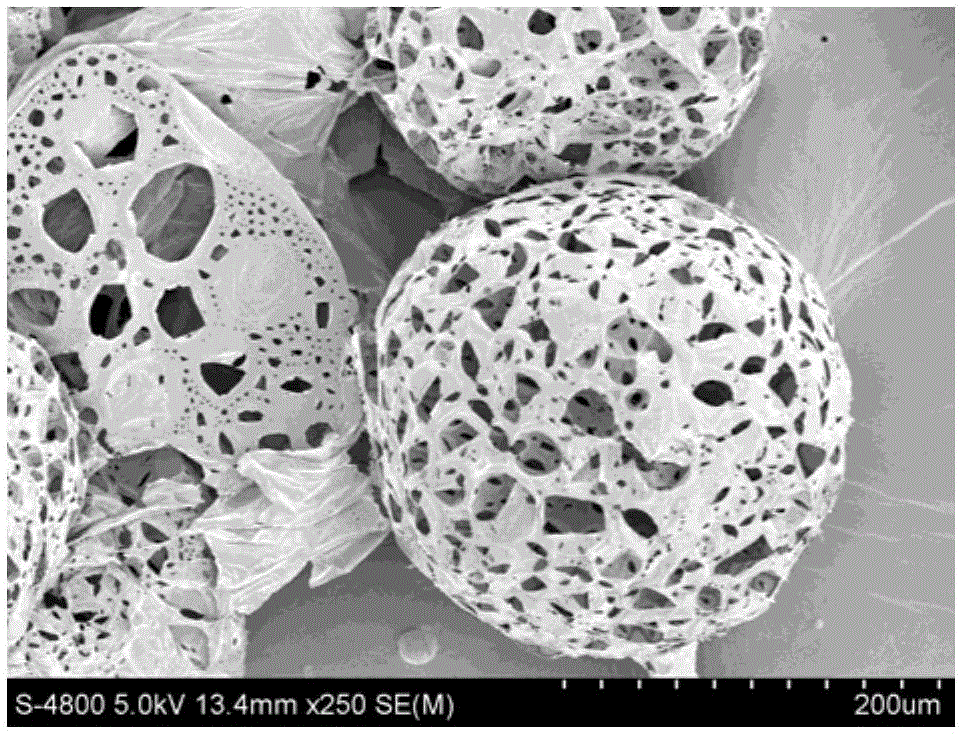
Subcritical carbon dioxide sintering method for co-loading porous microsphere scaffolds
A porous microsphere, carbon dioxide technology, applied in animal cells, vertebrate cells, artificial cell constructs, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable protein drug activity, difficult removal of organic solvents, poor cell compatibility, etc., and achieves favorable mass transfer. Effective with cell proliferation, volatile, and simple steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0042] a) At room temperature, add PLGA to the organic solvent dichloromethane, and obtain a homogeneous oil phase by stirring, wherein the concentration of PLGA is 6.25% (w / v), the molecular weight of PLGA is 40kDa, LA (lactic acid) and GA in PLGA (glycolic acid) in a mol ratio of 50 / 50;
[0043] b) Ammonium bicarbonate is added to distilled water, and a uniform aqueous phase is obtained by stirring, wherein the concentration of ammonium bicarbonate is 10% (w / v);
[0044] c) Disperse 2.5ml of the water phase obtained in step b into 15ml of the oil phase obtained in step a, and form a water-in-oil single emulsion through homogenization, wherein the volume ratio of the water phase to the oil phase is 1 / 6 ; The homogenization conditions are: stirring rate 8000rpm, stirring time 4min;
[0045] d) At a stirring rate of 200 rpm, disperse the single emulsion obtained in step c into a 0.5% (w / v) PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) aque...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0051] a) At room temperature, add PLGA to the organic solvent dichloromethane, and obtain a homogeneous oil phase by stirring, wherein the concentration of PLGA is 6.25% (w / v), the molecular weight of PLGA is 40kDa, and the molar ratio of LA to GA in PLGA is 50 / 50;
[0052] b) Ammonium bicarbonate is added to distilled water, and a uniform aqueous phase is obtained by stirring, wherein the concentration of ammonium bicarbonate is 10% (w / v);
[0053] c) Disperse 2.5ml of the water phase obtained in step b into 12.5ml of the oil phase obtained in step a, and form a water-in-oil single emulsion through homogenization, wherein the volume ratio of the water phase to the oil phase is 1 / 5. The conditions for homogenization are: stirring rate 8000rpm, stirring time 4min;
[0054] d) at a stirring rate of 200rpm, disperse the single emulsion obtained in step c into a 0.5% (w / v) PVA aqueous solution having a volume of 400ml ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0060] a) At room temperature, add PLGA to the organic solvent dichloromethane, and obtain a homogeneous oil phase by stirring, wherein the concentration of PLGA is 6.25% (w / v), the molecular weight of PLGA is 40kDa, and the molar ratio of LA to GA in PLGA is 50 / 50;
[0061] b) Ammonium bicarbonate is added to distilled water, and a uniform aqueous phase is obtained by stirring, wherein the concentration of ammonium bicarbonate is 10% (w / v);
[0062] c) Disperse 2.5 ml of the water phase obtained in step b into 8 ml of the oil phase obtained in step a, and form a water-in-oil single emulsion through homogenization, wherein the volume ratio of the water phase to the oil phase is 1 / 3.2 ; The homogenization conditions are: stirring rate 5000rpm, stirring time 3min;
[0063] d) at a stirring rate of 200rpm, disperse the single emulsion obtained in step c into a 0.1% (w / v) PVA aqueous solution having a volume of 400ml to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com